Method for detecting diarrhea shellfish toxin
A shellfish toxin and detection method technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of low sensitivity, poor accuracy, poor comparability and repeatability, etc., and achieve simple sample extraction, Low matrix effect and good specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
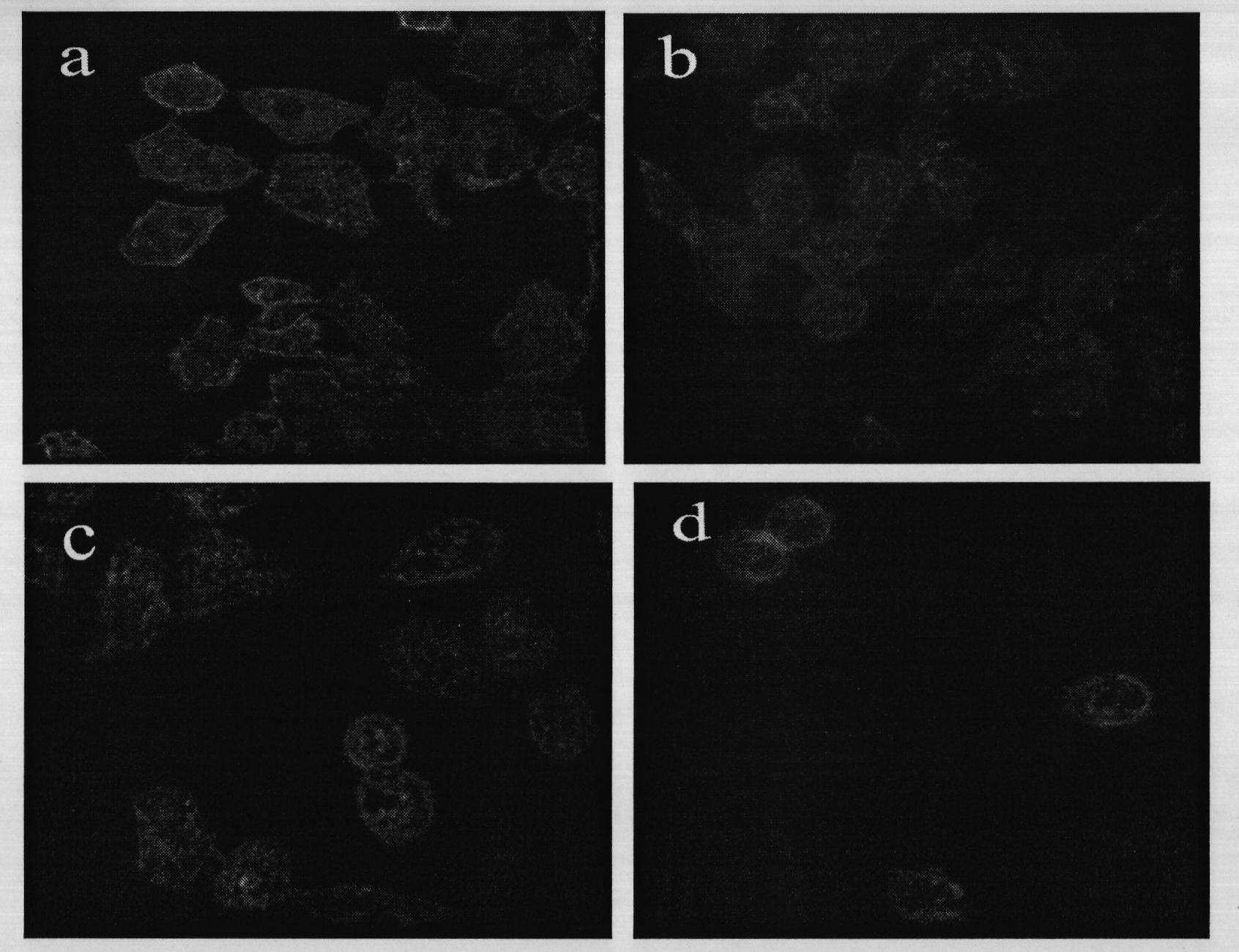
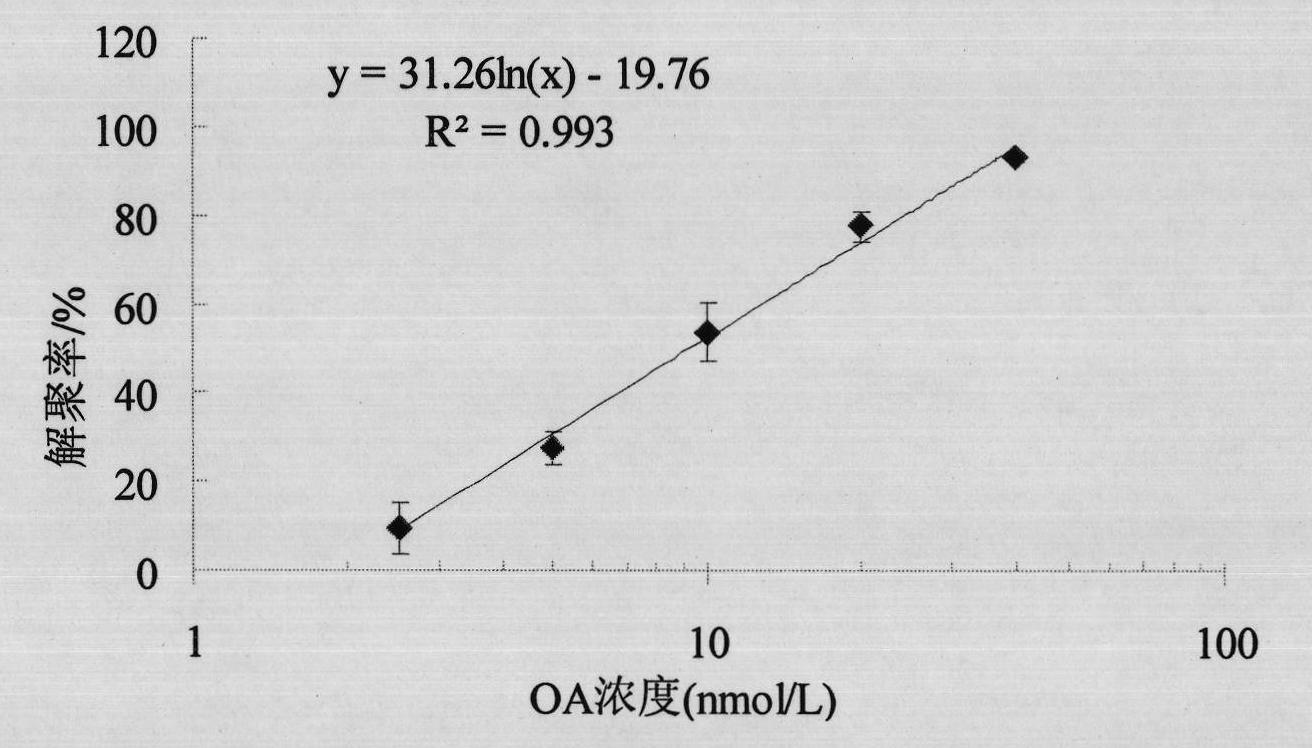
[0047] Example 1 Establishment of a standard curve for OA-induced F-actin depolymerization in HL-7702 hepatocytes
[0048] In this example, HL-7702 hepatocytes were used as the research object, and the research on the DSP cell detection method was carried out using OA standard products.
[0049] Use Oregon After 514phalloidin fluorescently labeled F-actin, it was observed using a confocal laser microscope.
[0050] experimental method:
[0051] After the cells grew to 80% confluence, they were digested with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA to collect the cells, centrifuged and resuspended (at a density of 5×10 5 cells / mL), inoculate 2 mL of cell suspension into a 6-well plate covered with glass, and culture in an incubator. After culturing for 24 hours, the medium was discarded, and HL-7702 hepatocytes were infected with 5, 10, and 20 nmol / L OA respectively, and methanol was used as a control. After 24 hours of OA exposure, wash with PBS twice, and stain according to the method of Phal...
Embodiment 2
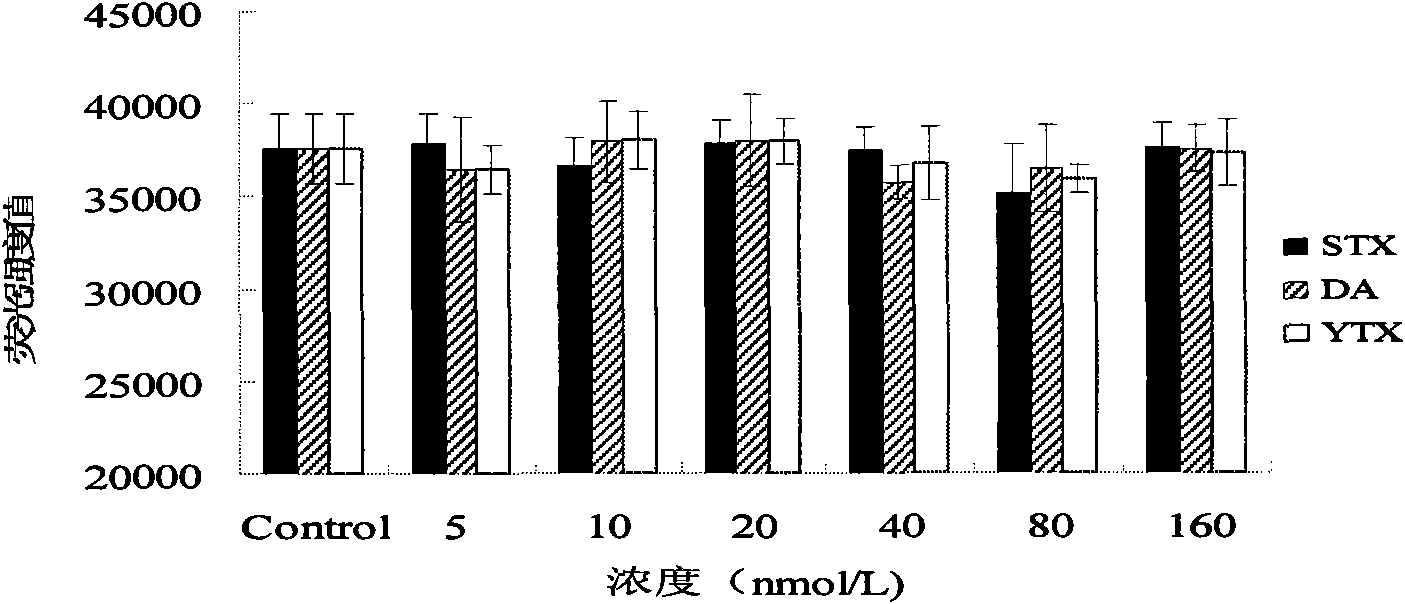
[0071] Example 2 Detection of diarrheal shellfish toxin
[0072] STX, the main component of paralytic shellfish toxin, and DA and YTX, the main components of amnestic shellfish toxin, were selected to act on HL-7702 hepatocytes at different concentrations (5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160nmol / L) (experimental The method is the same as in Example 1), and the specificity detection of the fluorescence detection method is carried out. Take the different concentrations of STX, DA and YTX as the abscissa, and the fluorescence intensity of each treatment group as the ordinate, such as image 3 as shown, image 3 It shows that other shellfish toxins that may be mixed with diarrheal shellfish toxins will not cause the depolymerization of F-actin in cells, and will not interfere with diarrheal shellfish toxins. SPSS 13.0 statistical software was used for one-way analysis of variance. In the range of 5-160nM, the fluorescence intensity values of STX, DA and YTX were not significantly different...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Repeatability experiment of embodiment 3 cell F-actin detection method
[0076] The 6 shellfish samples were repeatedly detected 3 times, the depolymerization rate was calculated, and the OA concentration was calculated corresponding to the standard curve of the cell F-actin detection method. The results are shown in Table 3. The coefficient of variation is 3.18% to 14.12%. The coefficient is 7.97%.
[0077] Table 3 Repeatability of cell F-actin detection method
[0078]
[0079]
[0080] Table 3 shows that the cell F-actin detection method has good stability and good repeatability in the detection of shellfish samples.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| coefficient of variation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com