Patents
Literature
44results about How to "High degree of insulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
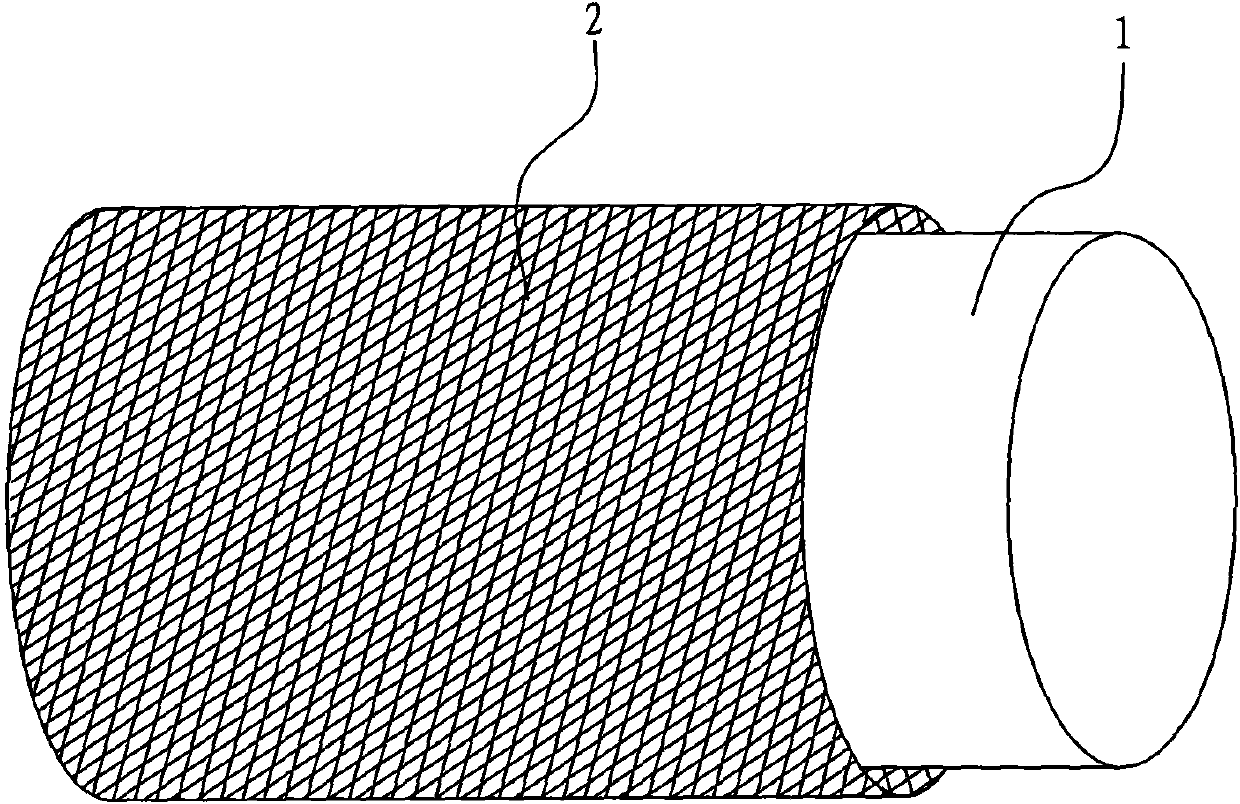
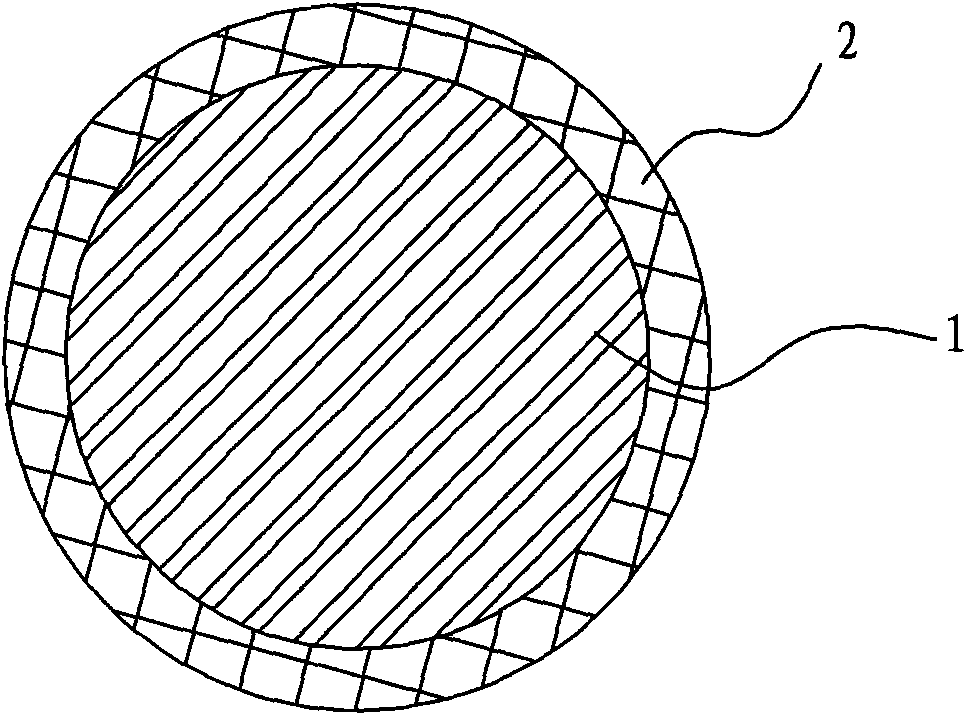
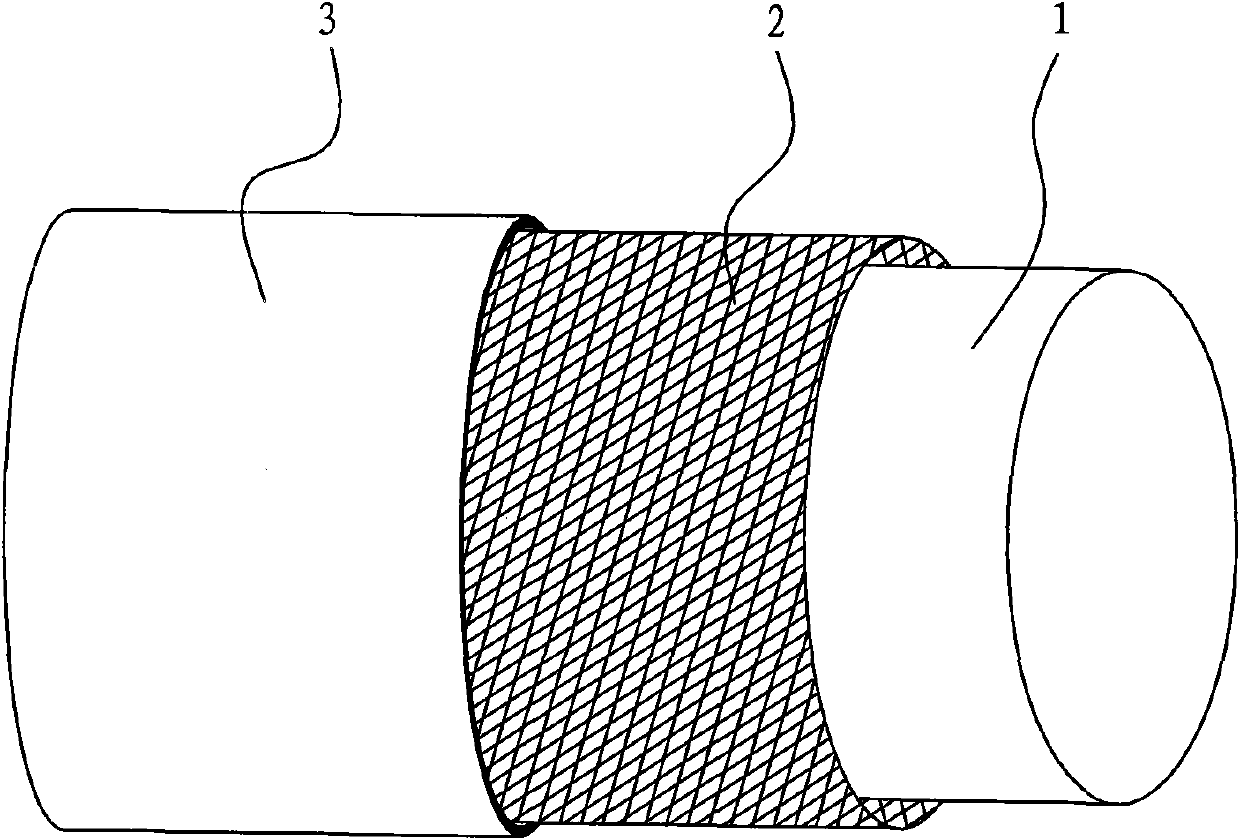
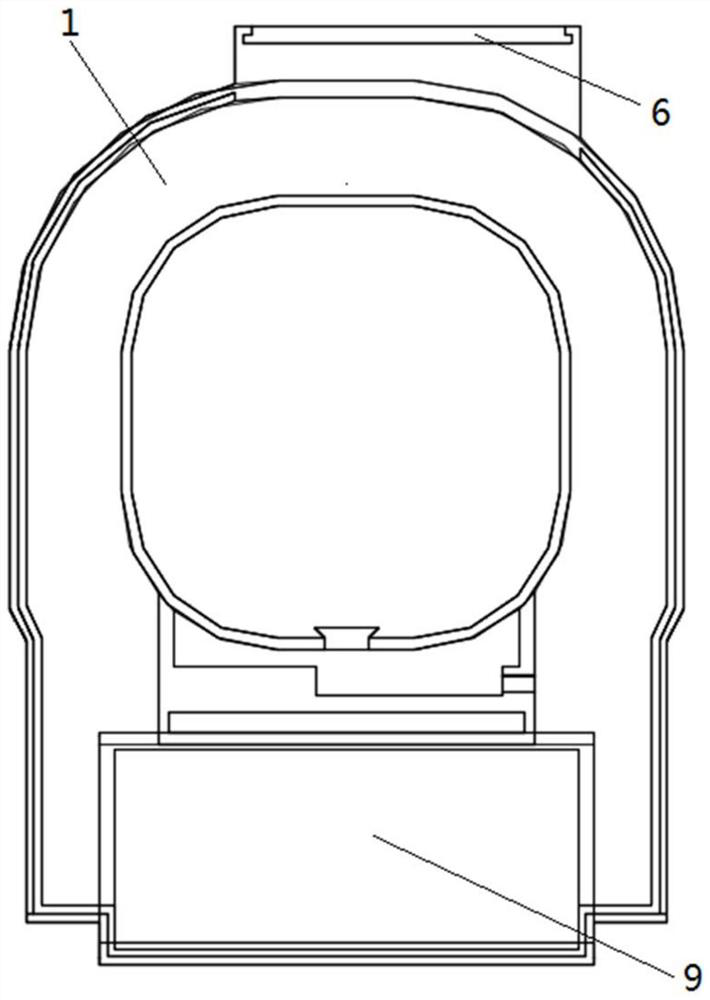
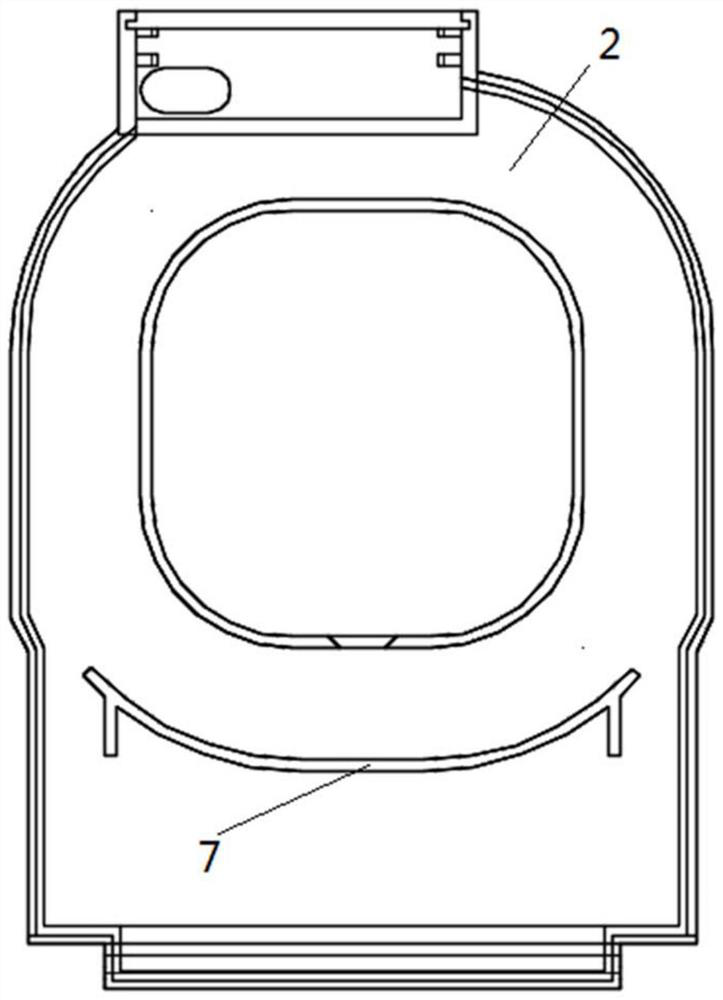
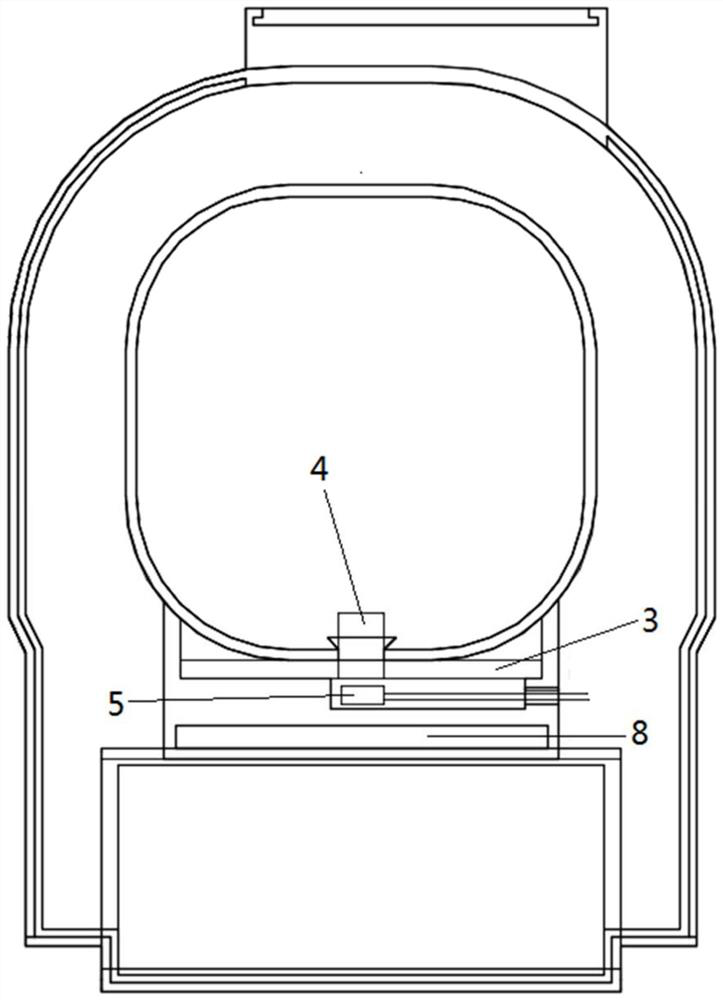
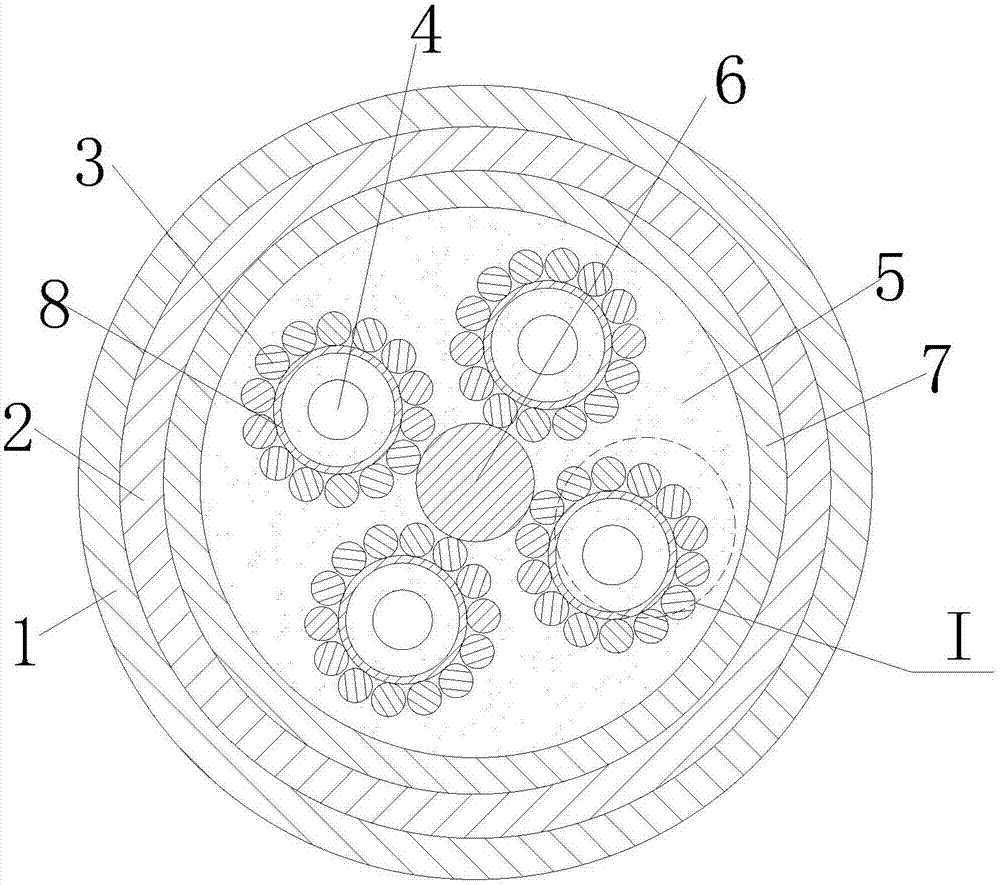
Composite material core used for enhanced cable, preparation process thereof and enhanced cable
InactiveCN102024517AImprove lateral strengthImprove fatigue resistance and fatigue resistanceInsulated cablesCable/conductor manufactureElectrical conductorFiber bundle
The invention relates to a composite material core used for an enhanced cable, a preparation process and the enhanced cable. The composite material core comprises an inner core and an outer layer, wherein the inner core is composed of fiber and thermosetting resin; the outer layer comprises a fiber woven pipe and thermosetting resin which are composited to form the outer layer; and the fiber woven pipe of the outer layer is a network structure which is woven by interlacing a plurality of fiber bundles. The transversal strength of the composite material core is greatly improved by the interlaced network structure, the fatigue resistance of the composite material core is greatly improved, and the service life of the composite material core and a power transmission cable is prolonged; and the problem that the composite material core is broken when the composite material core is stranded, wound and extruded by a conductor in the manufacturing process of the cable is completely avoided. As the fiber woven pipe is adopted by the outer layer, the flexibility of the outer layer is greatly increased by the interlaced and woven structure, thereby meeting the requirement of manufacturing composite material core with major diameter.
Owner:JIANGSU JIATAI TECH MATERIAL
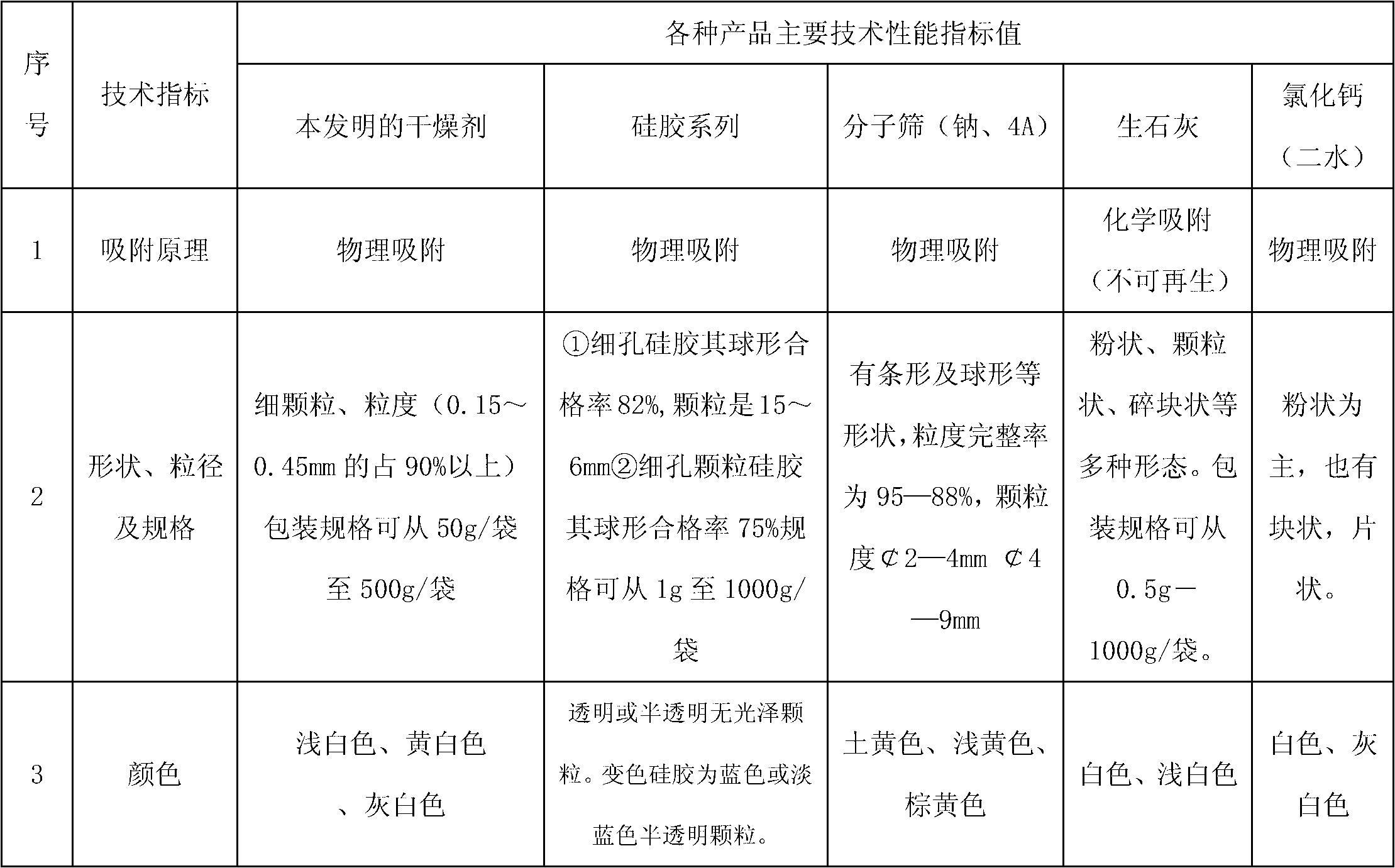
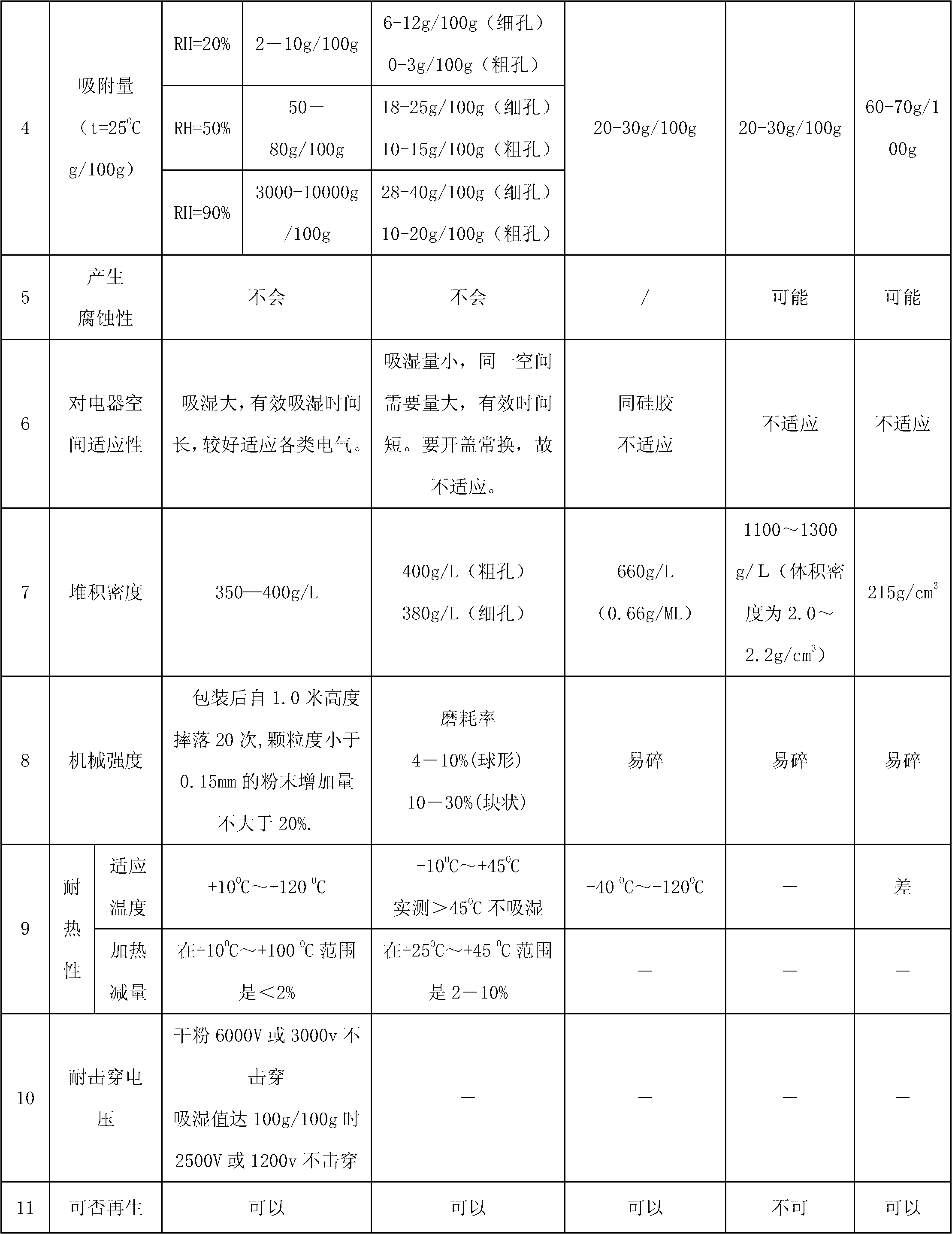
Drying agent for mine underground electric apparatus and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102698573ANot corrosiveNo tendency to explodeDispersed particle separationLow voltageAlkali metal halide
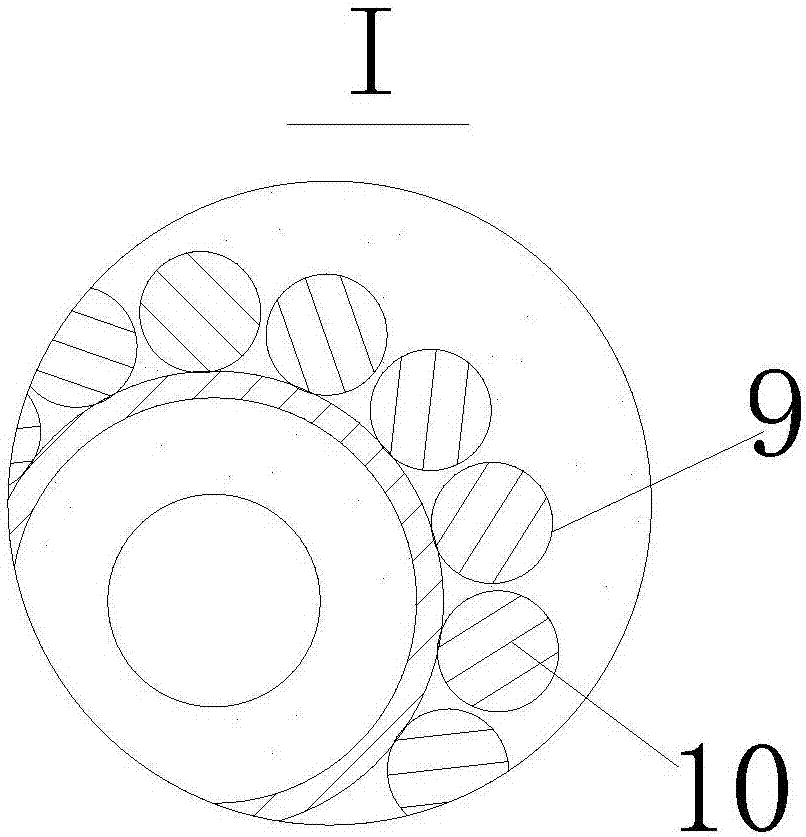
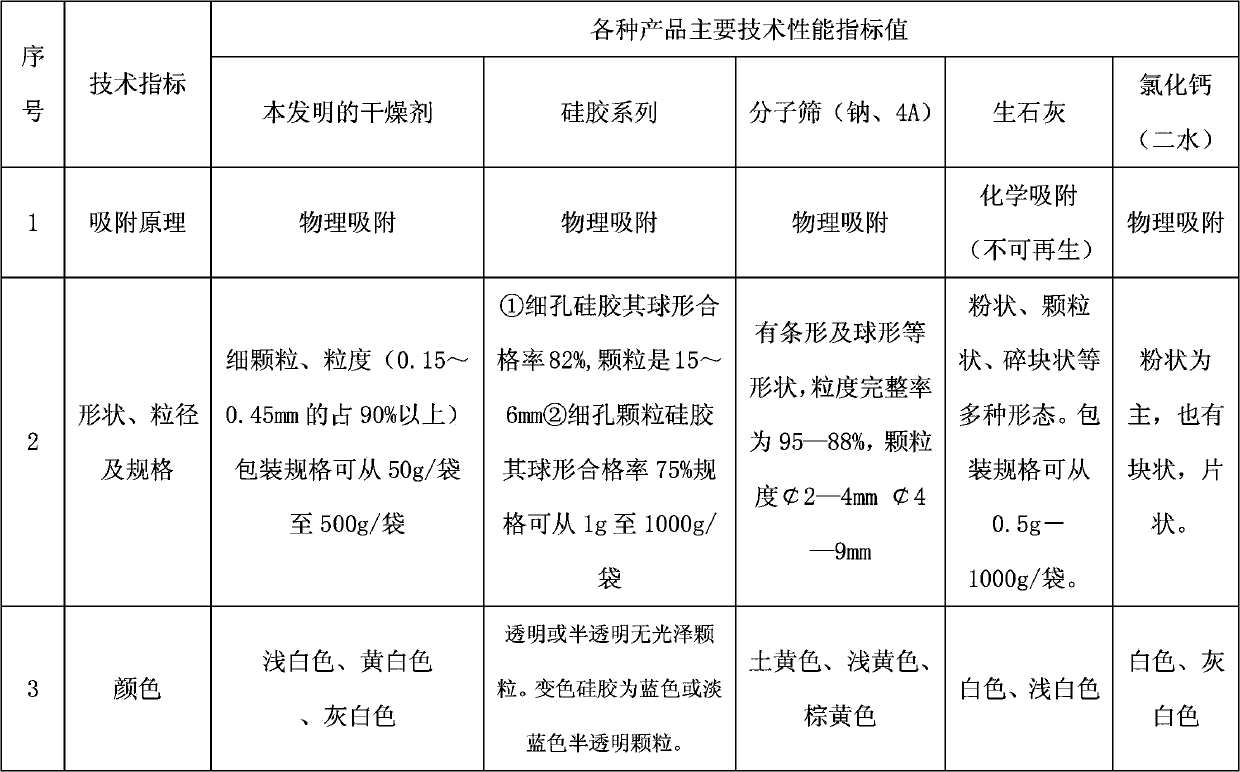
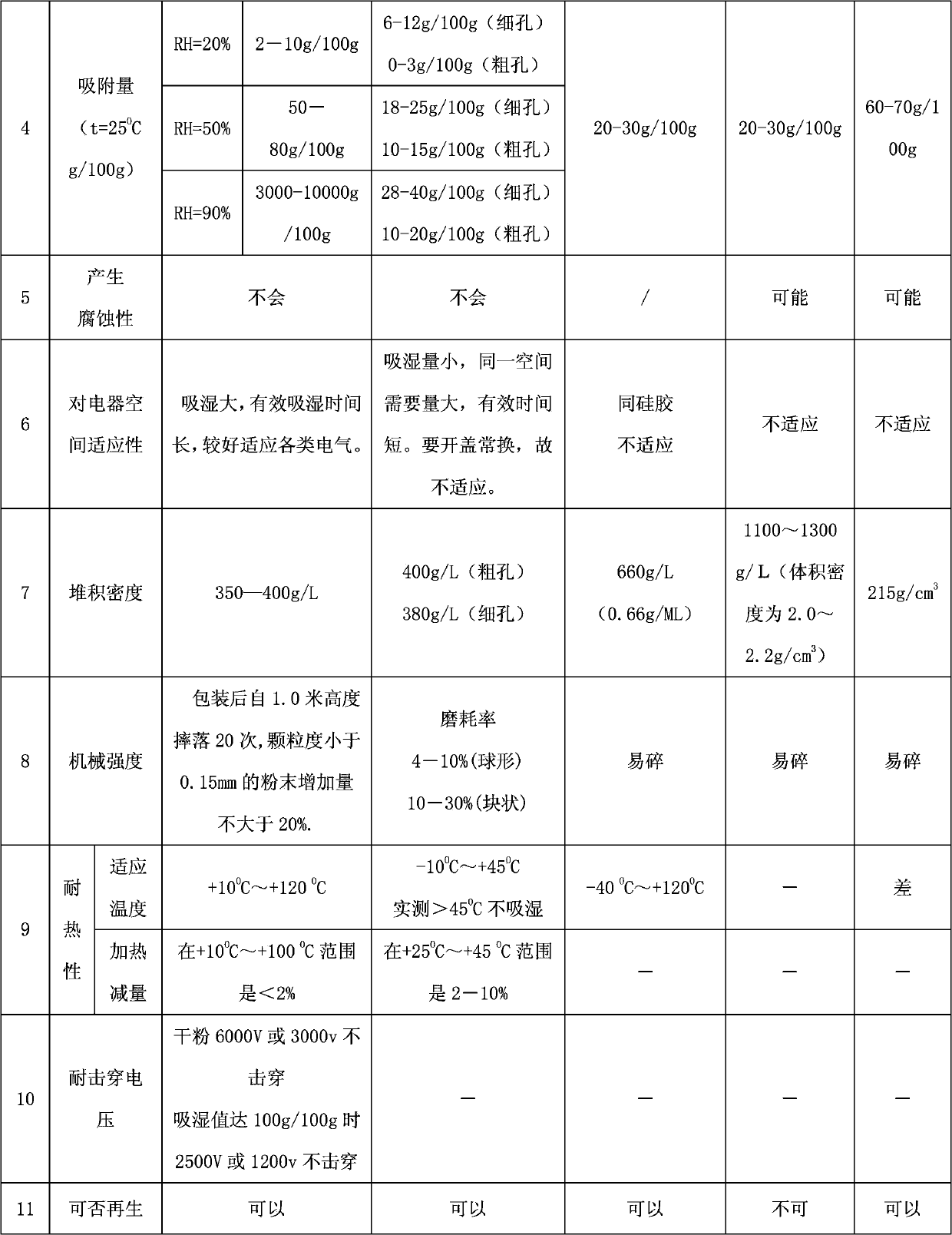
The invention discloses a drying agent for an mine underground electric apparatus and a preparation method of the drying agent, belonging to the field of drying agent, wherein macromolecule water absorbent, compound of silicon or calcium and alkali halide or modified starch are mixed so as to prepare the powdery draying agent according to part by weight; the macromolecule water absorbent is 35-70 parts; the compound of silicon or calcium is 25-55 parts; the alkali halide or a mixture of the alkali halide and the modified starch is 10-15 parts; the grain size of the macromolecule water absorbent is 0.20-0.40mm; and the drying agent is powdery. According to the invention, raw material is wide in source and is purchased easily on the market; the drying agent is used for high / low-voltage power supply appliances worked on a mine underground high-humidity condition (RH=80-100%); the dry powder resists 6000V voltage or does not be broken down under voltage of 3000V; when moisture rate reaches to 1g / g, the dry powder resists 2500V voltage or does not be broken down under voltage of 1200V.
Owner:徐州意创化工科技有限公司
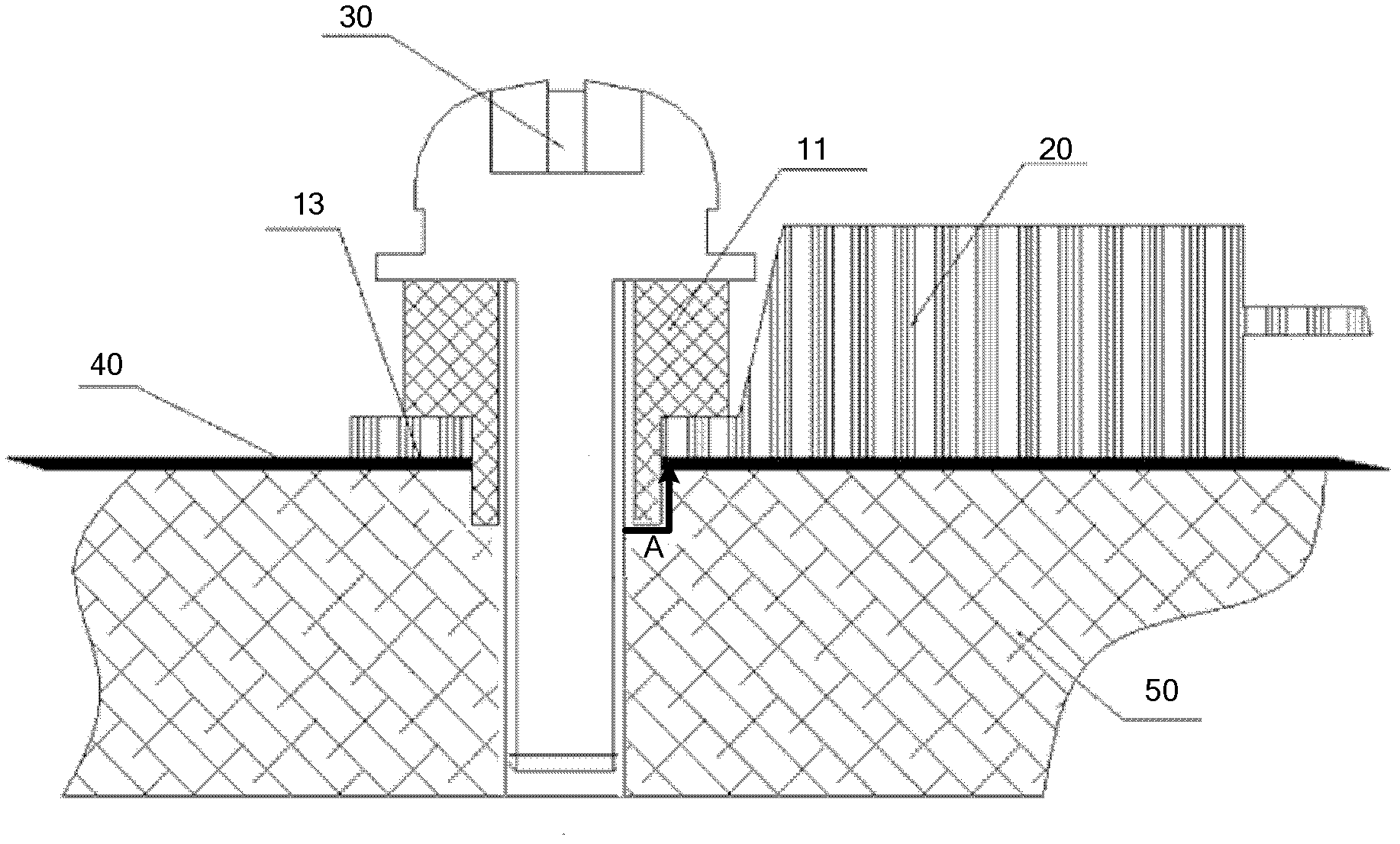
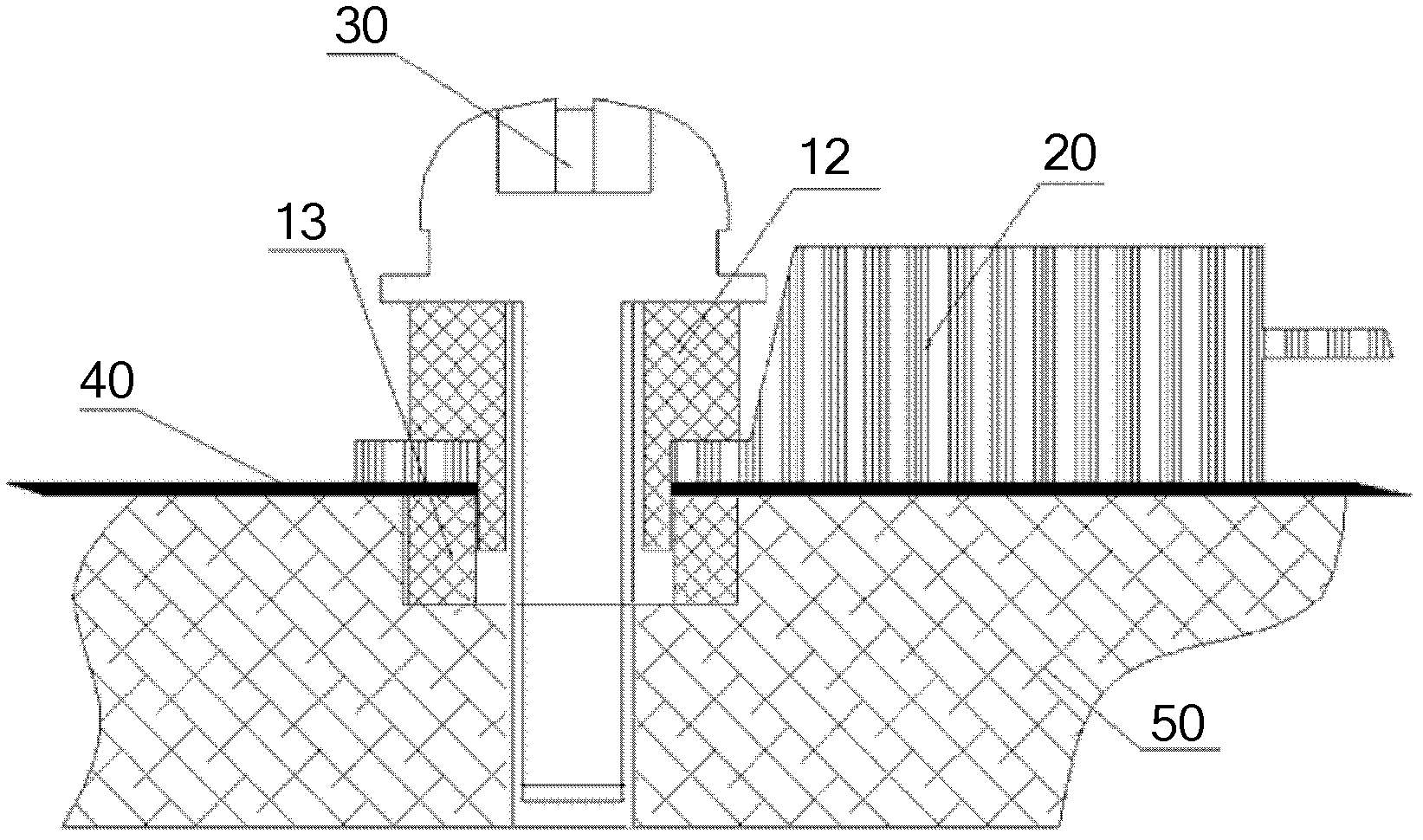
Insulation structure used for fixing electronic element, electronic element and component
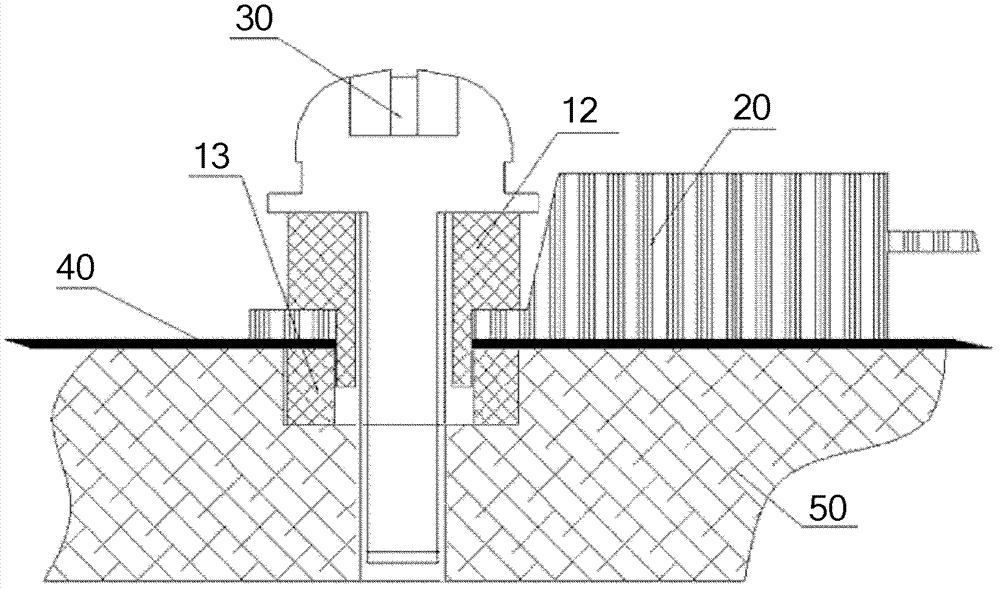
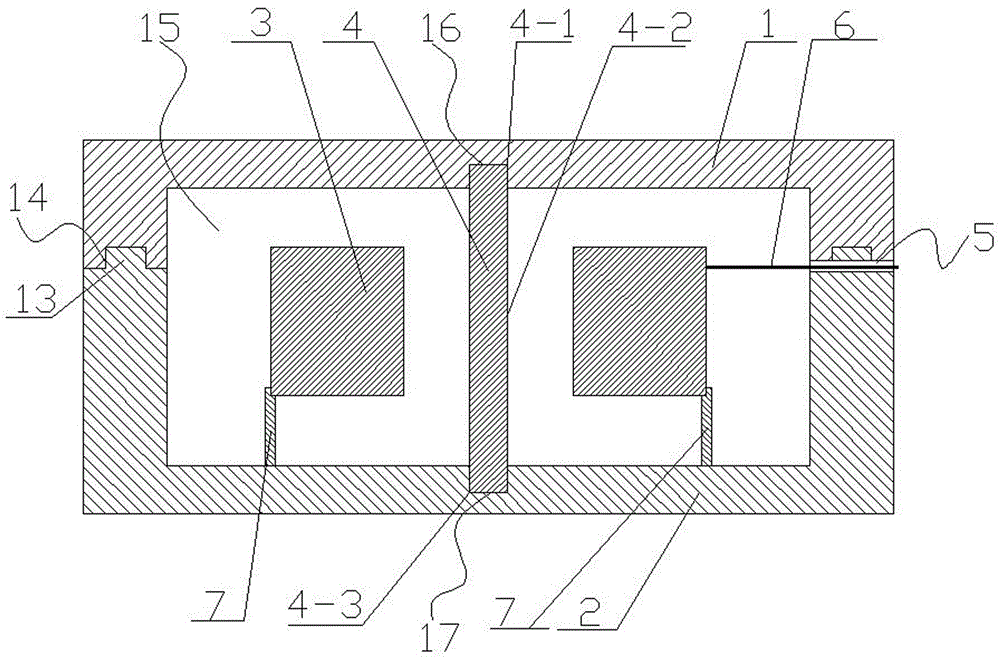
ActiveCN102573376AIncreasing the thicknessHigh degree of insulationResilient/clamping meansEngineeringElectronic component
The invention discloses an insulation structure used for fixing an electronic element, the electronic element and a component, relates to the field of communication, and has the advantages that the insulation distance can be extended, the insulation degree can be increased and the voltage withstanding grade can satisfy the requirement of insulation reinforcing. The insulation structure comprises a hollow first insulation member and a ring-shaped second insulation member, wherein the first insulation member comprises a thick part on the upper section and a thin part on the lower section; the outer diameter of the thick part is larger than the outer diameter of the thin part, and the inner diameter of the thick part is equal to the outer diameter of the thin part; the outer diameter size of the thin part satisfies the condition that when the thin part passes through a mounting hole of the electronic element, the outer surface of the thin part is attached to the mounting hole; the second insulation member is arranged in a mounting hole to be mounted on a heat dissipation plate; a mounting screw passes through the first insulation member; the thin part of the first insulation member passes through the mounting hole of the electronic element and the second insulation member; the second insulation member is jacketed at the thin part of the first insulation member; and the inner surface of the second insulation member is closely stuck to the outer surface of the thin part of the first insulation member. The insulation structure used for fixing the electronic element can improve the insulation effect of the electronic element.
Owner:FENGJIE DONGYANG BUILDING MATERIALS CO LTD
Adjustable type insulating sheath capable of preventing small animals
PendingCN109378786AImprove versatilitySolve the adjustmentElectrical apparatusSmall animalBiomedical engineering
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Enhanced composite resin insulating material and making method thereof
InactiveCN1838335AImprove insulation performanceImprove mechanical propertiesInsulating bodiesChemical industryHigh resistance
This invention relates to a reinforced compound resin insulating material and its making method, which belongs to chemical industry field, this invention uses non-alkali glass fiber cloth or middle-alkali glass fiber cloth as the base material, unsaturated polyester resin as the binder, polystyrene resin as the reinforcing agent, and aluminum hydroxide as the filter, it mixes the binder, reinforcing agent, filter, curing agent, catalyst and auxiliary substance up into the compound solution, and then makes the non-alkali glass fiber cloth or middle-alkali glass fiber cloth immerge into the compound solution, then it covers its face with borosilicate glass film, at last it is molded by the press. The advantages of this invention is that besides the material has high insulating, mechanism and physics capabilities, it also has high resistance, high impact resistance and fine flame-proof effect and mechanical processing capability, which can be made into the insulating cloth board, insulating cloth tube, insulating stick, insulating mat and so on.
Owner:李德和
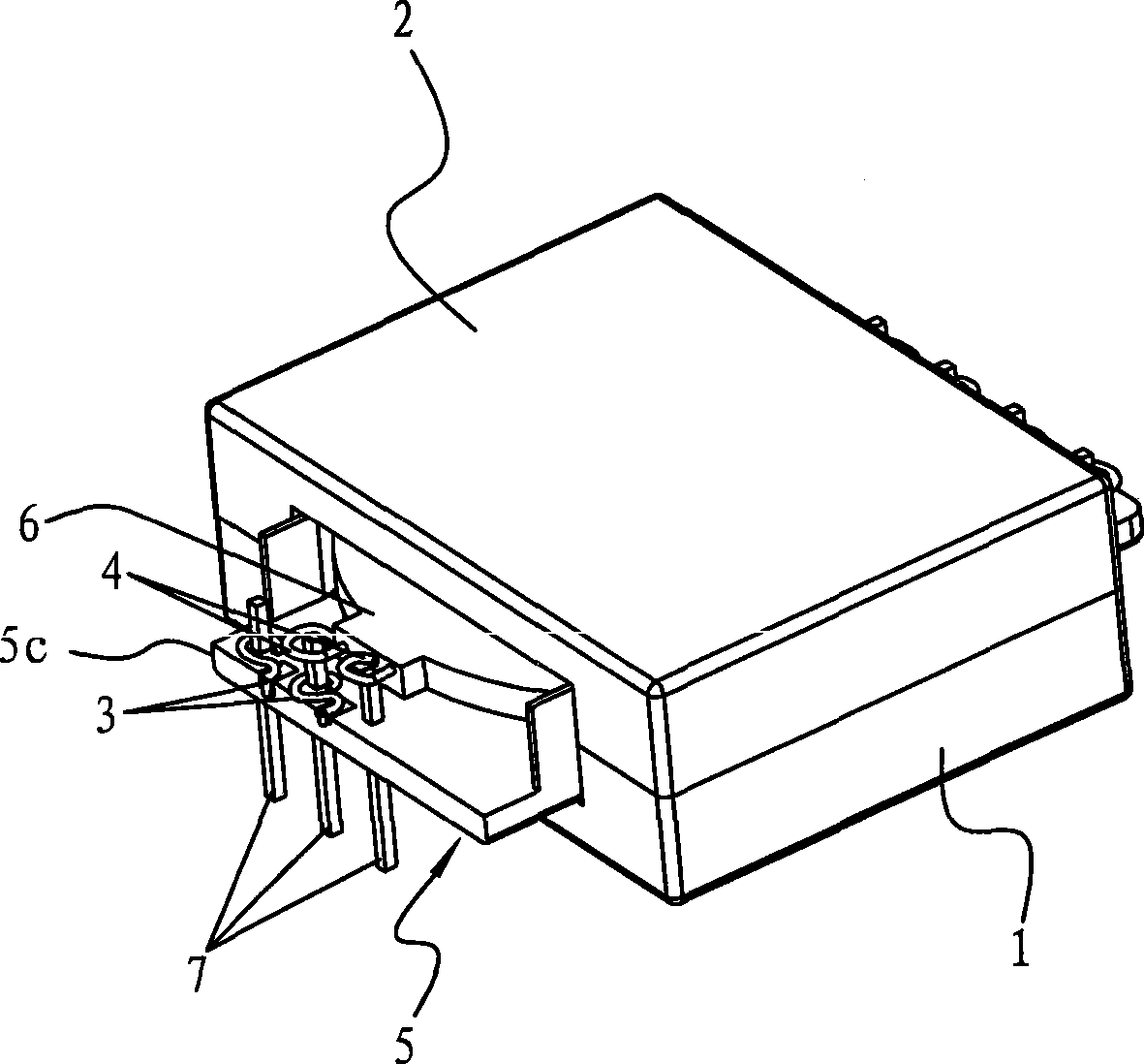
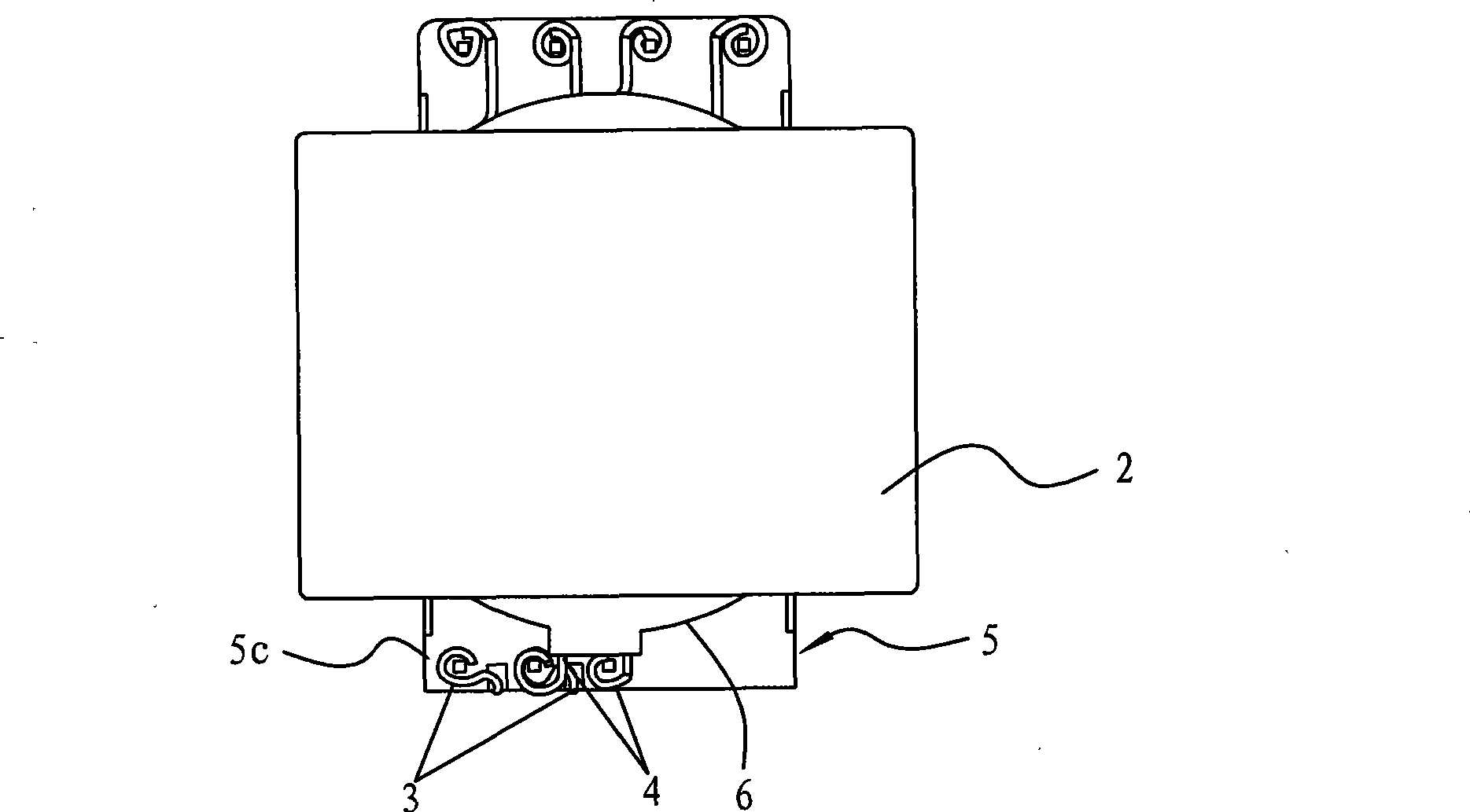
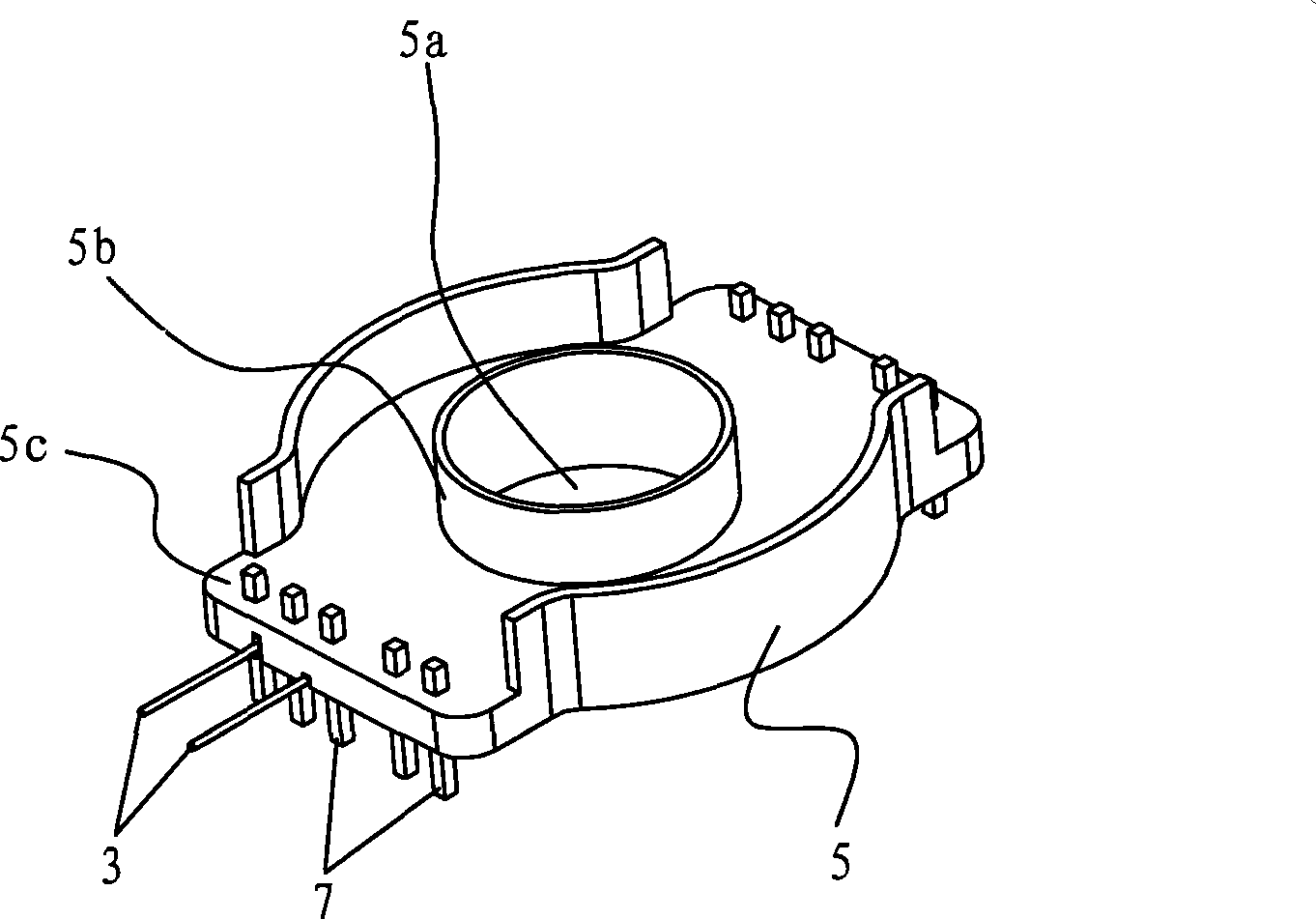
High-power planar transformer
ActiveCN101533705ASimple preparation processReduce volumeTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCoils manufactureManufacturing technologyEngineering
Owner:铂恩氏(东莞)电子有限公司
Electromagnetic relay with injection molded yoke
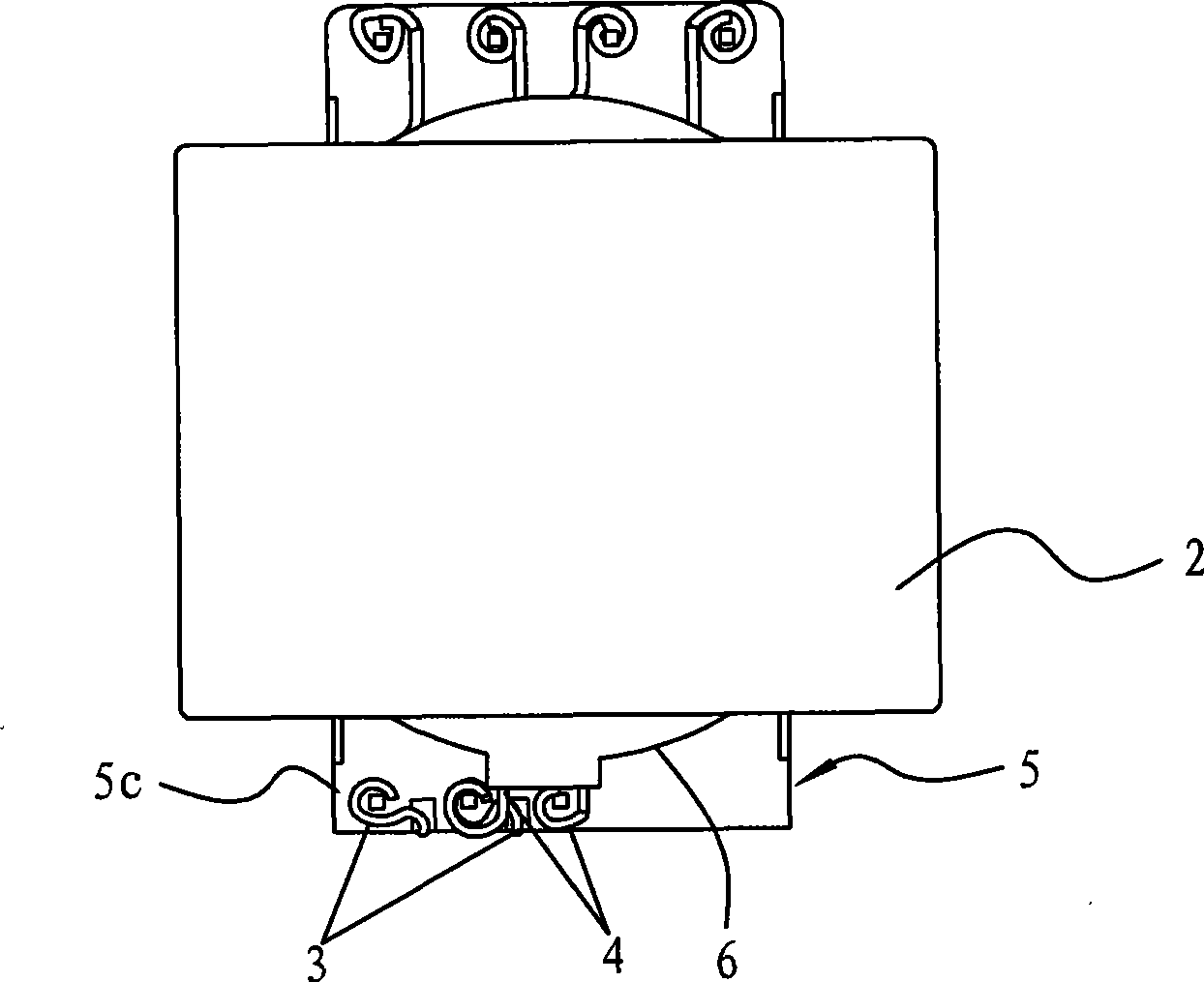
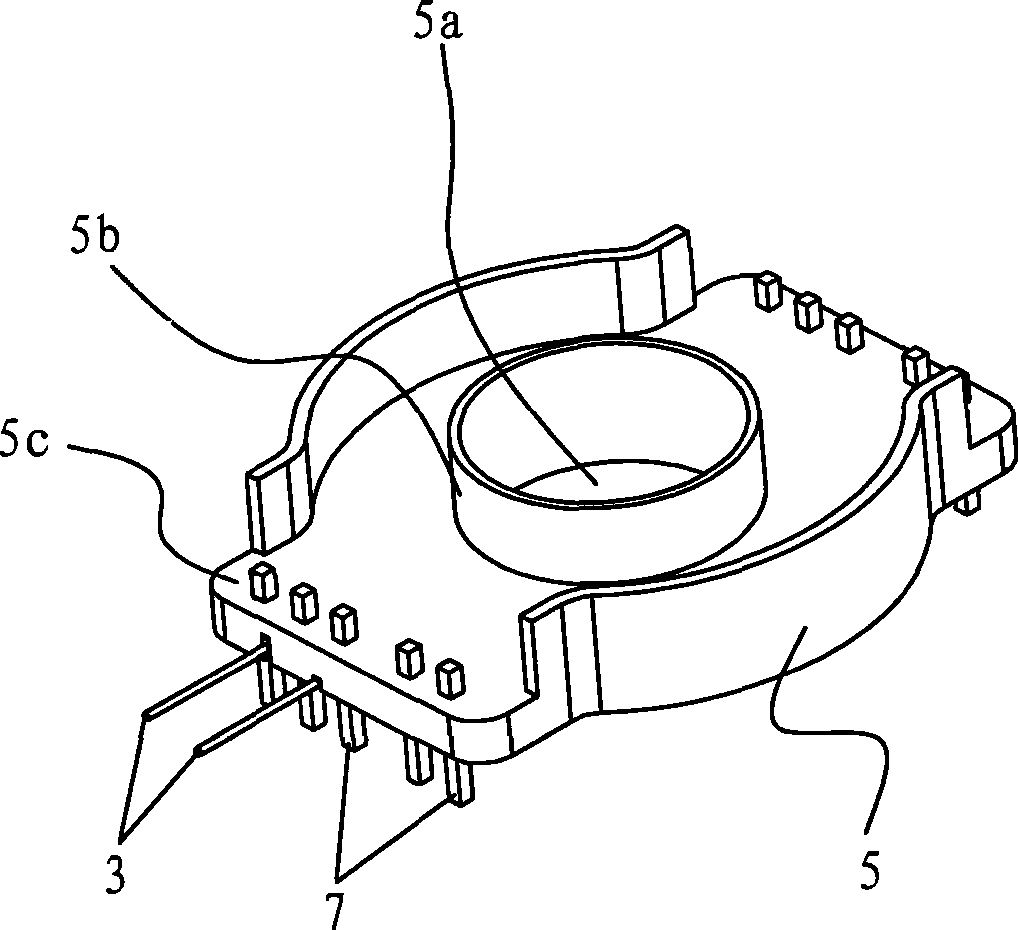
ActiveCN106206166AHigh degree of insulationWill not deformElectric switchesElectromagnetic relay detailsInjection mouldingRelay
The invention discloses an electromagnetic relay with an injection molded yoke. The electromagnetic relay comprises a movable spring, the yoke and a coil. The yoke is in an L shape, the horizontal side of the yoke and an iron core in the coil are fixed at the bottom of the coil, and the vertical side of the yoke is parallel to the axis of the iron core. In the vertical side of the yoke, a plastic layer is formed on the face facing the coil in an injection molding mode and is used for being arranged between the yoke and the coil in an insulation mode, a plastic protruding bud is formed on the face opposite to the coil in an injection molding mode, and the yoke and the movable spring are fixed through the plastic protruding bud. By means of the electromagnetic relay, on one hand, on the premise that the winding space is not influenced, the insulation degree of the yoke and the coil can be improved, the position precision of an insulation component can be ensured, and assembling procedures are effectively reduced; on the other hand, when the yoke and the movable spring are fixed, it can be avoided that the movable spring is deformed due to stress generated on the movable spring, and the size uniformity of the movable spring is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN HONGFA SIGNAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High-flexibility cable used for tomography medical instruments
ActiveCN104240818AEnsure safetyHigh degree of insulationCoaxial cables/analogue cablesInsulated cablesTransmission lineEngineering
The invention discloses a high-flexibility cable used for tomography medical instruments and belongs to the technical field of wires and cables special for medical equipment. The high-flexibility cable used for tomography medical instruments comprises a cable core and a master sheath, and is characterized in that the cable core comprises a power transmission line, a first control signal transmission line, second control signal transmission lines, a first measurement signal transmission line, second measurement signal transmission lines, a third measurement signal transmission line, a fourth measurement signal transmission line, a ground wire, a device interior current transmission line, a first indicator signal transmission line, a second indicator signal transmission line, a video signal transmission line, a cable core internal wrapping layer, a cable core shielding layer and a cable core external wrapping layer; the power transmission line is located in the middle of the cable core; the first control signal transmission line, the second control signal transmission lines, the first measurement signal transmission line, the second measurement signal transmission lines, the third measurement signal transmission line, the fourth measurement signal transmission line, the ground wire, the device interior current transmission line, the first indicator signal transmission line, the second indicator signal transmission line and the video signal transmission line are arranged on the periphery of the power transmission line and are wrapped together with the cable core internal wrapping layer; the cable core shielding layer is located outside the cable core internal wrapping layer; the cable core external wrapping layer wraps the cable core shielding layer; the master sheath covers the cable core external wrapping layer in an extruded mode.
Owner:SUZHOU CABLEPLUS PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Forming die of outdoor mutual inductor, and casting fixing and sealing method of outdoor mutual inductor
InactiveCN104526940APrevent radial offsetEasy to processInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureEngineeringInductor
The invention discloses a forming die of an outdoor mutual inductor, and a casting fixing and sealing method of the outdoor mutual inductor. The forming die comprises an upper die and a lower die which are used for forming a die cavity, the upper die is provided with a casting hole connected with the die cavity and an air outlet, a die core is arranged in the die cavity, the upper end and the lower end of the die core are connected with the upper die and the lower die respectively, the upper end and the lower end of the die core are jointed into the upper groove of the upper die and the lower groove of the lower die respectively, and the part of the die core positioned in the die cavity is cylindrical in shape; and a group of fixed pillars for supporting mutual inductor coils is arranged in the die cavity surrounding the die core, the fixed pillars are fixedly connected with the lower die, and the upper end of each of the fixed pillars is provided with a stepped clamping platform for jointing the external edge and the lower edge of each of the mutual inductor coils. The forming die and the method improve the resin casting fixing and sealing efficiency of the outdoor mutual inductor, reduce the unit energy consumption and the defective index of the outdoor mutual inductor and improve the insulation degree of the outdoor mutual inductor.
Owner:XUCHANG YONGXIN ELECTRIC
Insulation assembly for nuclear fusion reactor
ActiveCN104425042AHigh degree of insulationImprove reliabilityNuclear energy generationThermonuclear fusion reactorFiberNuclear reactor
The invention relates to insulation assembly design, in particular to an insulation assembly which is used for insulation between a direct-current glow electrode and the wall of a vacuum chamber in the nuclear fusion reactor. The insulation assembly comprises nuts, caps, concave-convex concentric annulus gaskets, flat plate type concentric annulus gaskets having different latus rectums, an electrode fixing plate, fixed bolts, concave-convex concentric annulus gaskets each of which has a sleeve structure, the wall in the vacuum chamber, and the like. The concave-convex concentric annulus gaskets having the sleeve structure, the electrode fixing plate, the flat plate type concentric annulus gaskets having different latus rectums, the concave-convex concentric annulus gaskets and the caps sequentially sleeve the fixed bolts in an overlapped manner; each cap for fastening a ceramic insulation piece and the electrode fixing plate is arranged on one end of the corresponding fixed bolt, and the other end of each fixed bolt is connected with the wall in the vacuum chamber. The insulation assembly disclosed by the invention is directly related to the processing effect of the wall of the nuclear fusion vacuum chamber, and further the determination of the quality of plasma discharge. The insulation assembly disclosed by the invention is especially applicable to a Tokamak device, of which the first wall is provided with black lead and employs fiber, in the vacuum chamber of the fusion device.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
Flame-retardant and environment-friendly cable
InactiveCN108109736AEven by forceReduce flammabilityInsulated cablesInsulated conductorsWear resistantEngineering
The invention discloses a flame-retardant and environment-friendly cable. The flame-retardant and environment-friendly cable comprises a cable main body, a cooling layer, cable cores and a wear-resistant layer, wherein buffer pads are arranged on an inner wall of the cable main body, tail ends of the buffer pads are connected with a flame-retardant layer, the cooling layer is fixedly arranged at an inner side of the flame-retardant layer, guide wires are fixedly arranged at an outer circle of the cooling layer at equal distance, an insulation ring is arranged at an inner side of the cooling layer, the cable cores are fixedly arranged at an inner side of the insulation ring, isolation pads are arranged at two sides of an outer wall of each cable core, the wear-resistant layer is arranged onan outer wall of the cable main body, a limitation groove is formed in a surface of the wear-resistant layer, an installation groove is formed in an outer side of the limitation groove, and crack-prevention layer is embedded into an outer circle of the wear-resistant layer. By design of the buffer pads, pressure generated by an outer side of the cable main body can be diffused, the uniform stressof the whole cable is ensured, moreover, external fire is prevented by the flame-retardant layer, the combustibility of the cable is reduced, and the loss degree of emergency condition is reduced.
Owner:温州包鹿新材料有限公司
10kv overhead insulation lead rapid insulation recovery apparatus and using method thereof
InactiveCN107069591AExtended service lifeImprove protectionOverhead installationApparatus for repairing insulation/armouring cablesAnti ageingSoft mass
The present invention is a 10kV overhead insulated wire rapid insulation recovery device and its use method, comprising a hard insulating shell, waterproof insulating cement, the hard insulating shell is cylindrical, one end of which is open, and the opening of the hard insulating shell is Connected by the locking device, the waterproof insulating glue is evenly coated on the inner peripheral surface of the hard insulating shell. The invention is easy to operate and is not affected by the technical level of the construction personnel. It can be fixed firmly only by fastening the lock buckle, and the installation quality is consistent; the insulation performance is good, and the insulating glue and the hard insulating shell are double-layer insulated, and its design insulation capacity The insulation ability is higher than that of the wire insulation layer; the anti-aging ability is strong, and the soft insulating cement with weak corrosion resistance but strong insulation ability is reliably protected by the hard insulating shell with strong corrosion resistance but weak insulation ability, which is extremely Greatly prolong the service life of insulating cement.
Owner:YINGKOU ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY +1
Built-electrode sensor for water level in steam drum
InactiveCN1661339AAccurate measurementHigh degree of insulationLevel indicators by physical variable measurementEngineeringWater level
The present invention discloses a drum level built-in electrode sensor. It is a boiler drum level measuring device. Its structure is characterized by that the electrode can be fixed and mounted on the position in the drum interior which is required for measurement, on the leading-out box mounted outside of drum the electrode cable can be sealed by means of fixing seat, gasket ring or ring seal and pressure cap, led out and connected to secondary meter. Said device can make the drum level be accurately positioned between two electrodes, so that it can fully monitor the drum level in the process of boiler operation.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO HUADIAN MEASUREMENT & CONTROL EQUIP
Transformer station combined protective electrical appliance
ActiveCN106451084ASave special cross armSave materialFuse disposition/arrangementSubstation/switching arrangement boards/panels/desksElectricityTransformer
The invention provides a transformer station combined protective electrical appliance, comprising a fuse, a lightning arrester and a connecting plate; the fuse comprises a porcelain sleeve, a sealed wire inlet sleeve is arranged at the top of the porcelain sleeve, an inlet wire is arranged in the wire inlet sleeve, a sealed rubber cover is arranged at the bottom of the porcelain sleeve, the rubber cover is provided with a fuse carrier inlet and a sealed wire outlet sleeve, an outlet wire is arranged in the wire outlet sleeve, a hoop is arranged outside the porcelain sleeve, and the hoop is provided with a connecting portion connected with a fuse cross arm; a metal connecting portion is formed at the top of the lightning arrester, an insulating cover is arranged at the bottom of the lightning arrester, a wire inlet lead and a wire outlet lead are arranged on the insulating cover, and he outlet wire on the fuse is electrically connected with the wire inlet lead on the lightning arrester; one end of the connecting plate is connected with the connecting portion on the hoop, the other end of the connecting plate is fixedly connected with the metal connecting portion of the lightning arrester, and a grounding terminal is arranged on the connecting plate. The transformer station combined protective electrical appliance is simple in structure and convenient to install, and can be widely applied in the field of power.
Owner:YUNCHENG POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID SHANXI ELECTRIC POWER +2
High-voltage transmission line insulator umbrella protection cap
InactiveCN106486218AHydrophobicReduce pollutionSuspension/strain insulatorsBird droppingsEngineering
The invention discloses a high-voltage insulator umbrella protection cap. The umbrella cap is formed integrally through injection of a polymer silica gel material; an umbrella cap fixing end is made on the upper part of the umbrella cap; the umbrella cap is in an opening state and is conveniently mounted and fixed on an insulator iron cap; and the opening of the umbrella cap adopts a lap joint mode, a lap joint convex strip is made on the upper lap joint edge, and an umbrella cap lap joint groove is made on the lower opening lap joint edge. In the case of use, the umbrella cap fixing end is fixed on the insulator iron cap conveniently by a fixing clip, and the umbrella cap lap joint convex strip and the umbrella cap lap joint groove are pressed together to form a whole. As the umbrella cap is made of the polymer material, the hydrophobicity is strong, rain, bird droppings and the like are not likely to be attached to the umbrella cap; as the umbrella cap has a large diameter, pollution to the upper part of the insulator is lessened; and the insulation degree of an insulator string is effectively improved, and the service life of the insulator string is prolonged.
Owner:山东特瑞电力器材有限公司
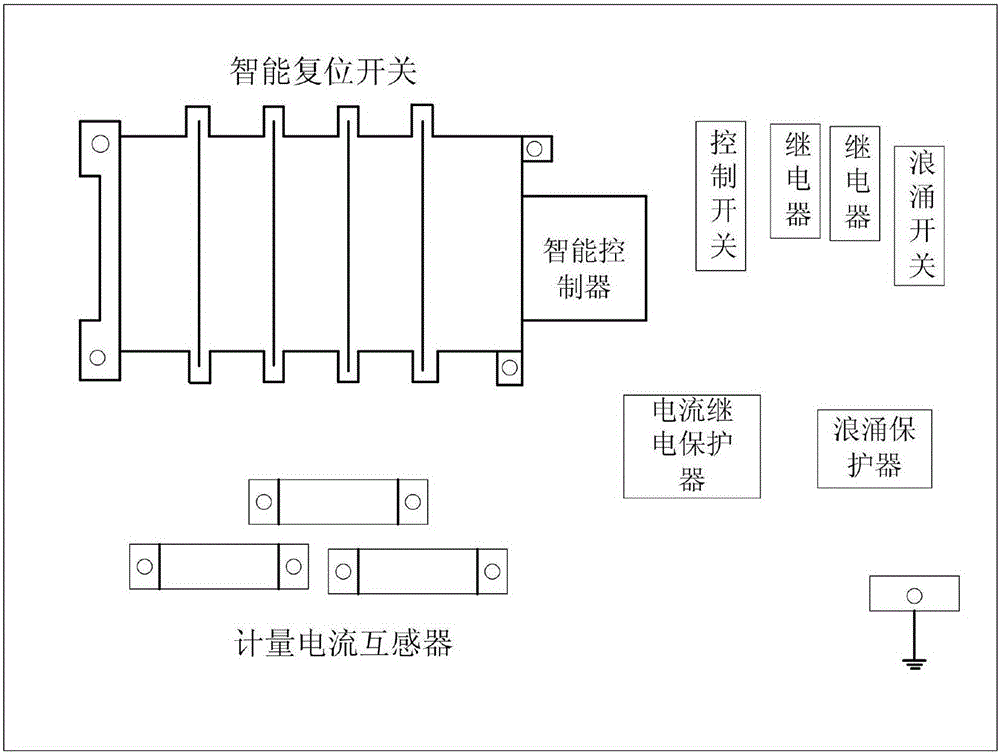
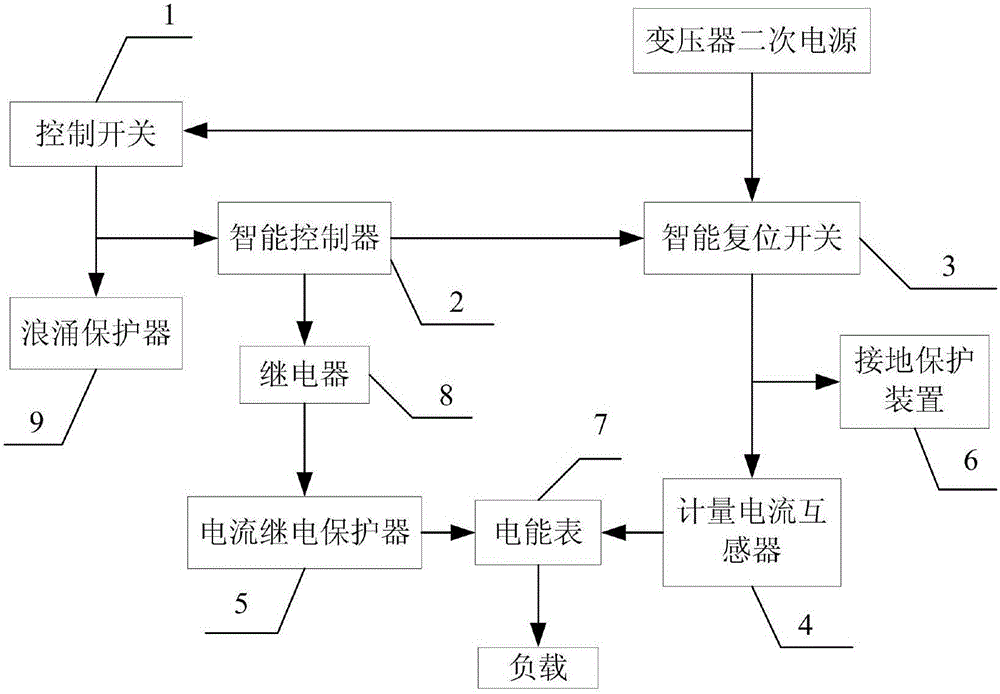
Distribution substation intelligent distribution box
ActiveCN105140786BEnsure safetyAvoid easy aging and overheatingBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsArrangements responsive to undervoltageDistribution transformerEngineering
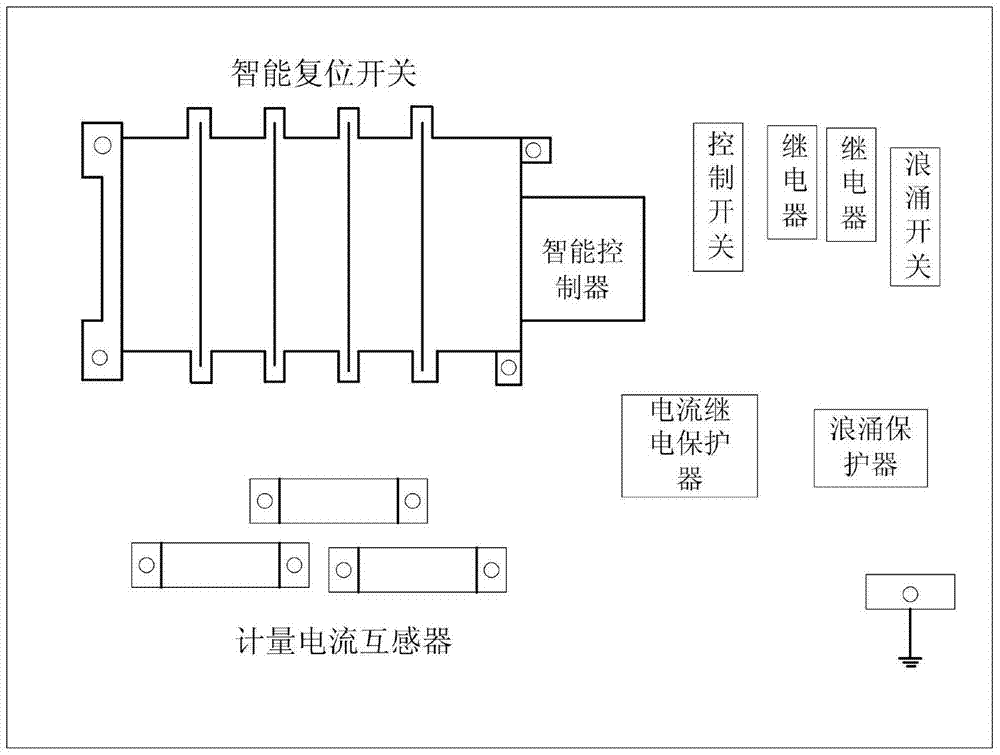
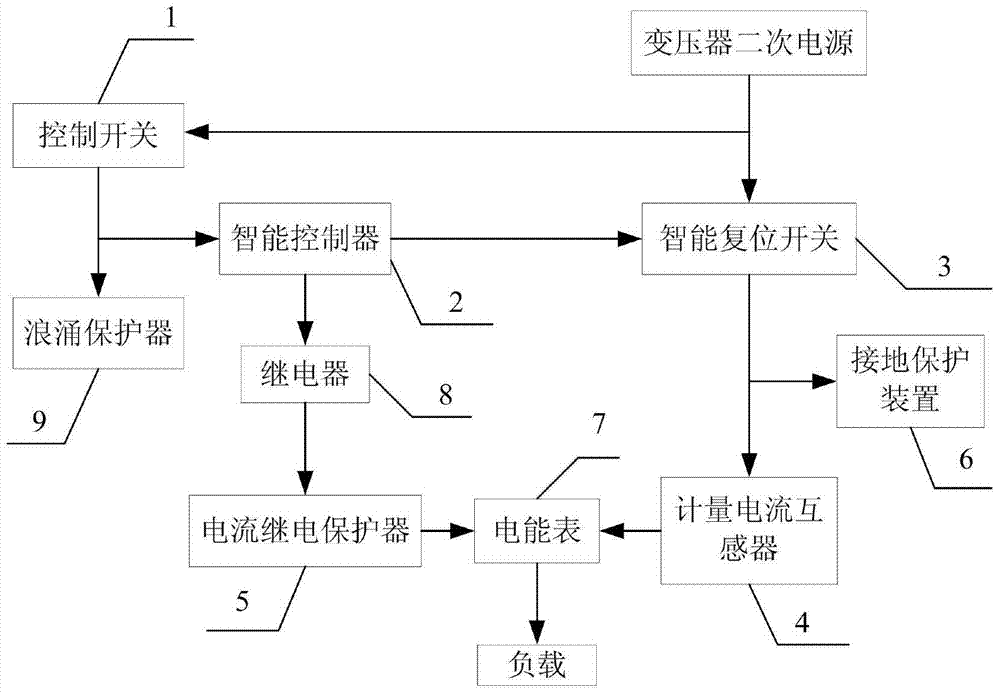
The invention provides an intelligent distribution box of a distribution transformer, relates to intelligent power supply distribution management equipment, and aims at solving the problems that the connected point of a box body of an existing distribution box and external main power supply is arranged outside the box, so that the insulating sealing property is poor, and the box body is easily filled with water or affected with damp to oxidize, and is easy to age or overheat and the like, and the problems that the labor intensity of power constructors is increased during power-off maintenance and the like. The intelligent distribution box comprises an intelligent reset switch, an intelligent controller, a current relay protector, a control switch, a grounding protection device and a metering current transformer; the intelligent reset switch, the intelligent controller, the current relay protector, the control switch, the grounding protection device and the metering current transformer are fixed in the box body; the control switch is connected with the intelligent controller; the intelligent controller is connected with the intelligent reset switch; the intelligent reset switch is connected with the metering current transformer; the metering current transformer is connected with the current relay protector and an electric energy meter; and the intelligent reset switch is connected with the grounding protection device and load respectively. According to the intelligent distribution box, the main power supply can be automatically cut off by a distribution line in a power failure; and a three-phase short circuit of a load line is grounded, so that the safety of power supply maintenance personnel is ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Air ion measuring instrument
InactiveCN1181338CHigh degree of insulationRestore performanceMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityElectrical battery
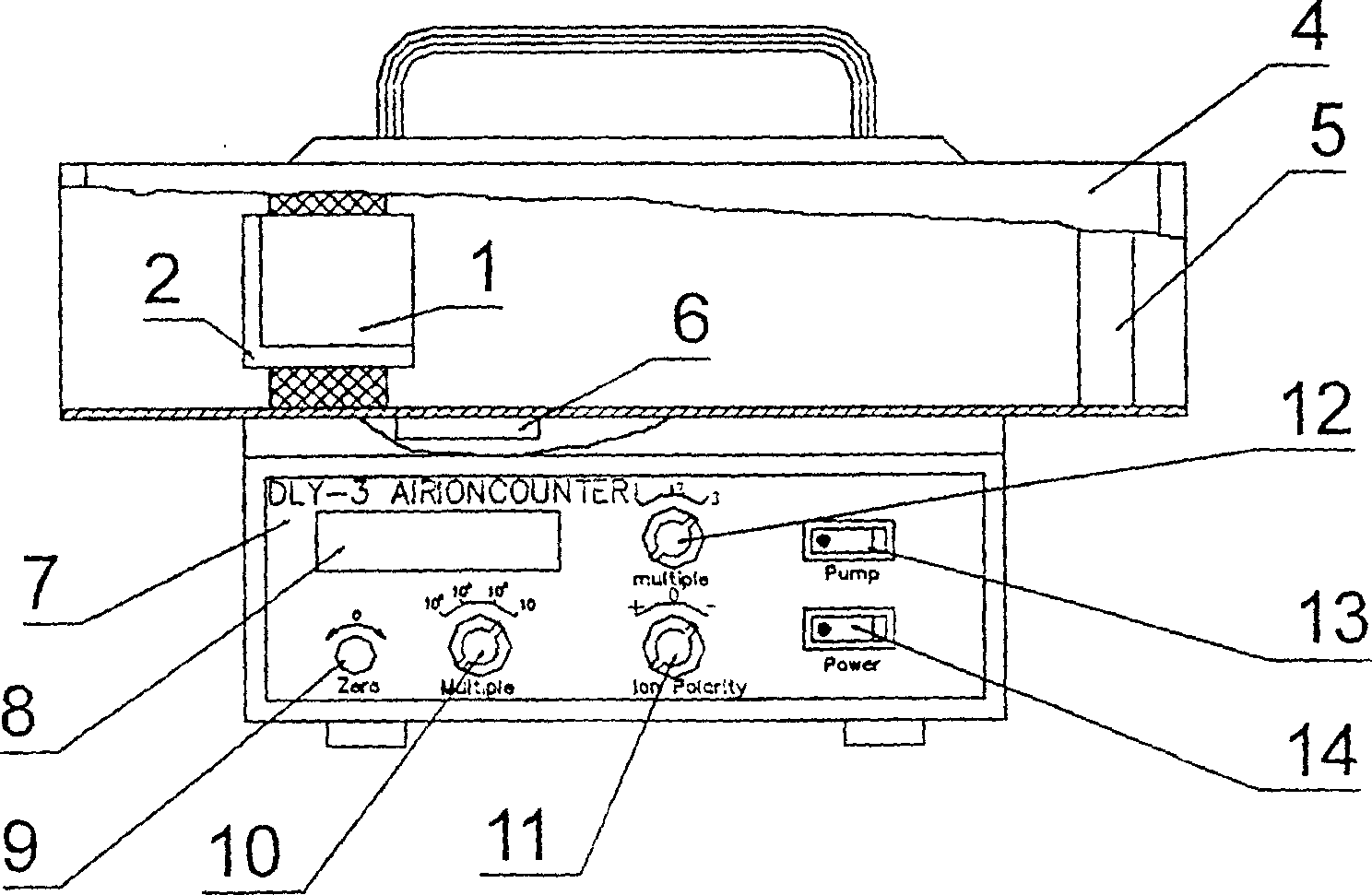
A measuring instrument of air ion with dehumidification function at middle part of insulation supporting frame and bottom part of collector outer shell in the ion collector can remove the humidity on the insulation supporting frame for raising the insulation ability to let the instrument to be used reliably in the wet environmental condition with the humidity up to 90%. The invented instrument has a built in rechargeable battery or to be charged with the electricity through external electric supply source. it is specially good for outdoor field use because of the advantages as above listed.
Owner:福建连胜电子技术有限公司
Transformer impregnating method
InactiveCN104465060AShort processing timeRaise the preheat temperatureInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureBoiling pointTransformer
The invention provides a transformer impregnating method. The method includes the steps of 1, drying a transformer in a drying box, at the controlled temperature 5 to 15 DEG C lower than a boiling point of paint solvent; 2, extracting the transformer when it is hot, and impregnating the transformer in paint at room temperature; 3, extracting the transformer, and drip-drying the same; 4, drying the transformer in the drying box. The method has the advantages that the process time is short, insulation degree of the transformer is increased, production efficiency is improved, energy consumption is lowered, and equipment investment is none.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
A bus slot for easy assembly
InactiveCN109088376AEasy to assembleStable structureCooling bus-bar installationsTotally enclosed bus-bar installationsCopperElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses a bus slot for easy assembly, which includes two U-shaped side panels, and two U-shaped side panels are arranged correspondingly in front and back, the central array of the twoU-shaped side panels is distributed with two sets of flame retardant separators, the number of the flame retardant partitions in each group is two, and the left and right flame retardant separators are arranged correspondingly, the front and rear sides of the U-shaped side panel are provided with assembly studs, and the assembling stud is connected with the flame retardant separator through the U-shaped side panel, the front and rear arrays of the left surface of the flame retardant separator are provided with placement grooves, and copper bars are arranged inside the placing grooves. The busslot is convenient to assemble, firm in structure and stable and durable; the positioning column is positioned in the middle of the positioning hole for the quick positioning of the bottom panel andthe U-shaped side panel, thereby increasing the positioning of the parts, facilitating the assembly, and bringing convenience to the use; the heat dissipation fin increases the heat dissipation degreeand prevents the safety accident from occurring when the heat of the bus slot is too high, and the epoxy resin improves the insulation degree.
Owner:江苏宏鹏电气科技有限公司
Intelligent distribution box of distribution transformer
ActiveCN105140786AEnsure safetyAssist in on-site judgmentBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsArrangements responsive to undervoltageDistribution transformerSupply & distribution
The invention provides an intelligent distribution box of a distribution transformer, relates to intelligent power supply distribution management equipment, and aims at solving the problems that the connected point of a box body of an existing distribution box and external main power supply is arranged outside the box, so that the insulating sealing property is poor, and the box body is easily filled with water or affected with damp to oxidize, and is easy to age or overheat and the like, and the problems that the labor intensity of power constructors is increased during power-off maintenance and the like. The intelligent distribution box comprises an intelligent reset switch, an intelligent controller, a current relay protector, a control switch, a grounding protection device and a metering current transformer; the intelligent reset switch, the intelligent controller, the current relay protector, the control switch, the grounding protection device and the metering current transformer are fixed in the box body; the control switch is connected with the intelligent controller; the intelligent controller is connected with the intelligent reset switch; the intelligent reset switch is connected with the metering current transformer; the metering current transformer is connected with the current relay protector and an electric energy meter; and the intelligent reset switch is connected with the grounding protection device and load respectively. According to the intelligent distribution box, the main power supply can be automatically cut off by a distribution line in a power failure; and a three-phase short circuit of a load line is grounded, so that the safety of power supply maintenance personnel is ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
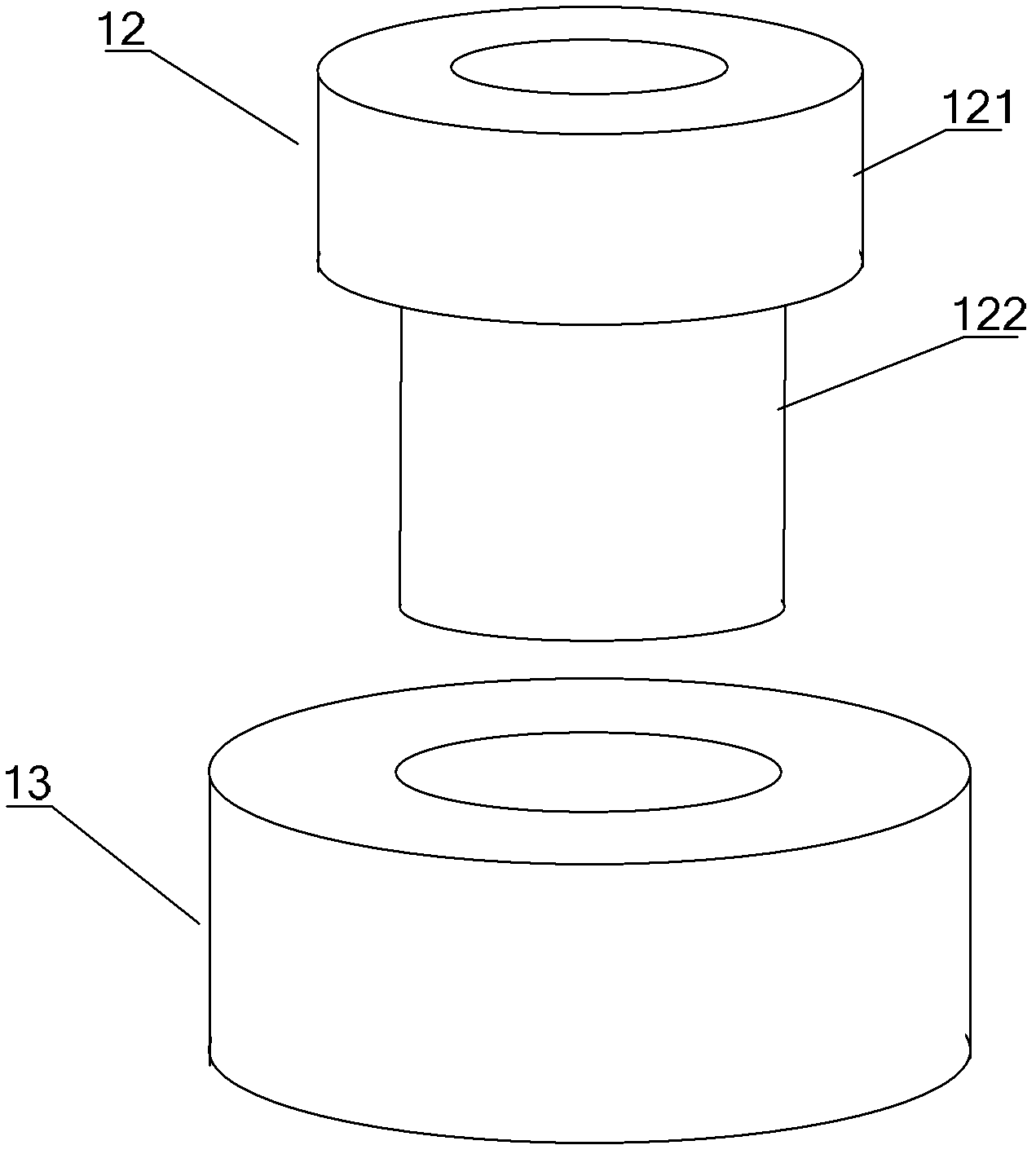
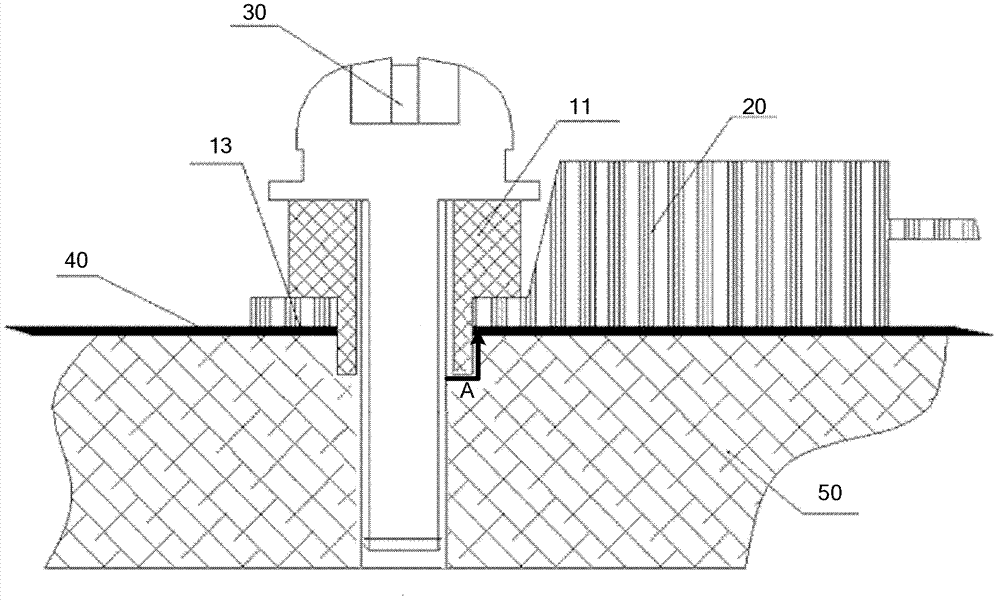
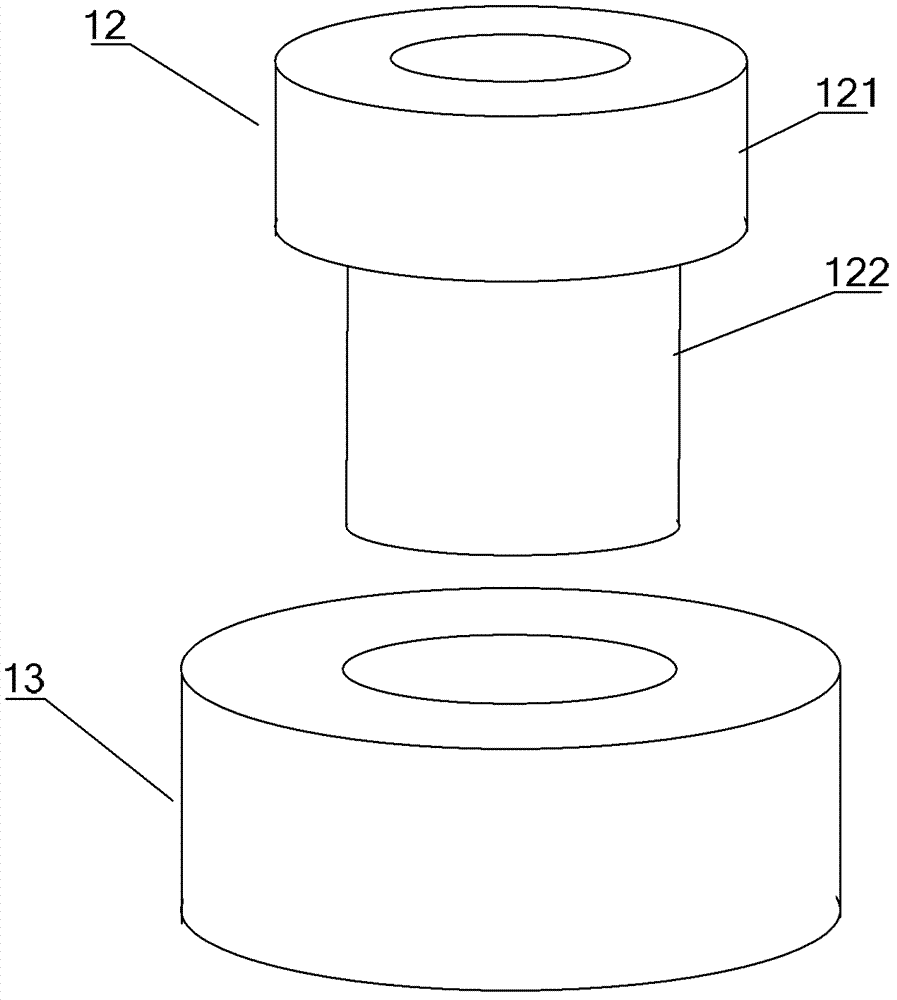
Insulation structure used for fixing electronic element, electronic element and component
ActiveCN102573376BIncreasing the thicknessHigh degree of insulationResilient/clamping meansEngineeringElectronic component
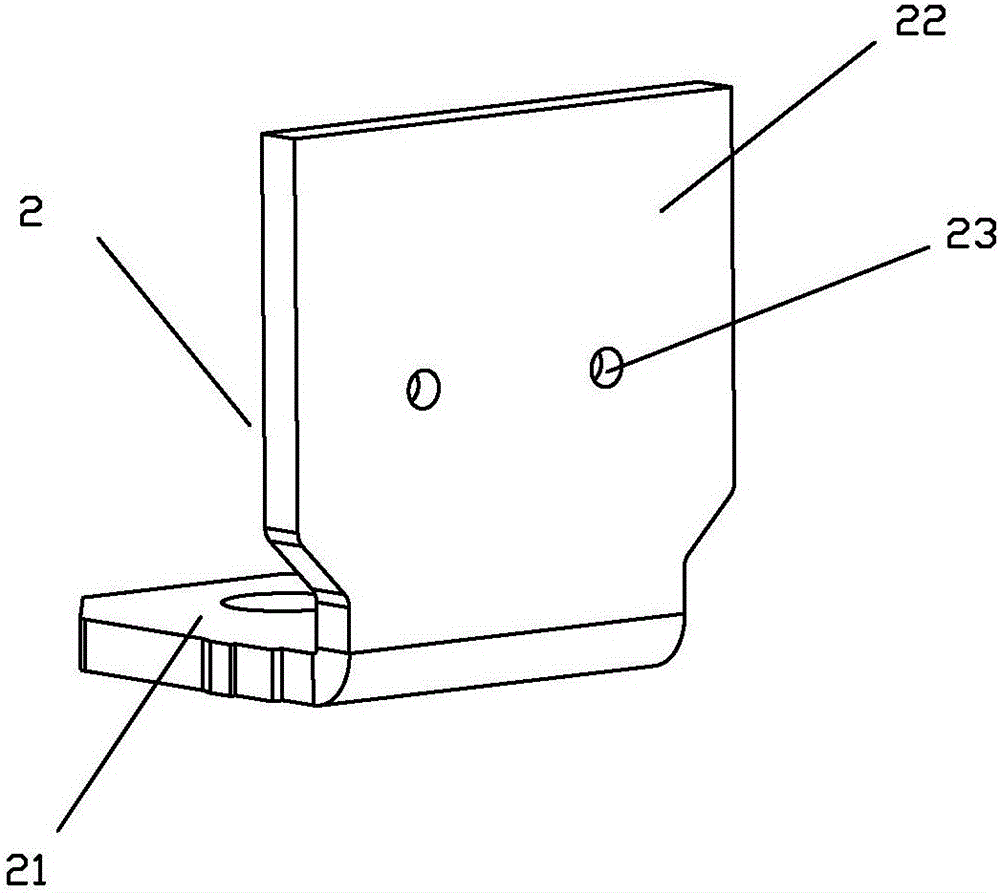
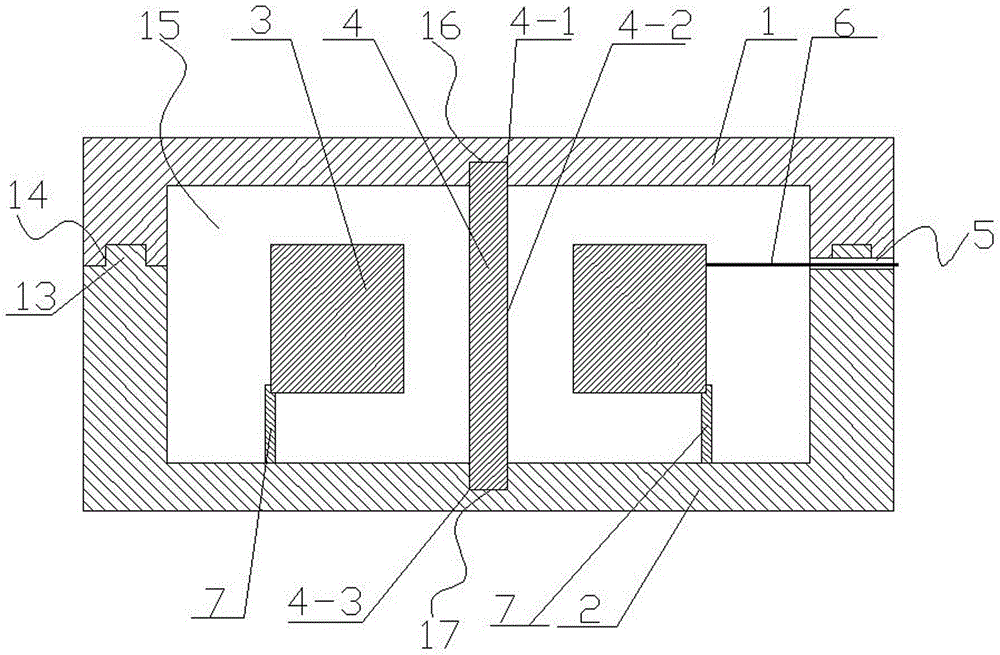
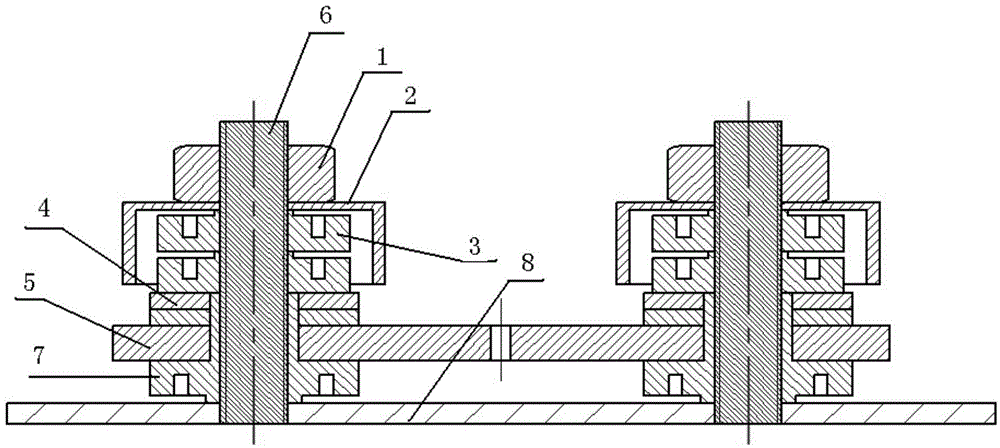
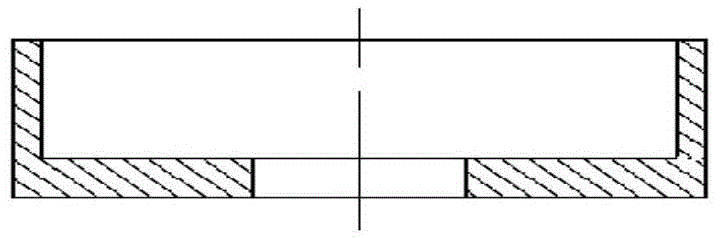
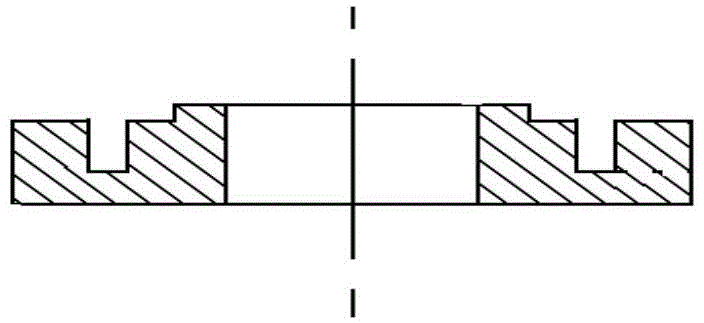
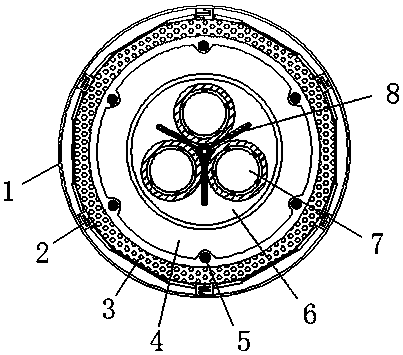
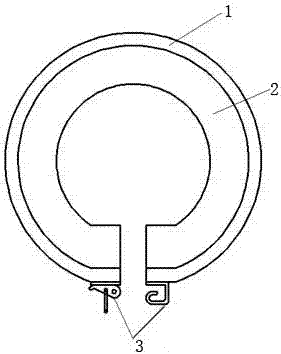
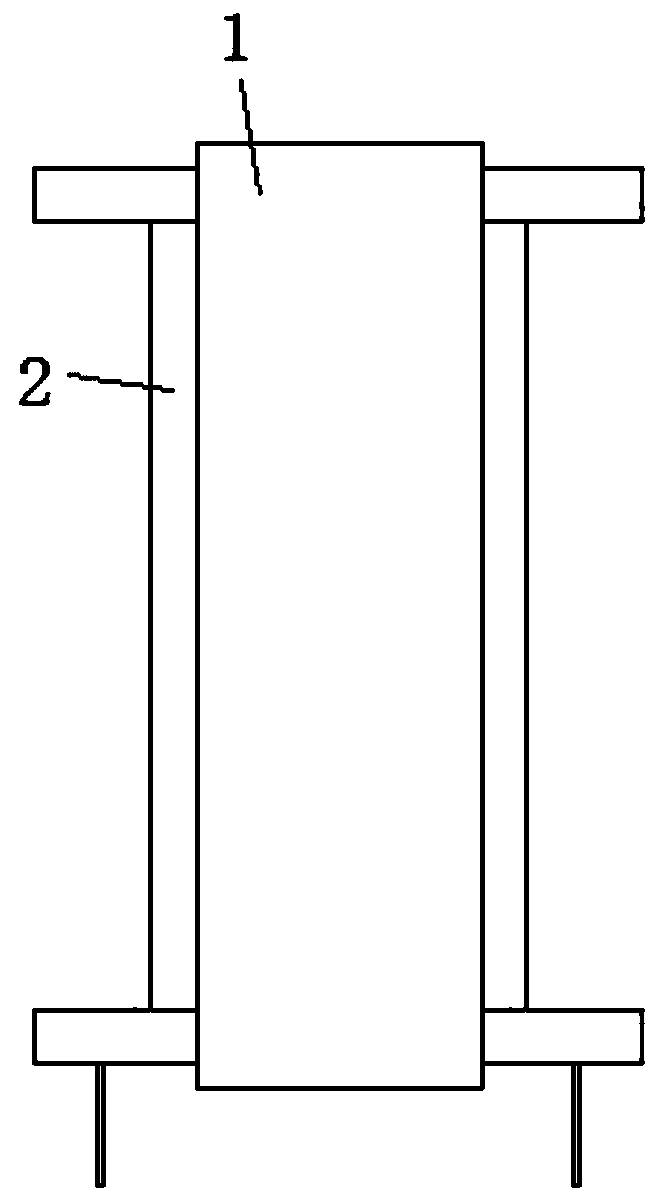
An insulation structure for fixing an electronic element, an electronic element and an assembly can extend insulation distances, and increase insulation degrees to enable the voltage-withstand level to meet the insulation requirements. The insulation structure comprises a first hollow insulation member (12) which comprises a thick part (121) of an upper section and a thin part (122) of a lower section, wherein the outer diameter of the thick part (121) is greater than that of the thin part (122), the inner diameter thereof is equal to that of the thin part (122), and the dimension of the outer diameter of the thin part (122) meets the following: when penetrating through a mounting hole of an electronic element, the outer surface of the thin part (122) is closely adhesive to the mounting hole; and a ring-shaped second insulation member (13) which is arranged in a mounting hole to be installed in a heat dissipation plate (50), wherein a mounting screw (30) penetrates through the first insulation member (12), the thin part (122) of the first insulation member (12) penetrates through the mounting hole of the electronic element and the second insulation member (13), the second insulation member (13) is sleeved outside the thin part (122) of the first insulation member (12), and the inner surface of the second insulation member (13) is closely adhesive to the outer surface of the thin part (122) of the first insulation member (12). The insulation structure is used for fixing an electronic element, so as to improve the insulation effect of the electronic element.
Owner:FENGJIE DONGYANG BUILDING MATERIALS CO LTD
High-power planar transformer
ActiveCN101533705BSimple preparation processReduce volumeTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCoils manufactureManufacturing technologyEngineering
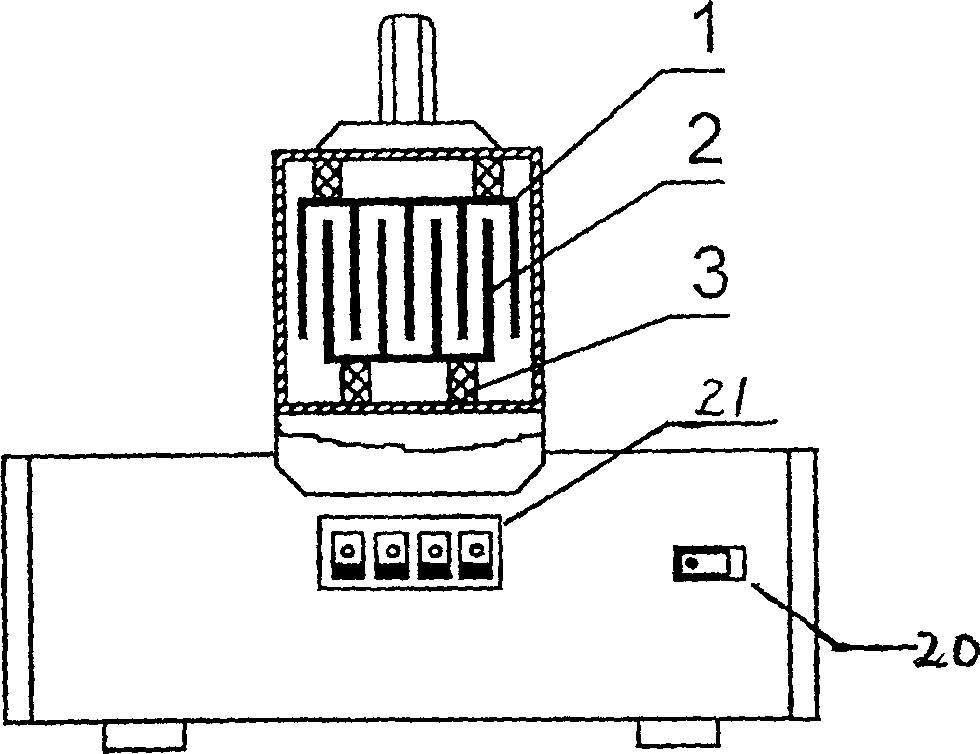
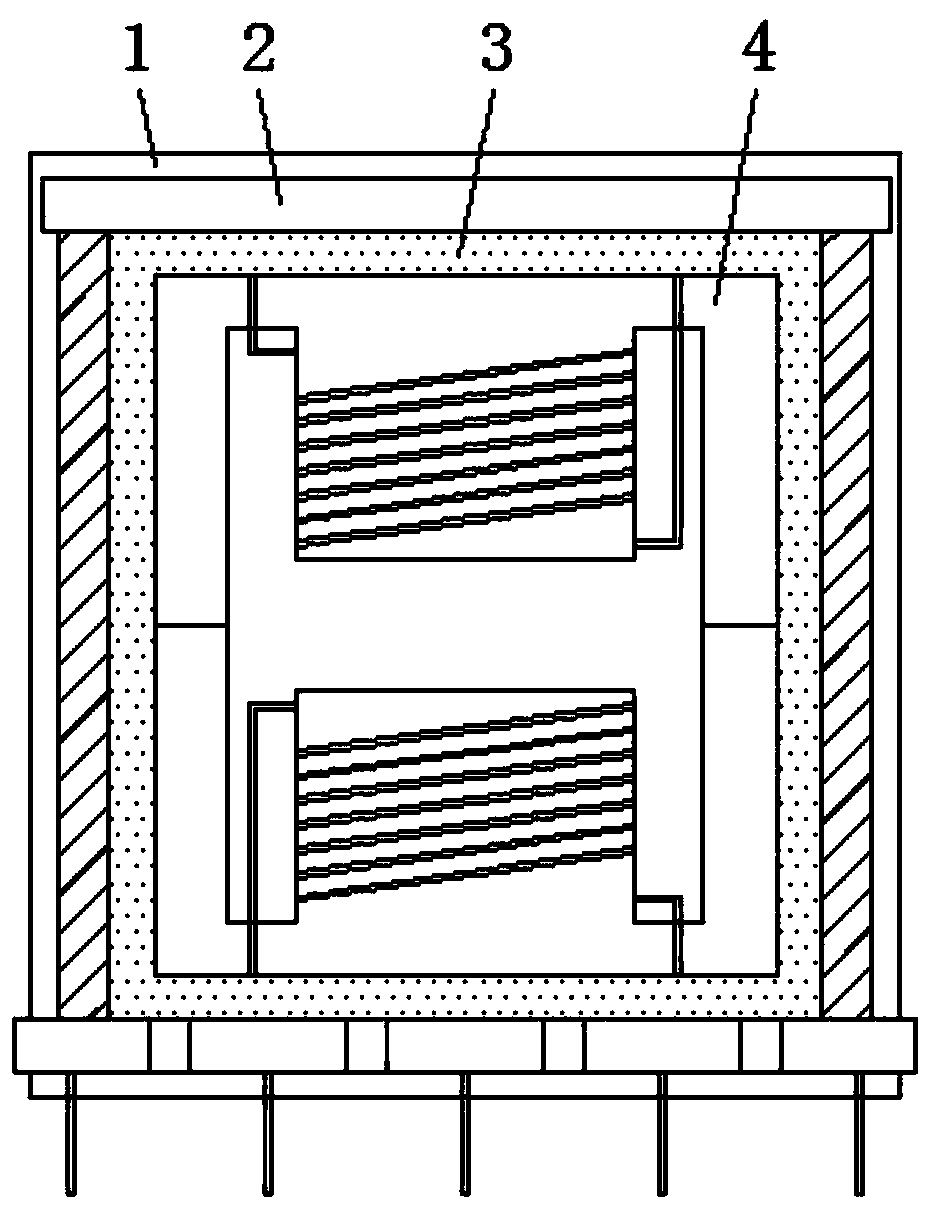
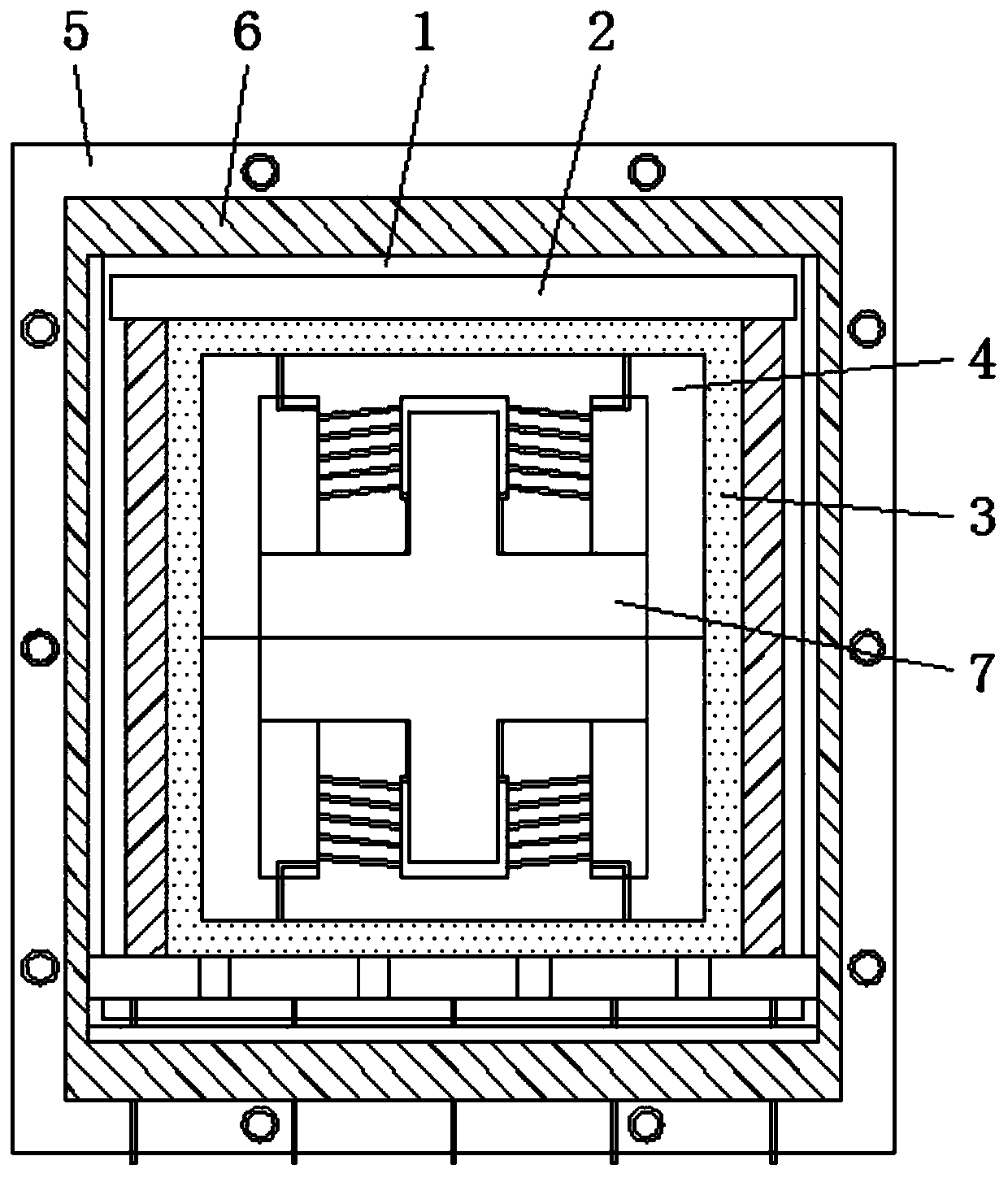
The invention relates to the technical field of transformers, in particular to a high-power planar transformer, which comprises a first magnetic core, a second magnetic core, a primary coil, a secondary coil and an insulating base, wherein the primary coil and the secondary coil are self-adhesion coils; the insulating base is provided with a centre shaft hole, the primary coil is arranged inside the insulating base and forms an integral structure with the insulating base, and the secondary coil is stacked on the insulating base; the first magnetic core and the second magnetic core are placed at two sides of the insulating base and form a magnetic path through the centre shaft hole; and the primary coil and the secondary coil are coupled. Because the coils are separately arranged inside aninsulator, the insulating degree is high, the manufacturing technology of the coils is simple, and the coils can be molded integrally through mold pouring; and because the coils are arranged inside the insulator, the structure can be more compact, the volume of the transformer is reduced, and the high-power planar transformer can be applied to thinner electronic products.
Owner:铂恩氏(东莞)电子有限公司
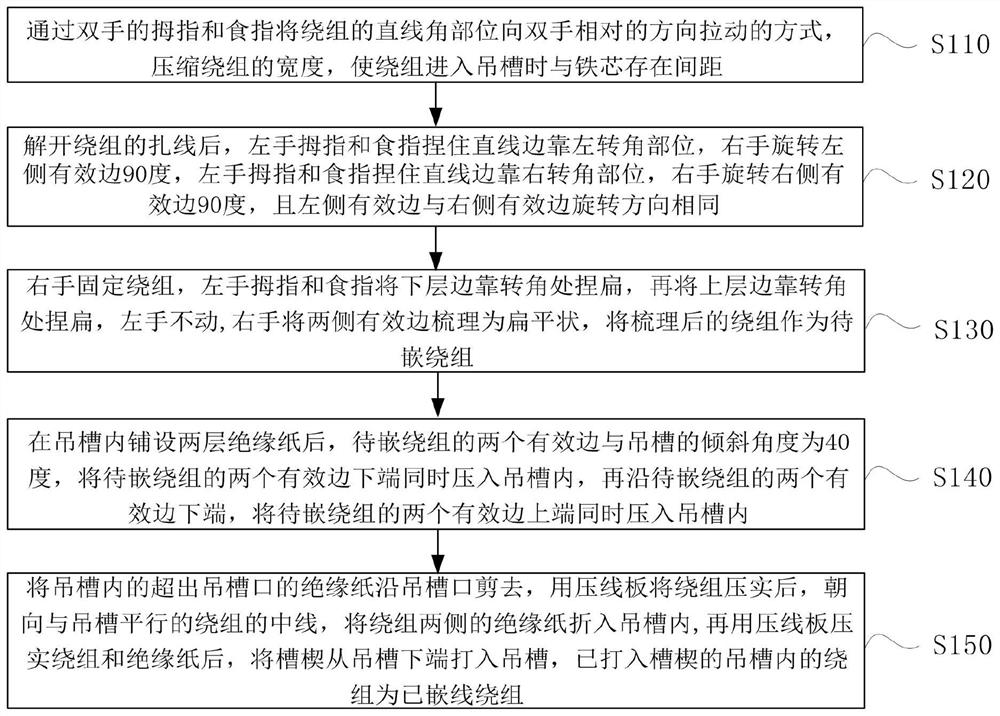
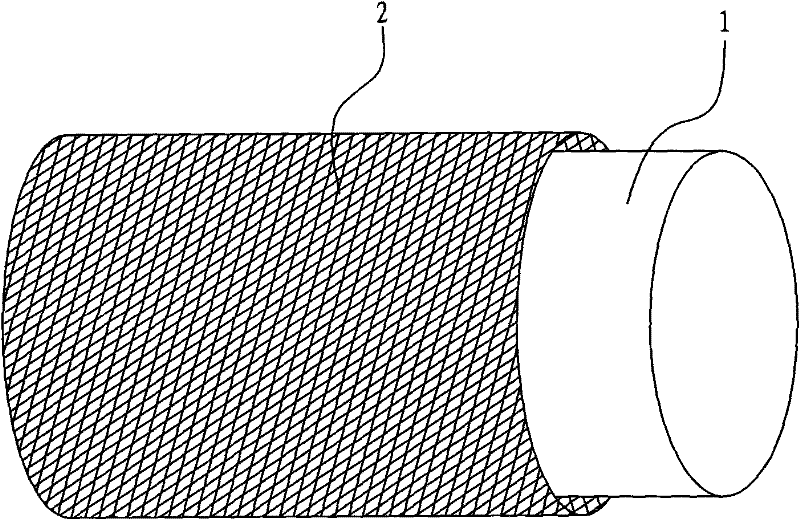
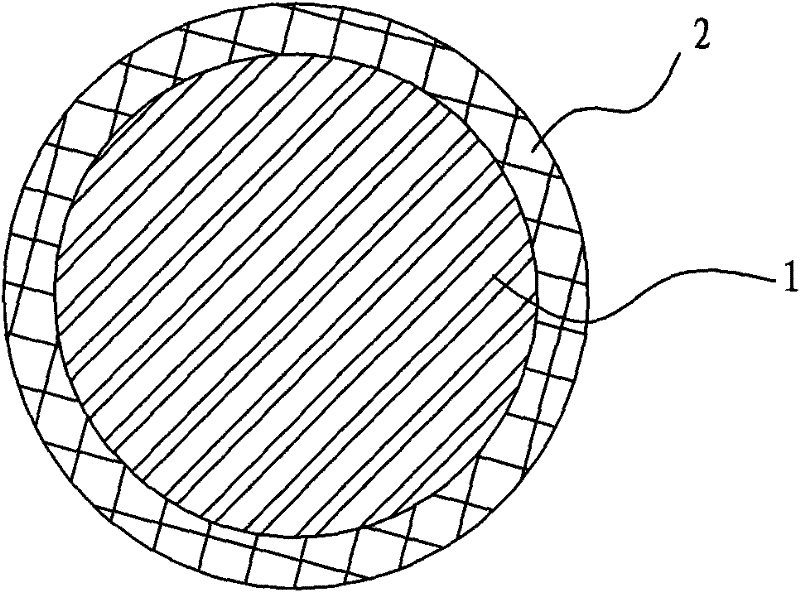
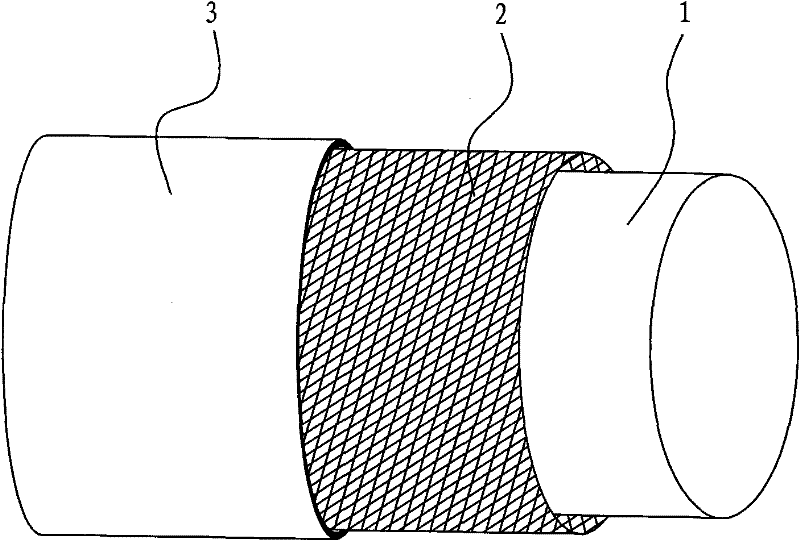
Motor winding wire embedding method
PendingCN114039465AAvoid damageAvoid crossingApplying solid insulationIndex fingerStructural engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a motor winding wire embedding method, which comprises the following steps that after a binding wire of a winding is unfastened, a thumb and an index finger of a left hand pinch a part, close to a left corner, of a straight line side, a left effective side is rotated by 90 degrees by a right hand, the thumb and the index finger of the left hand pinch a part, close to a right corner, of the straight line side, and the right effective side is rotated by 90 degrees by the right hand; the left side effective edge and the right side effective edge rotate in the same direction, the right hand fixes the winding, the thumb and the index finger of the left hand pinch the lower layer edge close to the corner to be flat, then the upper layer edge close to the corner is pinched to be flat, the left hand does not move, the right hand cards the two side effective edges into a flat shape, the carded winding serves as a winding to be embedded, and the two side effective edges of the winding are rotated by 90 degrees in the same direction, the effective edges on the two sides of the winding are combed to be flat, so that coils on the effective edges of the winding are parallel, intersection between turns and strands of the winding is avoided, the difficulty of driving slot wedges into the hanging grooves is reduced, the effective edges of the winding are embedded into the hanging grooves without using a marking-off plate, and damage to an insulating layer of the winding is avoided.
Owner:兖矿能源集团股份有限公司
Composite material core used for enhanced cable, preparation process thereof and enhanced cable
InactiveCN102024517BSolve the problem of no transverse fiber reinforcementImprove lateral strengthInsulated cablesCable/conductor manufactureFiber bundleElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a composite material core used for an enhanced cable, a preparation process and the enhanced cable. The composite material core comprises an inner core and an outer layer, wherein the inner core is composed of fiber and thermosetting resin; the outer layer comprises a fiber woven pipe and thermosetting resin which are composited to form the outer layer; and the fiber woven pipe of the outer layer is a network structure which is woven by interlacing a plurality of fiber bundles. The transversal strength of the composite material core is greatly improved by the interlaced network structure, the fatigue resistance of the composite material core is greatly improved, and the service life of the composite material core and a power transmission cable is prolonged; and the problem that the composite material core is broken when the composite material core is stranded, wound and extruded by a conductor in the manufacturing process of the cable is completely avoided. Asthe fiber woven pipe is adopted by the outer layer, the flexibility of the outer layer is greatly increased by the interlaced and woven structure, thereby meeting the requirement of manufacturing composite material core with major diameter.
Owner:JIANGSU JIATAI TECH MATERIAL
Busbar temperature taking device for frame circuit breaker
PendingCN113063511AConvenient temperature measurementHigh degree of insulationThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsBusbarStructural engineering
The invention relates to a busbar temperature taking device for a frame circuit breaker, which comprises a mutual inductor upper cover and a mutual inductor lower cover, the mutual inductor upper cover is provided with a mounting groove, the mounting groove is internally provided with a PCB, the PCB is provided with a metal sheet which is used for contacting with a busbar and receiving heat, and a PT platinum resistor is also arranged at a position, corresponding to the metal sheet, below the PCB in the mounting groove. Compared with the prior art, the device has the advantages of accurate temperature measurement, high heat transfer speed and the like.
Owner:上海亿盟电气自动化技术有限公司
Cross-linked polyethylene insulating halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant fire-resisting cable
InactiveCN107958737AGuaranteed stabilityIncreased strength and insulationInsulated cablesInsulated conductorsCross-linked polyethyleneAluminum metal
The invention relates to the field of cables, in particular to a cross-linked polyethylene insulating halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant fire-resisting cable. The cross-linked polyethylene insulating halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant fire-resisting cable comprises a plurality of cable cores, wherein each cable core comprises a conductor, each conductor is extruded with a cross-linked polyethylene insulating layer, each cross-linked polyethylene insulating layer is wrapped with a flexible metal-plastic mixed layer, the flexible metal-plastic mixed layers are extruded with a composite armor layer, the composite armor layer is extruded with a metal shielding layer, and the metal shielding layer is extruded with a halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant layer; each flexible metal-plastic mixed layer comprises an aluminum metal sleeve and flame-retardant nitrile rubber arranged in the aluminum metal sleeve; and a flexible metal isolating layer for supporting and fixing the cable cores and filled with glass powder is twisted among the cable cores. The cross-linked polyethylene insulating halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant fire-resisting cable ensures the internal stability ofthe cable, and can guarantee the use of the cable in a certain period of time in case of an accident; and the flexible metal-plastic mixed layers are extruded on the cable cores, so as to enhance thestrength and insulation degree of the cable.
Owner:安徽庆华电缆有限公司
Drying agent for mine underground electric apparatus and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102698573BSolve the problem of moisture absorption and dehumidificationPrevent accidents such as sudden power outagesDispersed particle separationLow voltageAlkali metal halide
The invention discloses a drying agent for an mine underground electric apparatus and a preparation method of the drying agent, belonging to the field of drying agent, wherein macromolecule water absorbent, compound of silicon or calcium and alkali halide or modified starch are mixed so as to prepare the powdery draying agent according to part by weight; the macromolecule water absorbent is 35-70 parts; the compound of silicon or calcium is 25-55 parts; the alkali halide or a mixture of the alkali halide and the modified starch is 10-15 parts; the grain size of the macromolecule water absorbent is 0.20-0.40mm; and the drying agent is powdery. According to the invention, raw material is wide in source and is purchased easily on the market; the drying agent is used for high / low-voltage power supply appliances worked on a mine underground high-humidity condition (RH=80-100%); the dry powder resists 6000V voltage or does not be broken down under voltage of 3000V; when moisture rate reaches to 1g / g, the dry powder resists 2500V voltage or does not be broken down under voltage of 1200V.
Owner:徐州意创化工科技有限公司
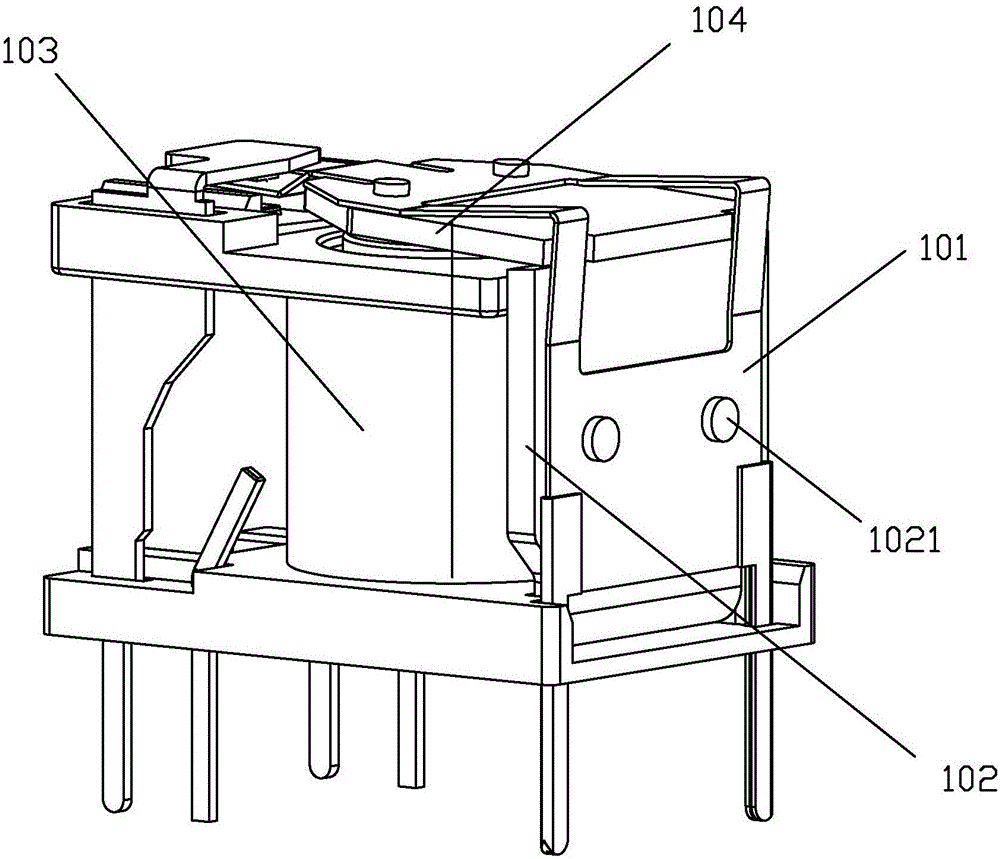
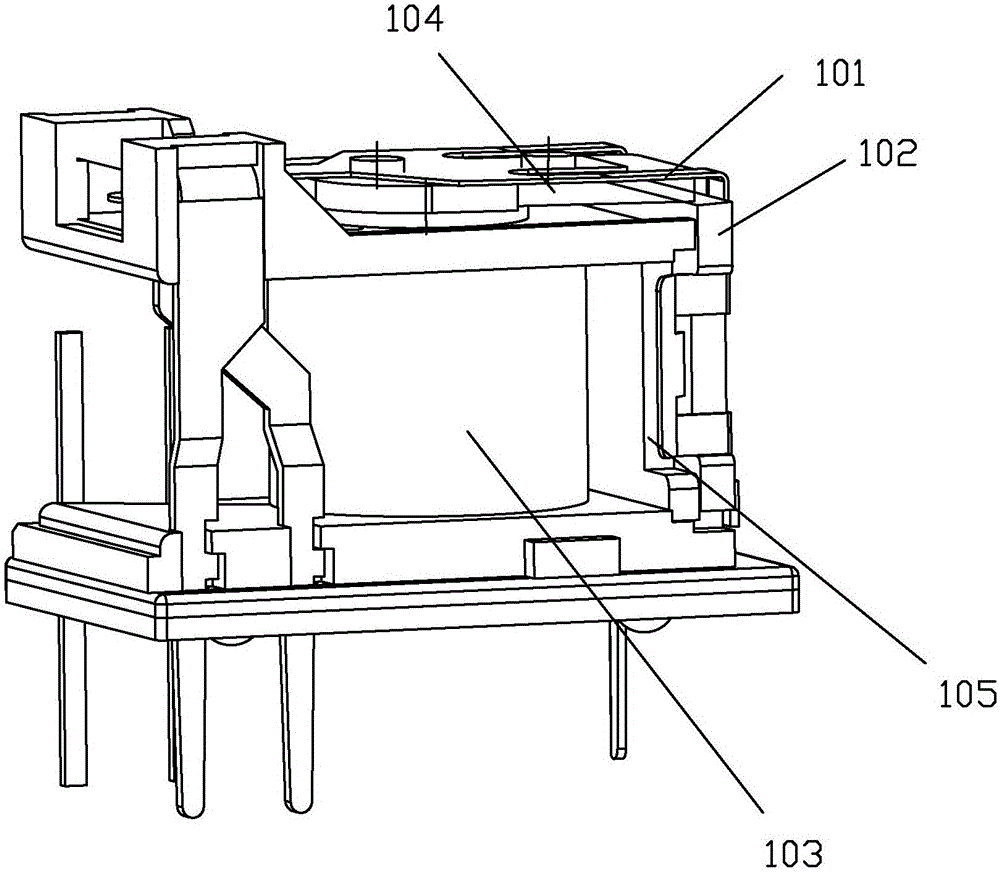
An ee type high frequency transformer
ActiveCN109285655BAchieve fixationHigh degree of insulationTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsFixed transformers or mutual inductancesTransformerStructural engineering
Owner:忠县南泰电子有限公司
Forming mold for outdoor transformer and its casting and sealing method
InactiveCN104526940BPrevent radial offsetEasy to processInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureTransformerInstrument transformer
The invention discloses a molding mold for an outdoor transformer and a pouring and sealing method thereof. The molding mold includes an upper mold and a lower mold for enclosing a mold cavity, and the upper mold is provided with a pouring mold that communicates with the mold cavity. holes and air vents, mold cores are provided in the mold cavity, the upper and lower ends of the mold cores are respectively connected with the upper mold and the lower mold, and the upper and lower ends of the mold cores are respectively snapped into the upper groove of the upper mold And in the lower groove of the lower mold, the part of the mold core located in the mold cavity is cylindrical; a set of fixed pillars for supporting the transformer coil are arranged around the mold cavity in the mold cavity, and the fixed pillars are connected with the lower mold core. The mold is fixedly connected, and the upper end of the fixed pillar is provided with a ladder-shaped clamping platform for clamping the outer edge and the lower edge of the transformer coil. The invention has the advantages of being able to improve the resin casting and solidifying efficiency of the outdoor transformer, reduce the unit energy consumption and waste rate of the outdoor transformer, and improve its insulation degree.
Owner:XUCHANG YONGXIN ELECTRIC
Convenient assembling and disassembling isolation tool for line hanging
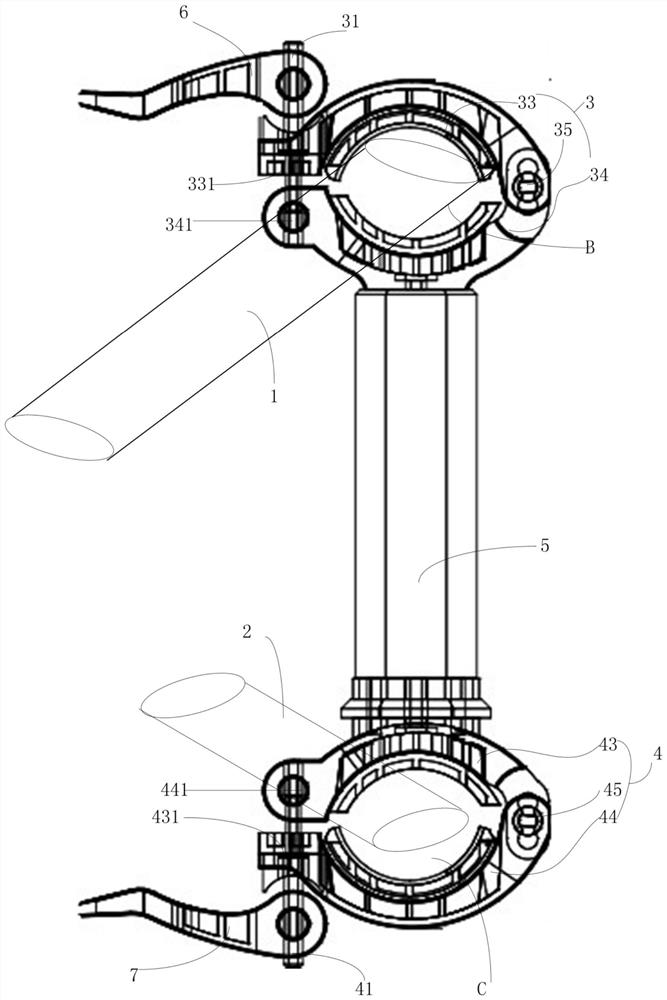
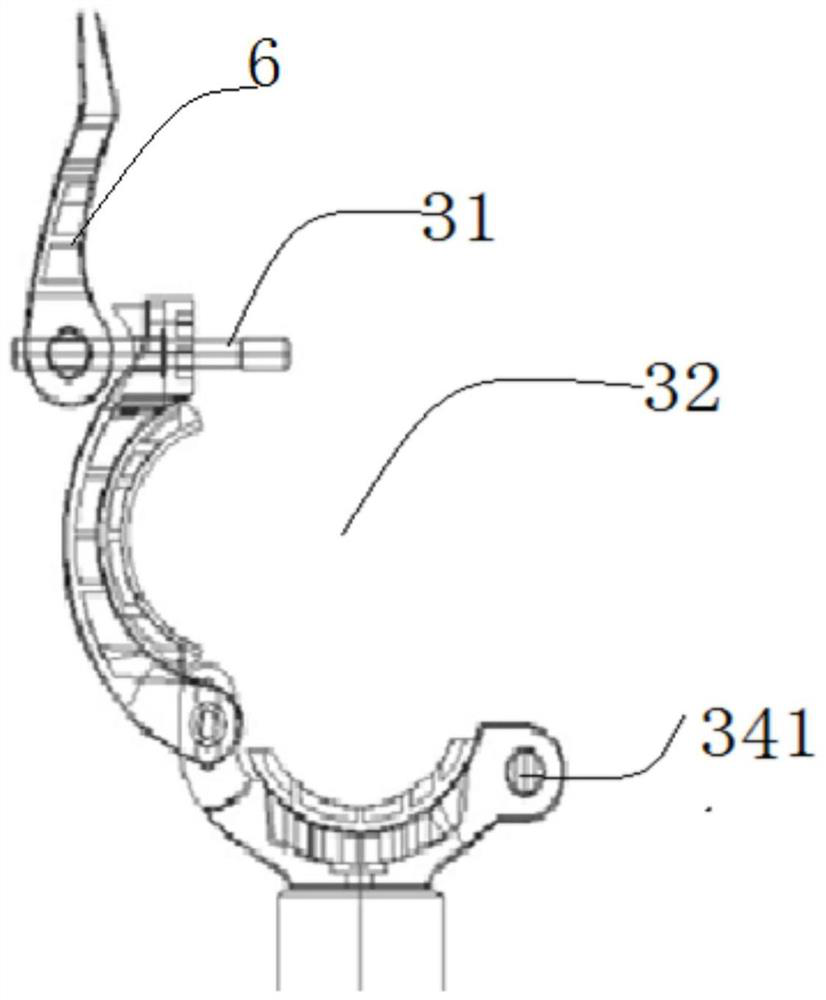
ActiveCN112531558AHigh degree of insulationFlexible assembly and disassemblyApparatus for overhead lines/cablesStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a convenient assembling and disassembling isolation tool for line hanging, and solves the problem that the life and property safety of people and the safety of electric power, communication and radio and television networks are threatened due to disordered hanging of lines. The tool is provided with a first assembling and disassembling hoop part, a second assembling and disassembling hoop part and a protection rod, the first assembling and disassembling hoop part clamp a first line, the second assembling and disassembling hoop part clamps a second line, a safe distance is kept between the first line and the second line which are mixed and matched through the protection rod, the first assembling and disassembling hoop part is rotationally connected with a center shaftof the upper end face of the protection rod, and the second assembling and disassembling hoop part is rotationally connected with a center shaft of the lower end face of the protection rod, so that the line crossing points hung at various angles are flexibly isolated. Directly through the adjustment of a first movable handle and a second movable handle, the first assembling and disassembling hooppart or the second assembling and disassembling hoop part forms a notch for the first line or the second line to enter a clamping area, so that the trouble of traditional assembling and disassemblingwith a screwdriver and rubber pliers is avoided, and the operation is convenient.
Owner:ZHANJIANG POWER SUPPLY BUREAU OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com