Probe for detecting lamivudine drug-resistant variant of hepatitis B virus and application method thereof
A technology of lamivudine and detection probes, which is applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of long detection process, limited popularization and application, complex and time-consuming operation, etc., and achieve the effects of saving treatment costs, good sensitivity, and large detection throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] The determination of the detection probe of embodiment 1 hepatitis B virus lamivudine drug-resistant variant
[0056] The present invention uses bioinformatics to determine the lamivudine resistance sites of hepatitis B virus as shown in Table 1, the nucleotide sequences at the 180th, 204th and nearby RT regions of HBV.
[0057] Table 1 The nucleotide sequences of the 180th, 204th and nearby RT regions of the constructed HBV full gene plasmid
[0058]
[0059] Note: The italic letters represent the codons at rt180 and rt204 respectively
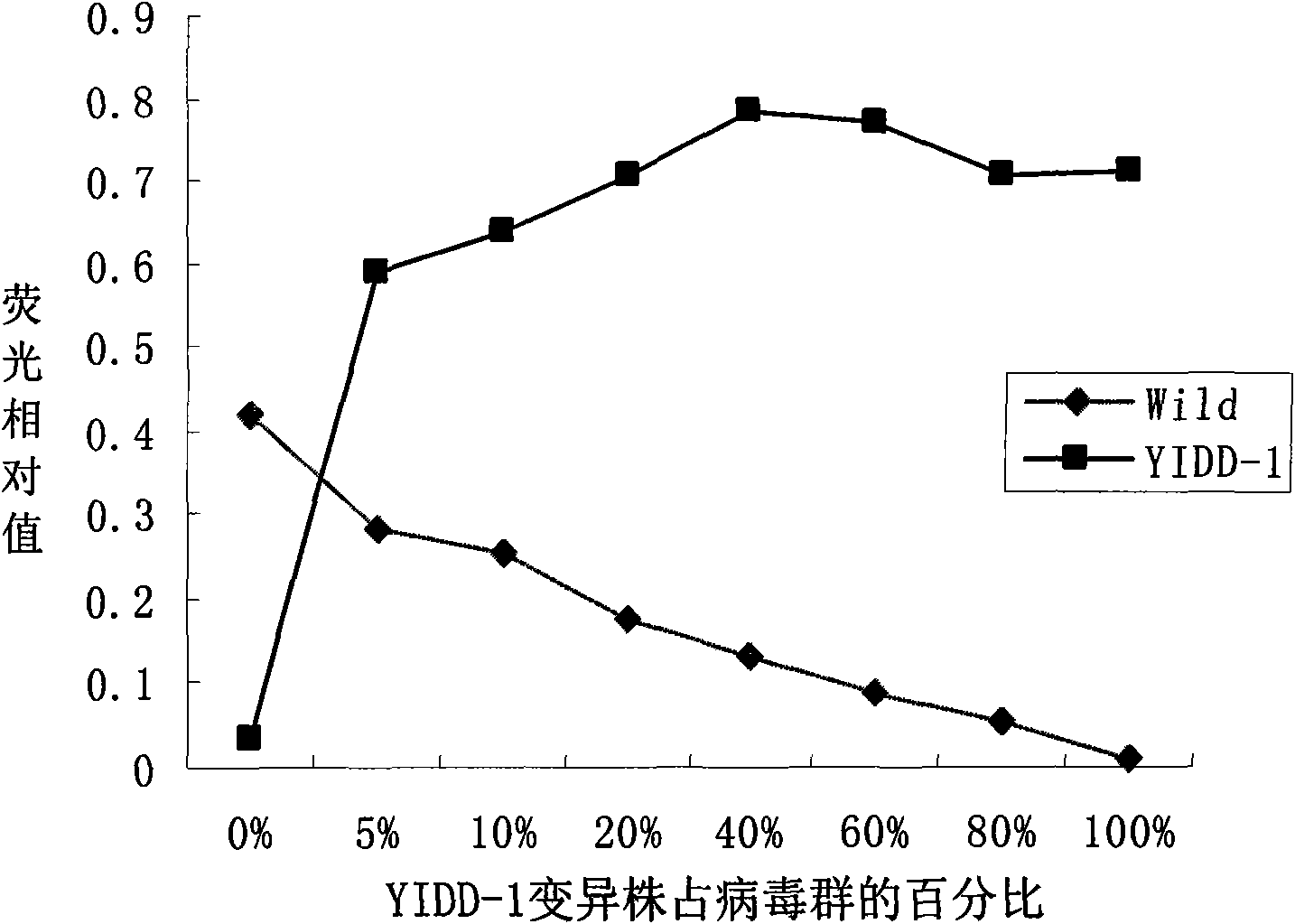
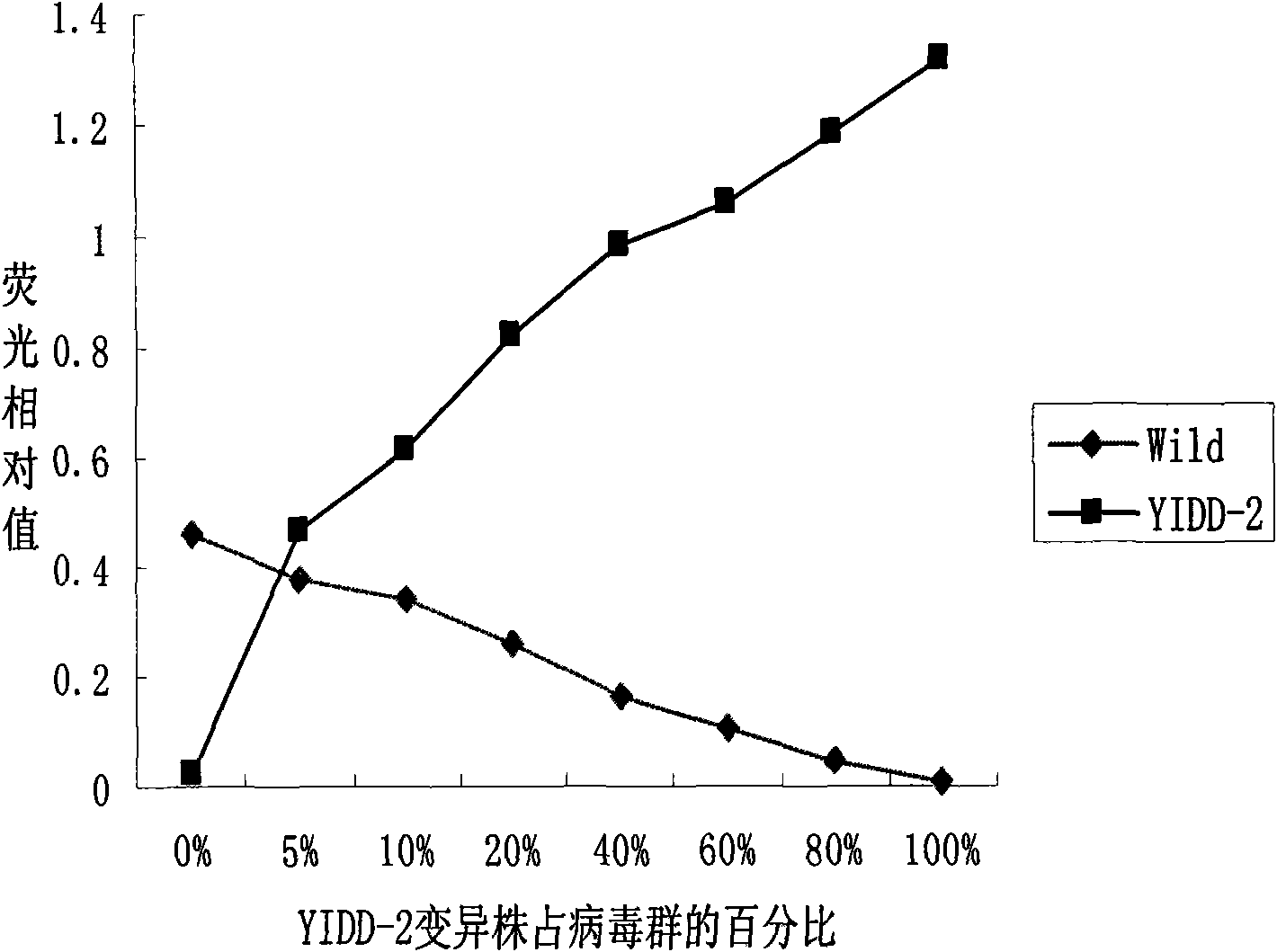
[0060] Then according to the obtained hepatitis B virus lamivudine drug-resistant site design detection probe in Table 1, after testing,
[0061] SEQ ID NO 12-19 of Table 2 can all be used as detection probes.
[0062] Table 2. Probe sequences
[0063]
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2 Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Lamivudine-resistant Mutants
[0065] 1. Sample pretreatment: HBV DNA, as a template for amplification;
[0066] 2. PCR amplification and biotin labeling of target fragments: clinical samples with a high viral load use HBV DNA as a template, and directly amplify with the inner primer (the 5' end of the downstream primer is biotin-labeled), including rt180 to 250 The sequence between amino acids, such as clinical samples with a high viral load, requires nested PCR, that is, use primers RTS1 and RTAS1 to amplify the RT region, and then use the inner primers of each site to perform the second step on the main variation region of the corresponding gene. Two rounds of PCR amplification (for primers, see the "Primer Sequence" table in the Summary of the Invention); PCR amplification conditions are: 94°C pre-denaturation for 5 minutes; 94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 72°C for 45s, cycle 35 times; the last cycle ends Then extend at 72°C for...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3 Serum Sample Detection
[0074] Blood samples were collected from patients, and serum HBV DNA was extracted with phenol-chloroform as an amplification template; detection was performed according to the method in Example 2, and the results are shown in Table 4.
[0075] Table 4 MASA detection of serum samples from patients with lamivudine-related HBV resistance
[0076]
[0077] Note: Fluorescence value = target gene fluorescence value / internal reference fluorescence value × 100, the negative and positive hybridization signal values of serum samples are represented by the median, Z value = -4.100, -4.588, -4.520, P<0.05, The difference was statistically significant.
[0078] The above results show that the detection results are consistent with the actual.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com