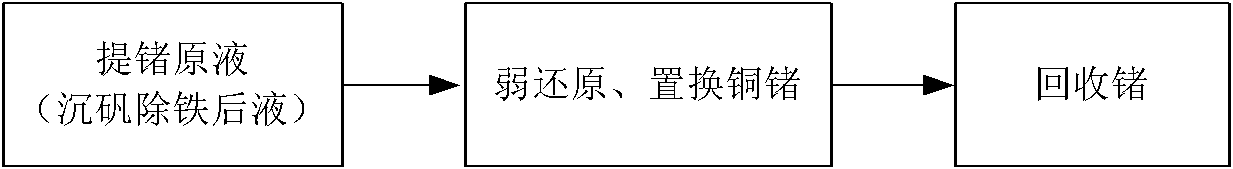
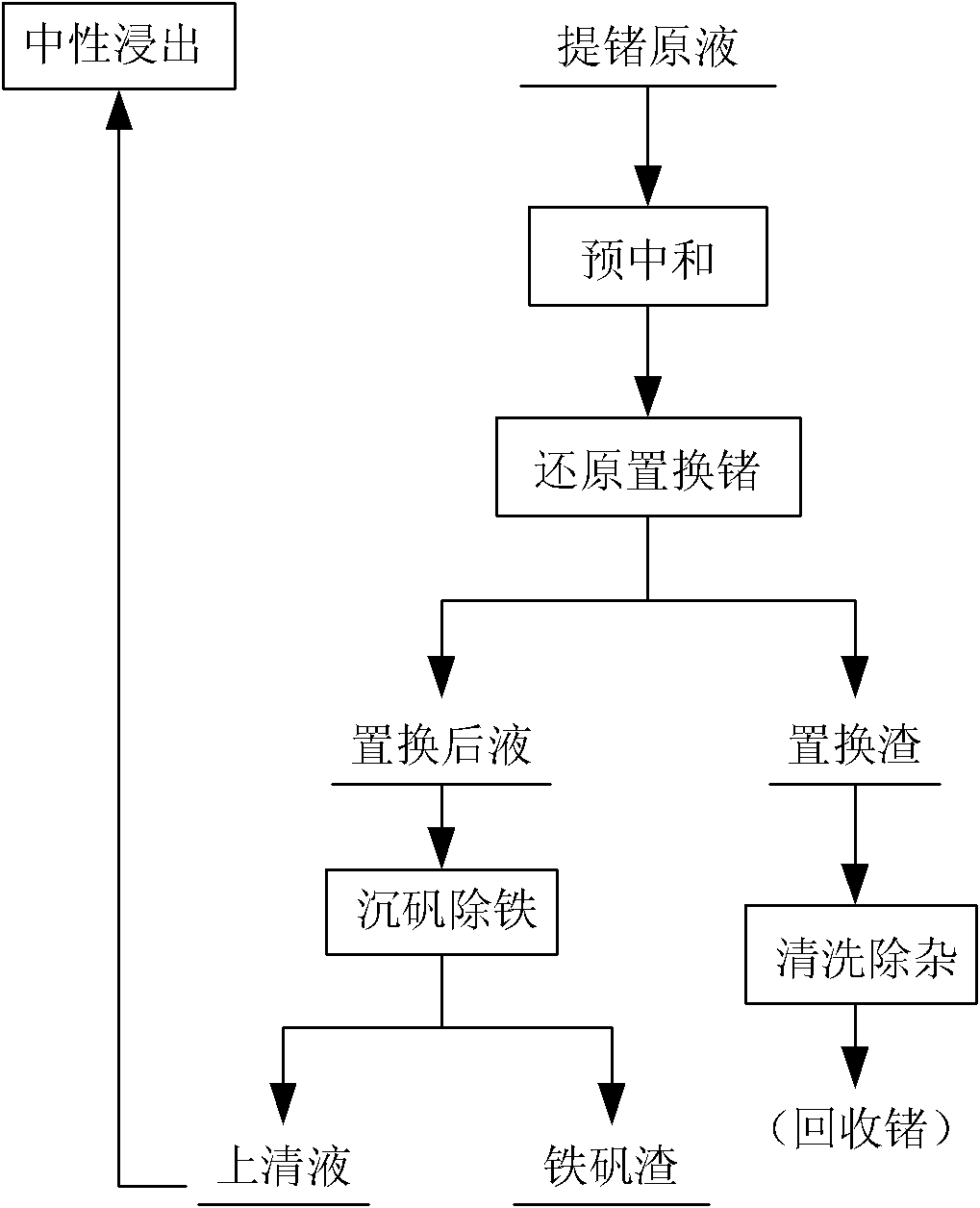
Method for enriching germanium from wet process zinc smelting system
A hydrometallurgical zinc smelting and enrichment technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of difficult solid-liquid separation of ferric hydroxide colloid, low grade of neutralized slag and germanium, affecting zinc electrolysis efficiency, etc., and achieves high replacement rate. , Process condition control, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] see figure 1 , add neutralizer zinc oxide calcine to the high-acid germanium extraction liquid (containing germanium 24mg / L) to adjust the pH to 4.5, control the heating temperature at 100°C, then add iron powder to reduce ferric ions, and control the temperature at 90°C After 20 minutes of reaction, a second batch of excess iron powder was added, the temperature was controlled at 95° C., the reaction time was 120 minutes, and the replacement rate of germanium could reach 96.2%. After liquid-solid separation, the replaced liquid needs to sink alum again to remove iron, and the replacement slag is washed with dilute sulfuric acid and used to extract germanium.
Embodiment 2
[0023] see figure 1 , add neutralizer zinc oxide calcine to the high-acid germanium extraction liquid (containing germanium 24mg / L) to adjust the pH to 1.0, control the heating temperature at 90°C, then add iron filings to reduce ferric ions, and control the temperature at 85°C After 20 minutes of reaction, a second batch of excess iron filings was added, the temperature was controlled at 95°C, the reaction time was 120 minutes, and the replacement rate of germanium could reach 93.8%. After liquid-solid separation, the replaced liquid needs to sink alum again to remove iron, and the replacement slag is washed with dilute sulfuric acid and used to extract germanium.
Embodiment 3
[0025] see figure 2 , add iron filings to reduce ferric ions to the liquid after iron removal (containing germanium 22mg / L), control the temperature at 95 ° C, after 20 minutes of reaction, add the second batch of excess iron filings, control the temperature at 85-95 ℃, the reaction time is 120min, and the replacement rate of germanium can reach 93.2%. After liquid-solid separation, the replaced liquid needs to sink alum again to remove iron, and the replacement residue is washed with dilute acid and used to extract germanium.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com