Thermo-chromatic infrared emitting ability ceramic sheet material and preparation method thereof
A technology of infrared emissivity and ceramic flakes, which is applied in the field of functional materials, can solve the problems of high cost and complex structure of electrovariable infrared emissivity materials, and achieve the effects of low cost, high strength and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] La 0.825 Sr 0.175 MnO 3 The preparation of thermally variable infrared emissivity ceramic sheet material comprises the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: According to the molar ratio of metal substances in the molecular formula, weigh 26.879 grams of high-purity La 2 o 3 , 5.1667 g SrCO 3 , 22.988 g MnCO 3 , plus 8.255 grams of 2-hydroxypropanetricarboxylic acid and 27.517 grams of pure water, ball milled for 4 to 7 hours and then dried.
[0028] Step 2: Pre-calcination: put the dried precursor into a calcination furnace, and calcine it at 700-1000°C for 4-7 hours at a heating rate of 5°C-10°C / min, and then cool down with the furnace.
[0029] Step 3: Sintering: Ball mill the obtained calcined product in ethanol for 2-4 hours, dry it, raise the temperature (10-20°C / min) to 900-1450°C, heat-preserve and calcinate for 3-5 hours, and cool down naturally to obtain La 1-x Sr x MnO 3 (0.1≤x≤0.3) Sintered powder.
[0030] Step 4: Preparation of green ceramic sheet: An...
Embodiment 2
[0036] La 0.775 Sr 0.225 MnO 3 The preparation of thermally variable infrared emissivity ceramic sheet material comprises the following steps:
[0037] Step 1: According to the molar ratio of metal substances in the molecular formula, weigh high-purity La 2 o 3 25.25 g, SrCO 3 6.6429 g, MnCO 3 22.988 grams, plus 8.232 grams of 2-hydroxypropanetricarboxylic acid and 27.44 grams of pure water, dried after ball milling for 4 to 7 hours.
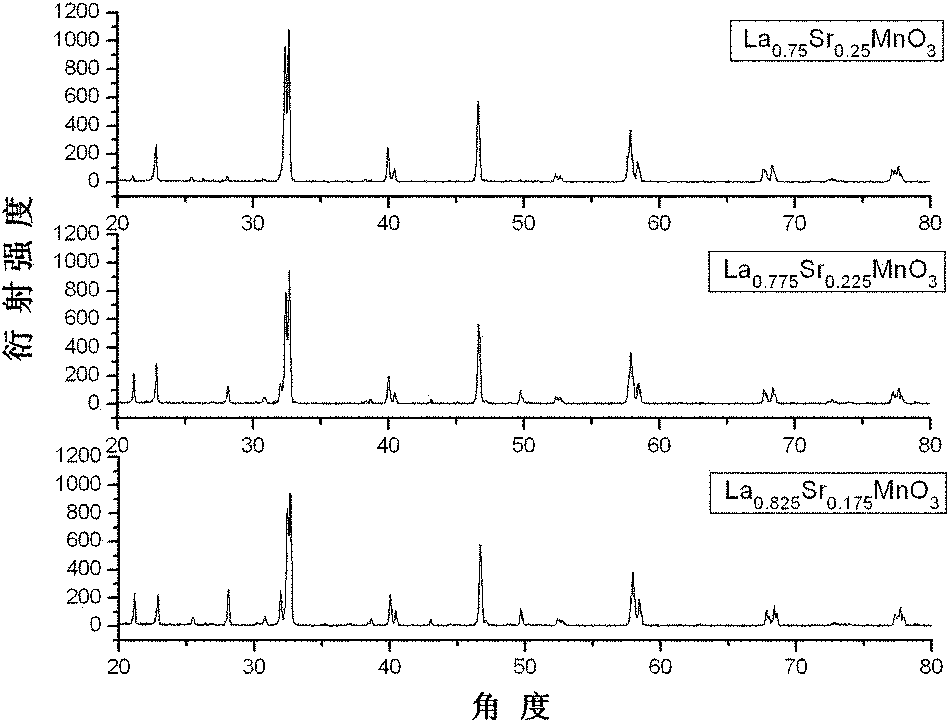
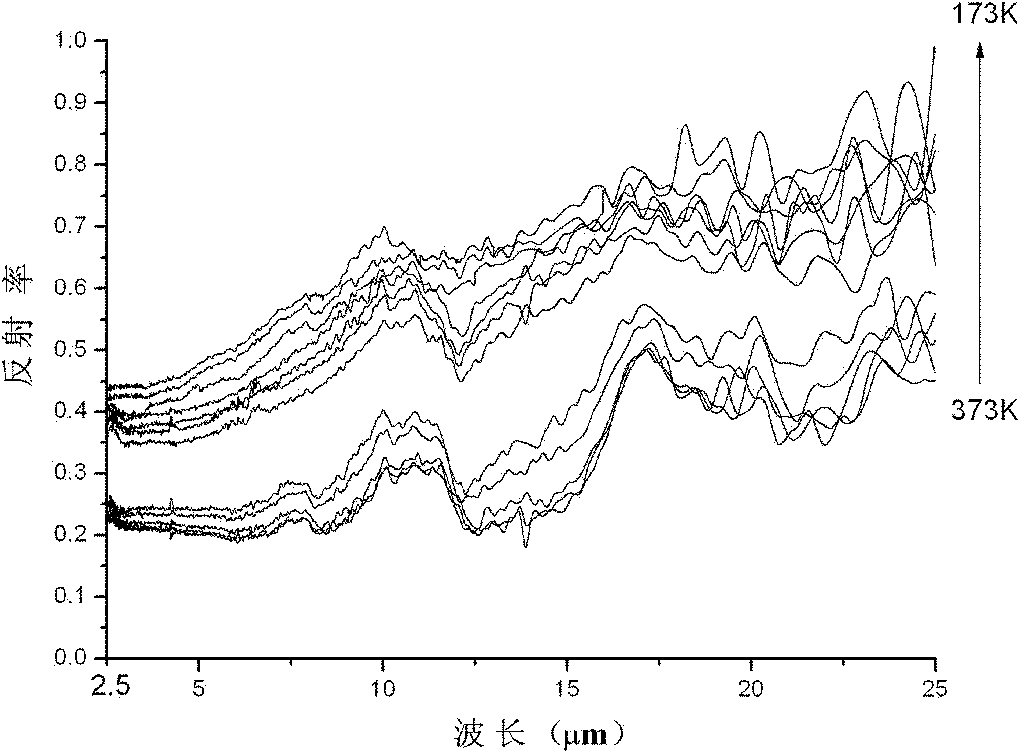
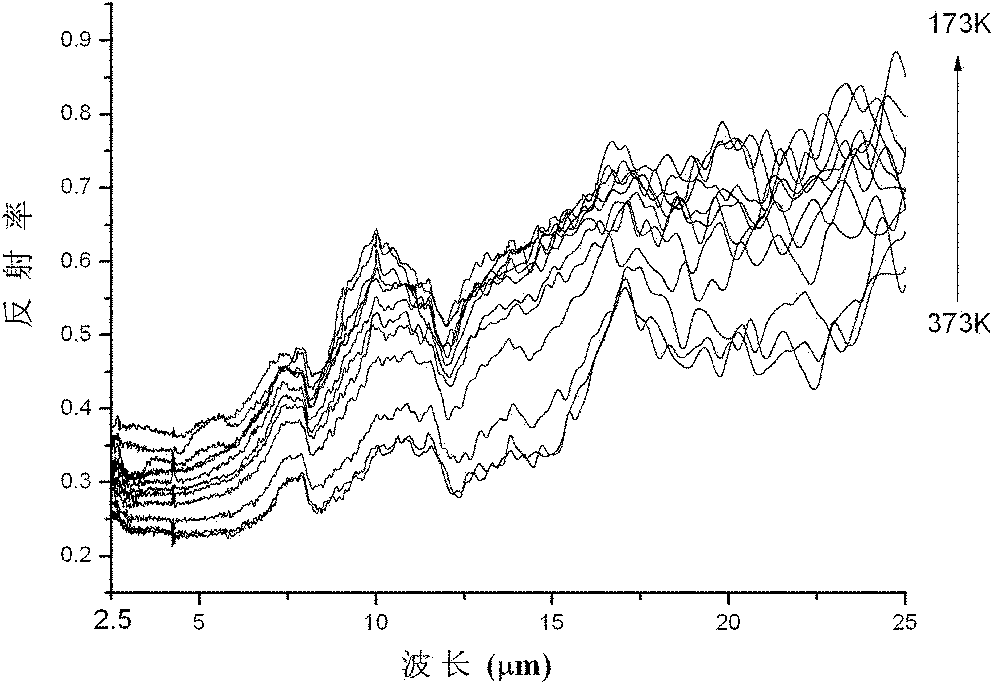
[0038] Steps 2 to 6 are similar to steps 2 to 6 of Example 1, and finally La 0.775 Sr 0.225 MnO 3 Thermally variable infrared emissivity ceramic sheet material, the sample is determined by the Philips X'Pert Pro Mpd X-ray diffractometer in the Netherlands to determine the phase structure, and the Tensor27 Fourier infrared spectrometer of Bruker Spectroscopy Instrument Company is used to measure its temperature at 173K, 193K, Infrared reflectivity of 213K, 233K, 253K, 273K, 283K, 303K, 323K, 343K, 363K and 373K, and calculate the emissiv...
Embodiment 3
[0040] La 0.75 Sr 0.25 MnO 3 The preparation of thermally variable infrared emissivity ceramic sheet material comprises the following steps:
[0041] Step 1: According to the molar ratio of metal substances in the molecular formula, weigh high-purity La 2 o 3 24.436 g, SrCO 3 7.381 g, MnCO 3 22.988 grams, plus 8.221 grams of 2-hydroxypropanetricarboxylic acid and 27.403 grams of pure water, dried after ball milling for 4 to 7 hours.
[0042] Steps 2 to 6 are similar to steps 2 to 6 of Example 1, and finally La 0.75 Sr 0.25 MnO 3 Thermally variable infrared emissivity ceramic sheet material, the sample is determined by the Philips X'Pert Pro Mpd X-ray diffractometer in the Netherlands to determine the phase structure, and measured by the Tensor27 Fourier infrared spectrometer (additional mid-infrared integrating sphere) of Bruker Spectrum Instruments Its infrared reflectance at 173K, 193K, 213K, 233K, 253K, 273K, 283K, 303K, 323K, 343K, 363K and 373K temperature points...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com