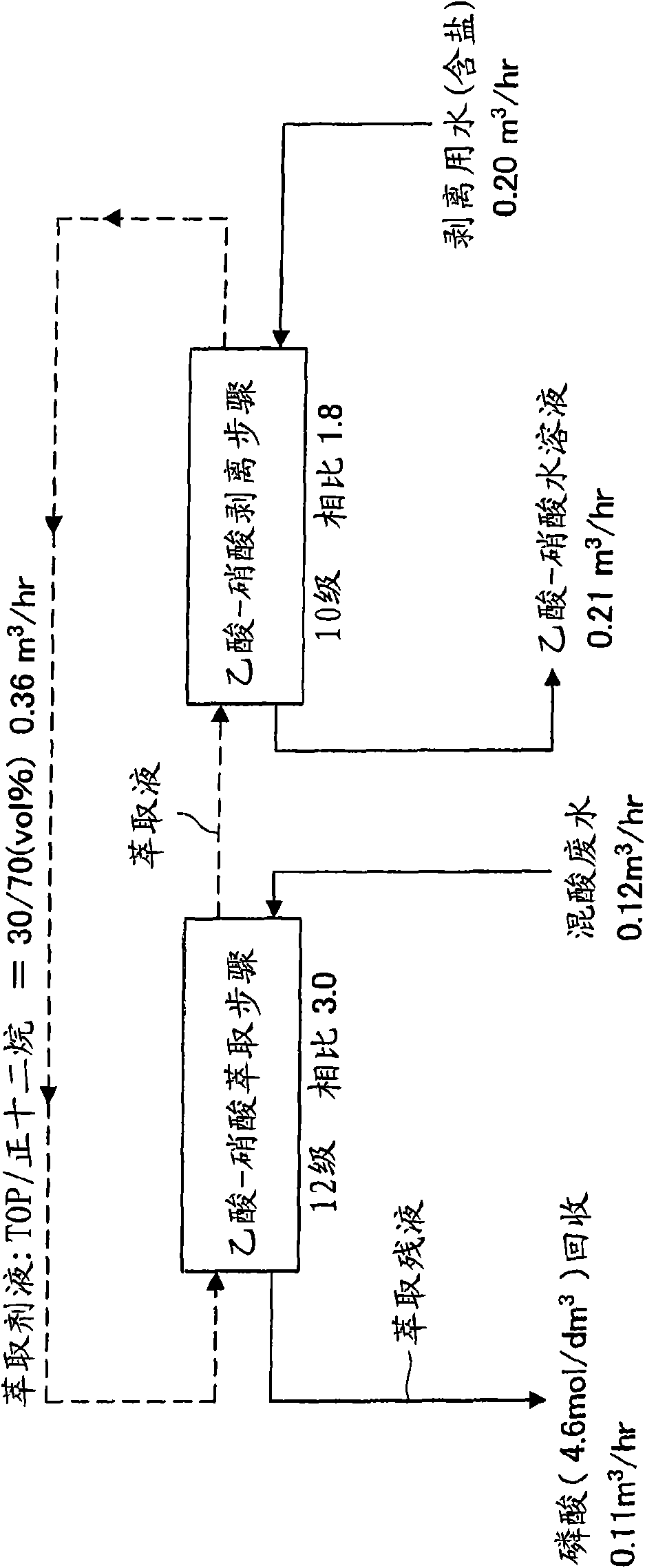
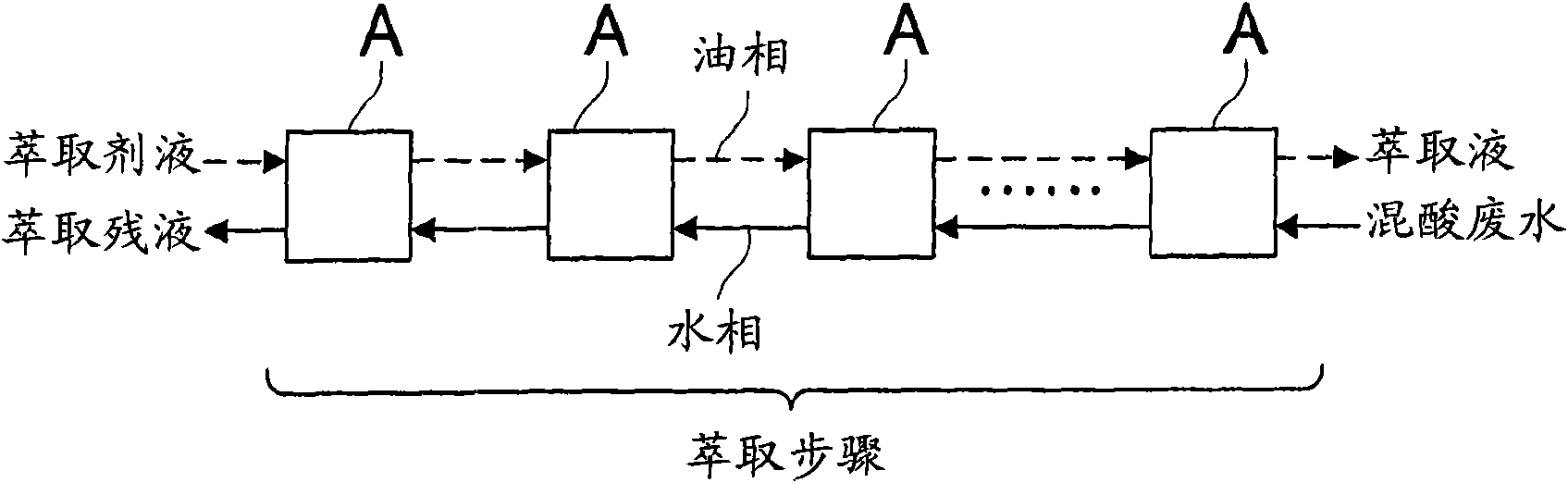
Method for separating and recovering phosphoric acid from acetic acid-nitric acid-phosphoric acid series mixed acid waste liquor
A technology of waste liquid separation and nitric acid, applied in phosphoric acid, phosphorus oxyacid, extraction water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low separation between oil phase and water phase, poor separation, difficult extraction, etc., and achieve extraction selectivity The effect of improving, improving separability, and improving peelability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
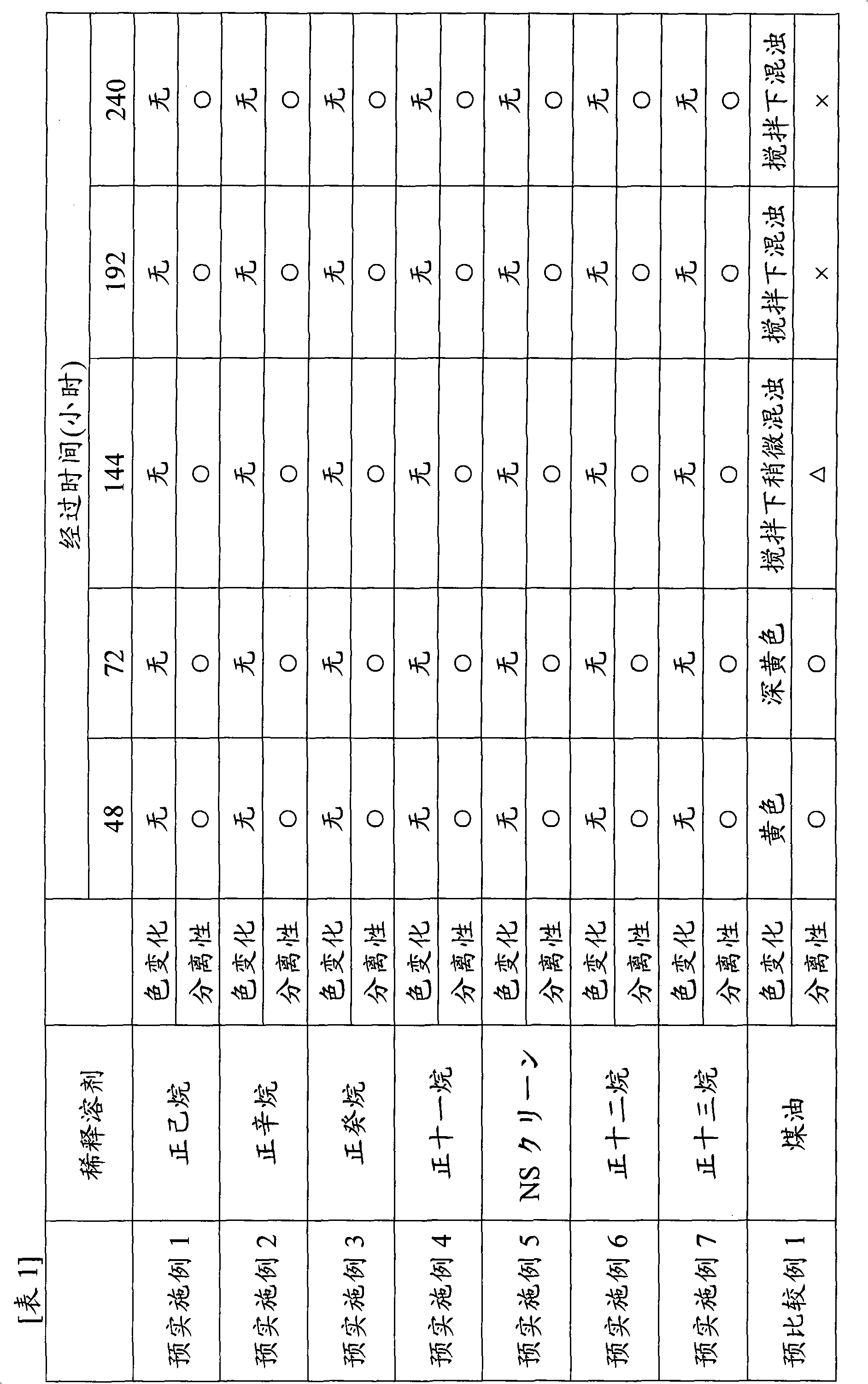
[0049] The extractant liquid containing the composition of tris (2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (TOP) / n-hexane=30 / 70 (volume ratio) is mixed with the mixed acid wastewater containing the composition shown in Table 2 in a ratio of 1:1 , put the mixed solution into a 100 mL glass container, and install it in a thermostat (always 35° C.). After installation (starting) at 10:00 AM, shake the glass container containing the above mixed liquid with a shaker for 1 minute at 10:00 AM every day, and then evaluate the separation of the oil phase and the water phase based on the following evaluation criteria (two layer separation) was evaluated.
[0050] (Evaluation criteria for the separability of oil phase and water phase)
[0051] "○"...It takes less than 1 minute until the oil phase and water phase are separated, and the separation property is good
[0052] "△"...Time to separate into oil phase and water phase is 1 minute or more and less than 5 minutes
[0053] "x"... The time until sepa...
Embodiment 2
[0055] As the extractant liquid, the extractant liquid containing the composition of tris (2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (TOP) / n-octane=30 / 70 (volume ratio) was used, except that it was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1. , to evaluate the separation of the oil phase and the water phase.
Embodiment 3
[0057] As the extractant liquid, the extractant liquid containing the composition of tris(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (TOP) / n-decane=30 / 70 (volume ratio) was used, except that it was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1. , to evaluate the separation of the oil phase and the water phase.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com