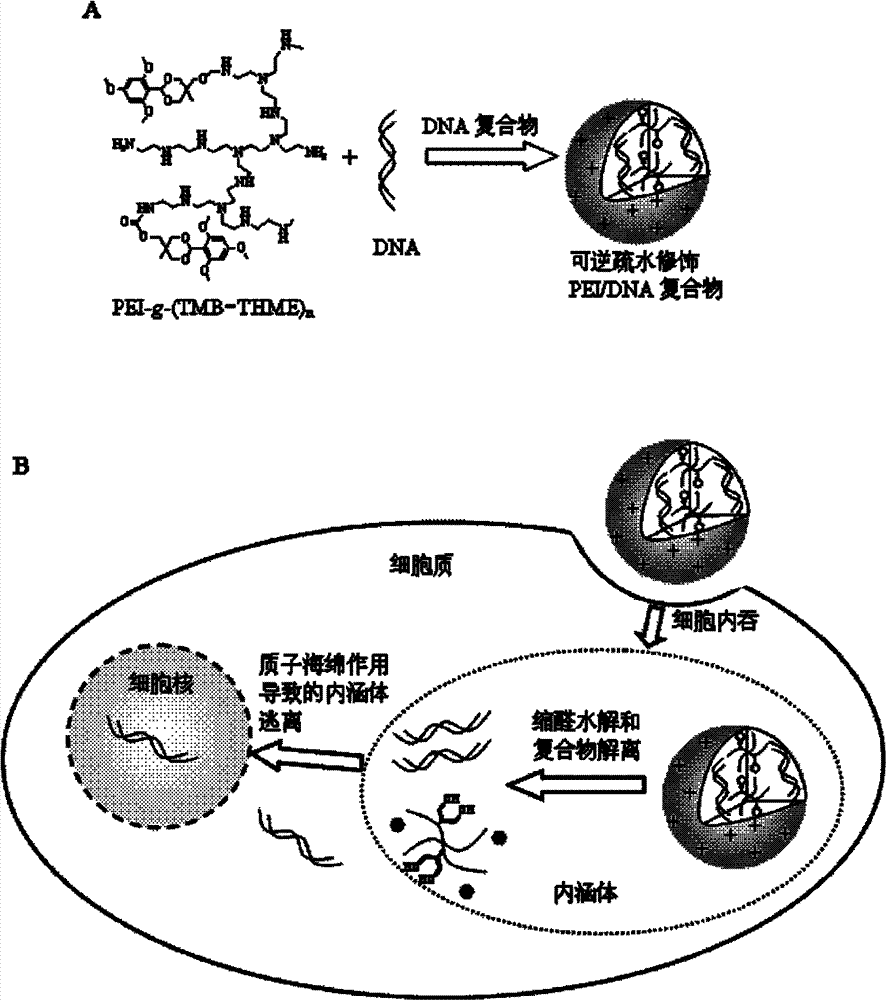
Hydrophobic-group-modified polyethyleneimine derivative and application thereof
A polyethylenimine, hydrophobic group technology, applied in the use of vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as low transfection efficiency, and achieve high transfection efficiency, low cytotoxicity, and efficient delivery. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
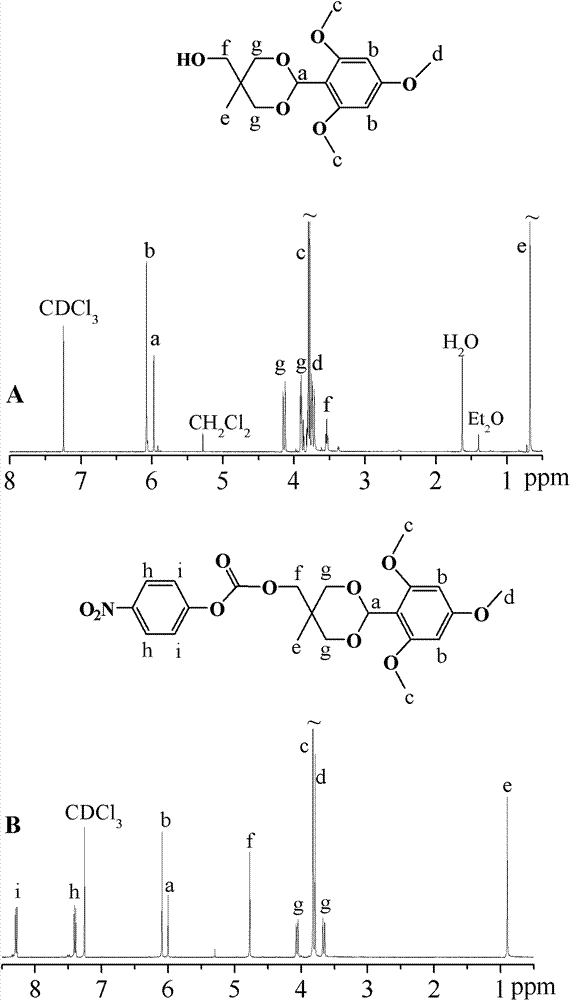
[0043] Example 1: Synthesis of Trimethoxybenzyl-Trihydroxyethane (TMB-THME)
[0044] 1,1,1-Trihydroxyethane (THME, 6.667 g, 55.5 mmol) and p-toluenesulfonic acid (0.5278 g, 2.775 mmol) were first dissolved in 100 mL tetrahydrofuran at 50 °C, and then 2, 4, 6-Trimethoxybenzaldehyde (TMB, 3.63 g, 18.5 mmol) and 7.5 g of 4 Å molecular sieves were added. After reacting overnight at 50°C, 7 mL of triethylamine was added and diluted with 75 mL of dichloromethane. The molecular sieves were filtered off and washed with dichloromethane, and spin-dried under reduced pressure to obtain a white solid. The solid was dissolved in dichloromethane and extracted three times with 0.1 M pH 8.0 PB buffer solution. The organic phase was collected and dried overnight with anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The next day Magnesium sulfate was filtered off and spin-dried under reduced pressure to obtain a white solid, which was dried in a vacuum oven for 2 days. Yield: 54.6%.
[0045] The NMR characteriz...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment two: p-nitrophenyl chloroformate ( p -NC) Activated trimethoxybenzyl-trihydroxyethane (TMB-THME-PC)
[0047] The white product TMB-THME (2.31 g, 7.8 mmol) in Example 1 was dissolved in 70 mL of dichloromethane, and triethylamine (2.36 g, 23.4 mmol), pyridine (0.60 g, 7.8 mmol) , p-nitrophenyl chloroformate (1.565 g, 9.13 mmol) was added thereto, and reacted overnight at room temperature. After the reaction was completed, the reaction liquid was added to 300 mL of anhydrous diethyl ether (precipitated triethylamine hydrochloride), and the filtrate was filtered to precipitate into ice n-hexane, and a light brown solid was obtained by filtration, which was dried in vacuum for 2 days. Yield: 60%.
[0048] The NMR characterization of TMB-THME-PC is shown in the appendix figure 2 B: 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ): d 8.30 (d, 2H), d 7.42 (d, 2H), d 6.10 (s, 2H), d 6.00 (s, 1H), d 4.77 (s, 2H), d 4.05 (d, 2H), d 3.83 (s, 6H), d 3.79 (s, 3H), d 3.68 (d, 2H), d 0.9...
Embodiment 3
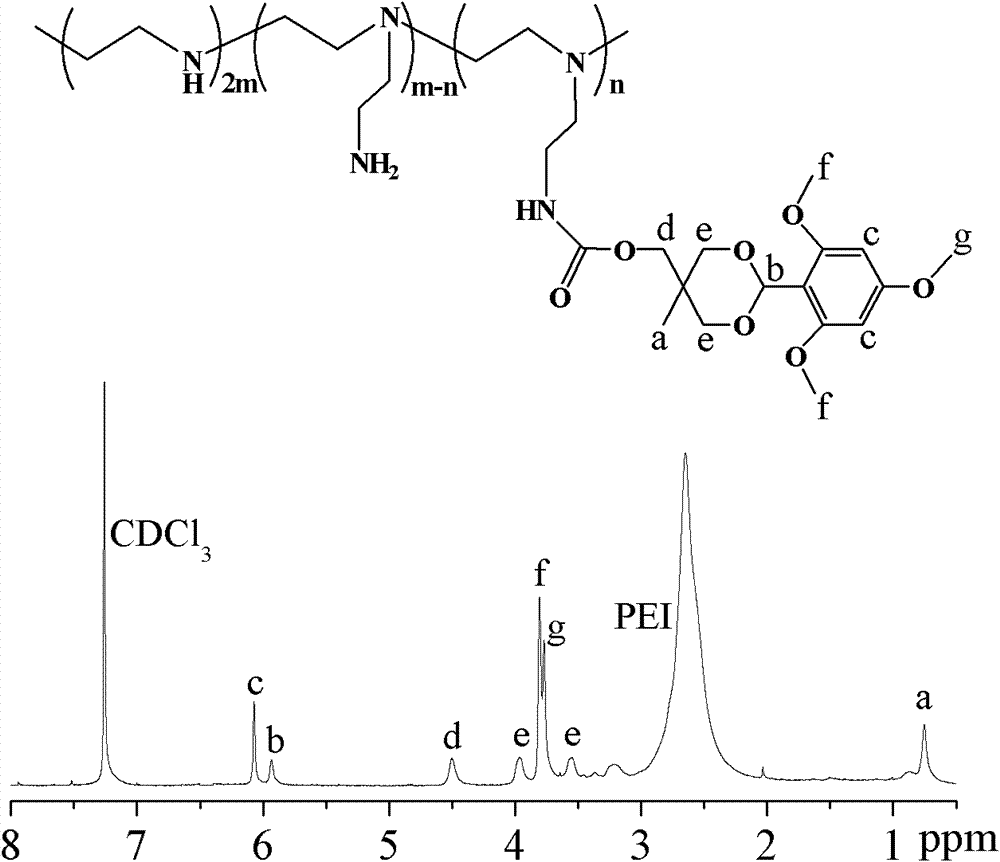
[0049] Embodiment three: modified 10 kDa PEI (PEI (10 kDa)- g -(TMB-THME) n )Synthesis
[0050] 10 kDa PEI (0.3 g, 6.97 mmol) was dissolved in 6 mL of dichloromethane, TMB-THME-PC (0.497 g, 1.1 mmol) was dissolved in CH 2 Cl 2 , under the protection of nitrogen, TMB-THME-PC was added dropwise to 10 kDa PEI in dichloromethane solution, after the addition was complete, the reaction was carried out at room temperature for 24 hours. After the reaction, the reaction solution was first precipitated three times in glacial ether, and then the product was dissolved in secondary water, dialyzed with MWCO 3500 dialysis bag to remove p-nitrophenol, and freeze-dried for 2 days to obtain a yellowish solid. Get PEI (10 kDa)- g -(TMB-THME) 9 , yield 73%.
[0051] where PEI (10 kDa)- g -(TMB-THME) 9 The NMR characterization is as follows image 3 : 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ): d 6.07 (s, 2H), d 5.93 (s, 1H), d 4.50 (s, 2H), d 3.97 (s, 2H), d 3.81 (s, 6H), d 3.75 (s, 3H), d 3.57 (s, 2H...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com