2,4-D pesticide production waste water pretreatment method
A kind of waste water production, 4-D technology, applied in 2 fields, can solve the problems of high COD value of waste water, high water solubility of extractant, complex recovery phase components, etc., achieve high removal rate, obvious environmental and economic benefits, save The effect of alkali removal operation and materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
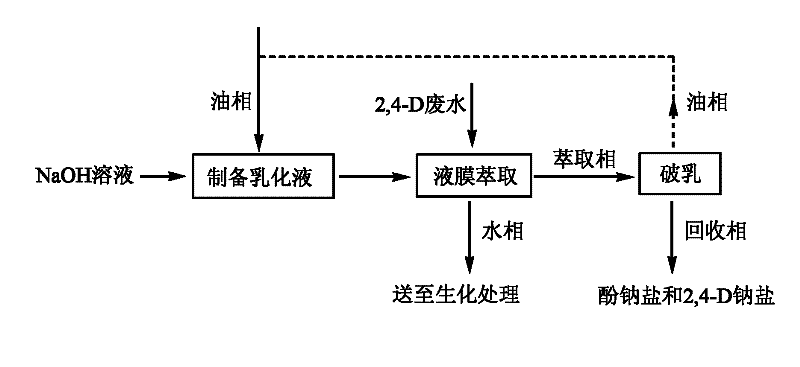
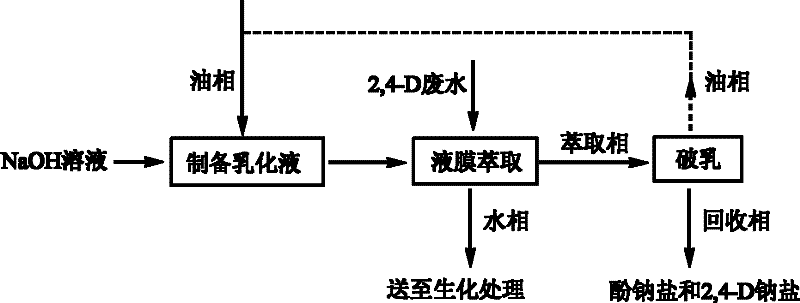
[0024] Take 30L of surfactant L-113A, 60L of additive liquid paraffin, and 910L of film solvent aviation kerosene to form an oil phase, put it into a milk maker, add 500L of 15% sodium hydroxide solution at the same time, and high shear at 3000 rpm Cut and emulsify for 30 minutes to obtain a milky white water-in-oil emulsion.
[0025] Disperse 1000L of the above-mentioned emulsion in 6000L of waste water to be treated, stir and extract for 30 minutes at a speed of 130 rpm, and let stand to separate layers. After the lower water phase is clarified, the oil and water phases are separated, the water phase enters the biochemical treatment device for conventional treatment, and the upper oil phase (extraction phase) enters the electrostatic demulsification device.
[0026] Control the operating voltage of the electrostatic demulsification device to 23V, current 8-10A, after 30 minutes of demulsification time, separate the oil phase and water phase, the oil phase is reused to make t...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Take 20L of surfactant L-113A, 50L of additive liquid paraffin, and 930L of film solvent kerosene to form an oil phase, put it into a milk maker, add 500L of 20% sodium hydroxide solution at the same time, and high shear at 3000 rpm Cut and emulsify for 30 minutes to obtain a milky white water-in-oil emulsion.
[0029] Disperse 750L of the prepared emulsion in 6000L of waste water to be treated, stir and extract for 60 minutes at a speed of 130 rpm, and let stand to separate layers. After the lower water phase is clarified, the oil and water phases are separated, the water phase enters the biochemical treatment device for conventional treatment, and the upper oil phase (extraction phase) enters the electrostatic demulsification device.
[0030] The operation of electrostatic demulsification separation is the same as in Example 1, and the obtained water phase contains 24.3% sodium 2,4-dichlorophenate and 0.7% sodium 2,4-D, which is reused in the condensation section.
Embodiment 3
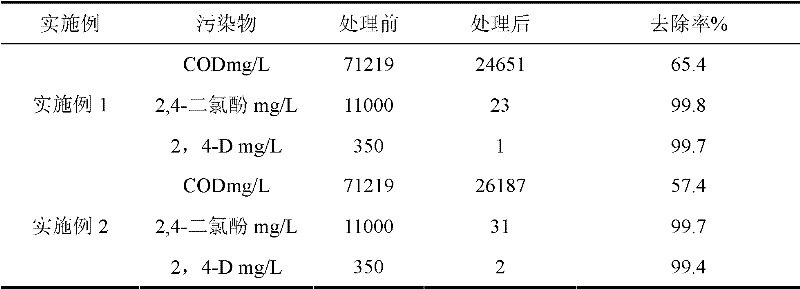
[0032] The waste water after being treated by the waste water pretreatment method of the present invention is analyzed, and each index before and after treatment is shown in the following table:
[0033] Table 1
[0034]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com