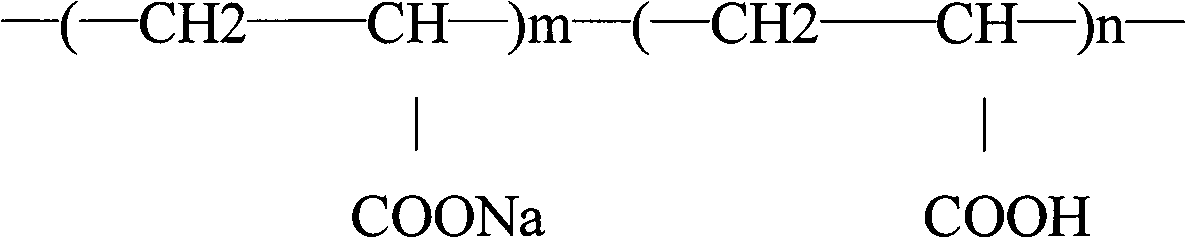Hydrogel patch and preparation method thereof
A hydrogel patch and hydrogel technology, applied in anti-inflammatory agents, pharmaceutical formulations, non-central analgesics, etc., can solve problems such as poor viscosity of hydrogels, and achieve the effect of meeting the requirements of adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0075] The preparation method of hydrogel patch of the present invention is:
[0076] (1) Disperse and dissolve the adhesive, chelating agent, and excipient with an appropriate amount of humectant, stir evenly, and set aside;
[0077] (2) disperse and dissolve the crosslinking agent with a dispersant, stir evenly, and set aside;
[0078] (3) Add the prepared part of step (2) into step (1), and stir evenly until there is no agglomerate, and it becomes a milky white suspension;
[0079] (4) Add liquid extract, transdermal accelerator, pH regulator, filler, thickener and deionized water, stir and knead evenly, and apply on the machine after vacuum defoaming.
Embodiment 1~6
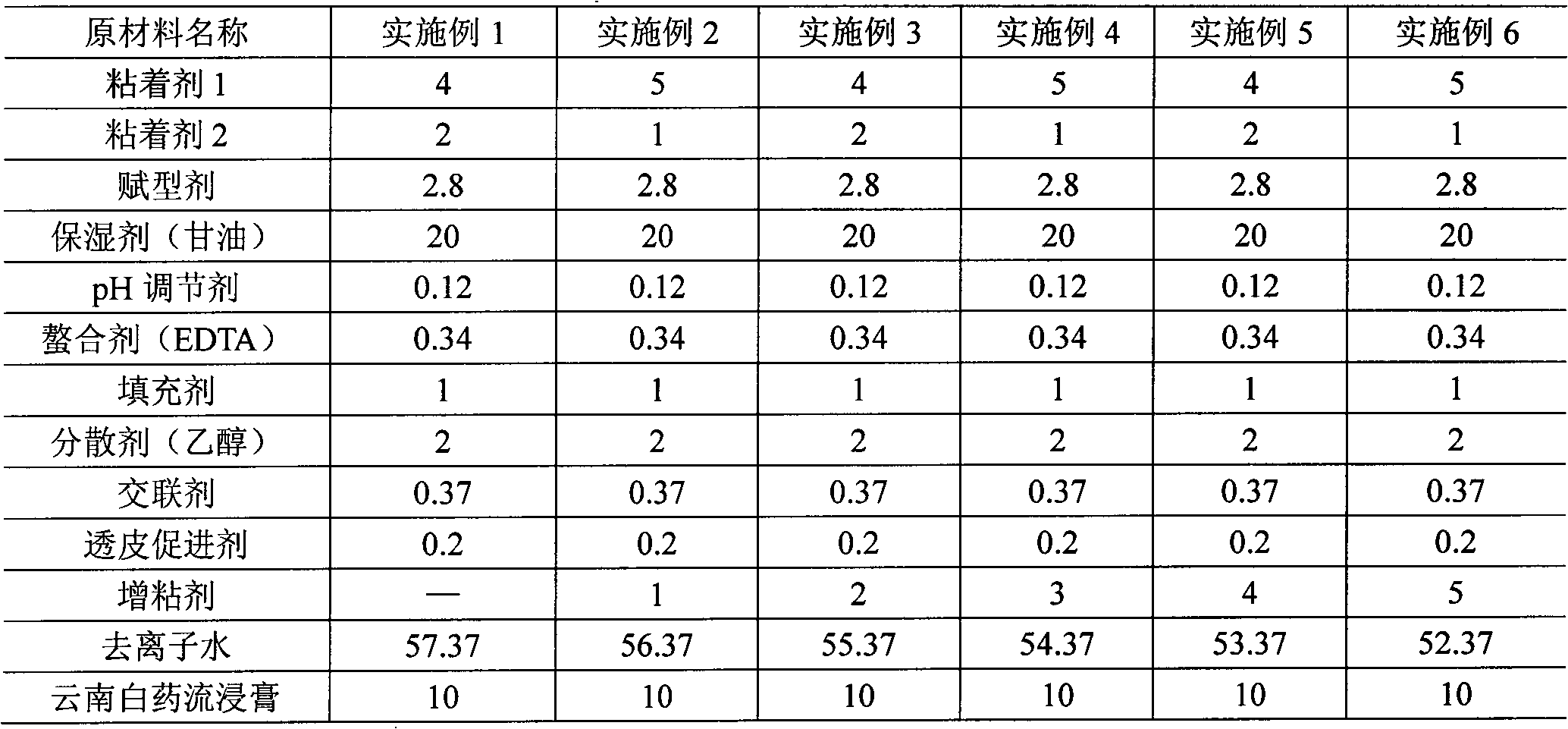
[0082] See Table 1 for the weight of each ingredient required, unit: g
[0083] Table 1 Examples 1-6
[0084]
[0085] Preparation and test steps:
[0086] 1. Accurately weigh adhesive 1, adhesive 2, chelating agent (EDTA), excipient and humectant (glycerin) according to the formula, stir and disperse evenly, and this is part A. Adhesive 1, adhesive 2, chelating agent (EDTA) and excipients in part A are all insoluble in humectant (glycerin), but can be well dispersed in humectant (glycerin). Thick.
[0087] 2. Accurately weigh the cross-linking agent according to the formula, dissolve and disperse it with dispersant (ethanol) to form part B. The cross-linking agent in part B is also insoluble in ethanol, but is dispersed in ethanol as a slightly white suspension.
[0088] 3. Add the prepared part B into part A, and stir until there is no aggregate and uniform milky white suspension; the crosslinking agent in component B first reacts with the chelating agent in component...
Embodiment 7~12
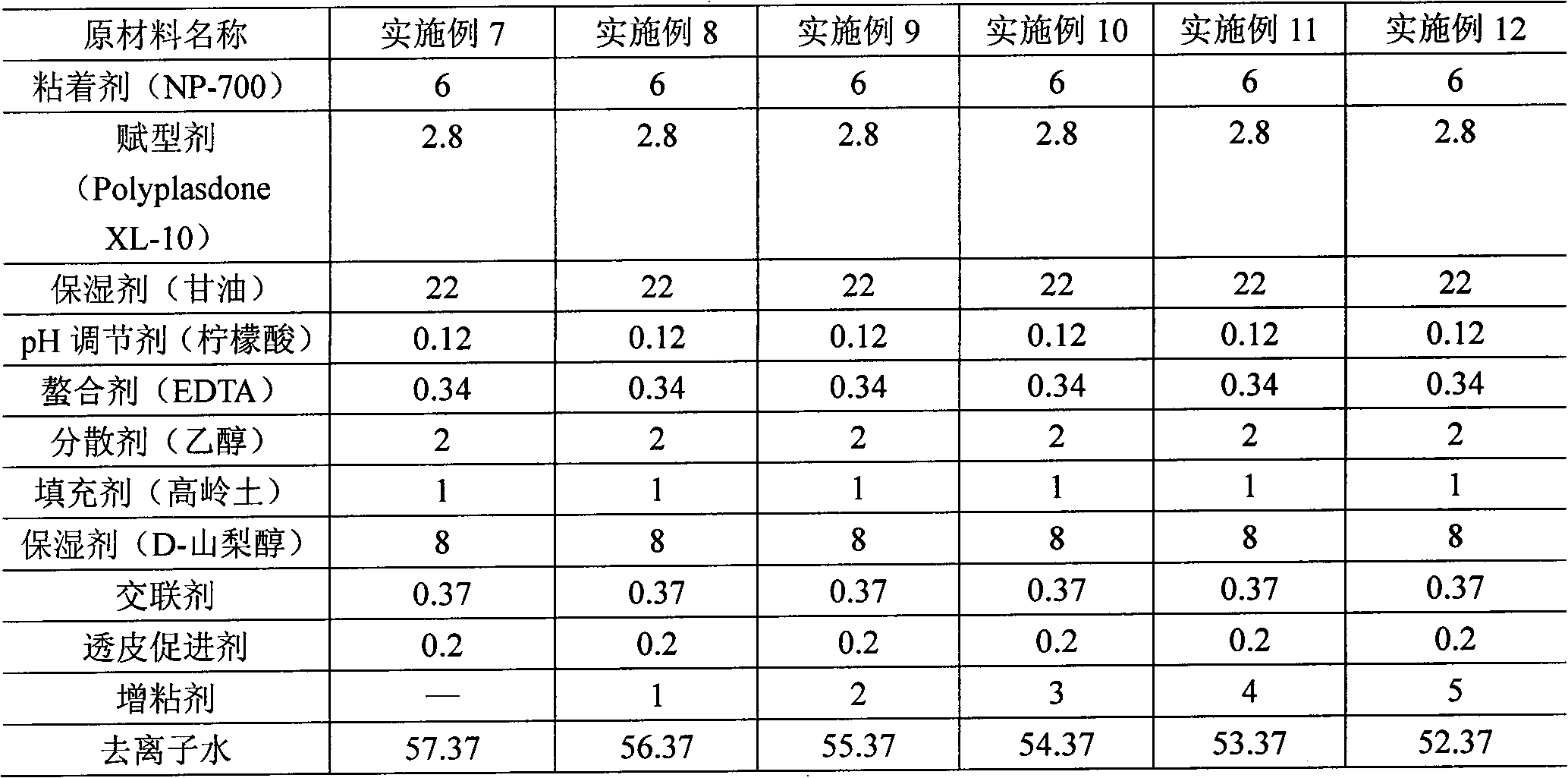
[0098] See Table 2 for the weight of each ingredient required, unit: g
[0099] Table 2 Embodiment 7~12
[0100]
[0101] The preparation and test steps of Examples 7-12 are basically the same as those of Examples 1-6, except that Yunnan Baiyao liquid extract is not added in Step 4, so it is convenient to test the hydrogel matrix itself. The test results of its initial adhesion performance are shown in Table 3.
[0102] Table 3 The test of initial adhesion performance (30 degree slope rolling ball method)
[0103]
[0104] It can be seen from Table 3 that the addition of tackifiers has a significant effect on changing the initial adhesive properties of hydrogel matrix colloids. With the increase of the added amount of tackifier, its initial tack increases gradually, but when its content reaches 5%, the rise of colloid's initial tack is relatively gentle.
[0105] In addition, it is considered that with the increase of the added amount of tackifier and the increase of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com