Short fiber food waste residue-based nano cellulose and preparation method thereof
A technology of nano-cellulose and short fibers, which is applied in the fields of pulping with salt/acid anhydride, pretreatment with water/steam, washing/replacing pulp treatment liquid, etc. It can solve the problems of large particle size range, long hydrolysis time, and utilization rate of less than 10 % and other problems, to achieve the effect of weak compactness of crystal region, large proportion of amorphous region and loose structure of crystal region
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Preparation of nanocellulose with sweet potato residue
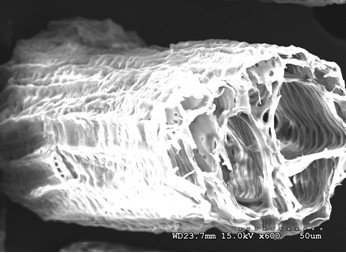
[0035] Use a colloid mill to refine the sweet potato residue to less than 50 μm, wash it twice with water, adjust the washed sweet potato residue to a mass concentration of 30% with phosphate buffer, heat it to 100°C and keep it for 10 minutes, add an amount equivalent to the dry weight of sweet potato residue 2% high-temperature α-amylase, hydrolyzed at 90°C for 1 hour, then washed 3 times with water, and dehydrated by centrifugation to obtain sweet potato slag fiber. For details, see figure 1 ; Send the sweet potato residue fiber into the acid hydrolysis tank with stirrer, add the hydrochloric acid aqueous solution that is equivalent to 10 times the weight of the sweet potato residue fiber, and the concentration is 2mol / L, after stirring evenly, under the condition of 85 ℃, stir at 300 rpm React for 240 minutes. After the hydrolysis, add 2% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to neutralize the reaction s...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Preparation of Nanocellulose from Potato Residue
[0037] Use a colloid mill to refine the potato residues below 40 μm, wash them twice with clean water, adjust the washed potato residues to a mass concentration of 35% with phosphate buffer, heat them to 100°C for 10 minutes, and add an amount equivalent to the mass fraction of potato residues 2% high-temperature α-amylase, hydrolyzed at 90°C for 1 hour, then washed 3 times with water, centrifuged and dehydrated to obtain potato slag fibers, sent the potato slag fibers into an acid hydrolysis tank with a stirrer, and added Add a hydrochloric acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 3mol / L that is 20 times the mass of potato residue fibers, stir evenly, and react at a low speed of 100-300 rpm for 200 minutes at 85°C, and add hydrogen with a concentration of 2% after the hydrolysis is completed Sodium oxide aqueous solution neutralizes the reaction solution to pH 6.5 to obtain acid hydrolyzed potato residue...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3 Preparation of Nanocellulose from Wheat Bran
[0039]Add wheat bran to 5 times of water and mix, use a colloid mill to refine the wheat bran to less than 80 μm, wash it with water for 3 times, adjust the washed wheat bran to a mass concentration of 35% with a phosphate buffer, and pH9 .0, add alkaline protease equivalent to 1% of the dry weight of wheat bran, and hydrolyze it for 2 hours at 50°C; then adjust the solution to pH 4.5, heat it to 100°C for 5 minutes, and add 2 % high-temperature α-amylase, hydrolyzed at 90°C for 1 hour, then washed 3 times with water, and centrifuged the dehydrated wheat bran residue. Put the wheat bran residue into the acid hydrolysis tank with agitator, add sulfuric acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 4mol / L equivalent to 50 times of the wheat bran residue, stir evenly, and stir at 90°C at 300 rpm React for 100 minutes. After the hydrolysis, add 2% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to neutralize the reaction solution ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com