Method for isolating and purifying schwann cells from adipose tissue
A technique for Schwann cells and adipose tissue, applied in the field of cell biology, can solve the problems of high cost and low purification purity, and achieve the effect of promoting proliferation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
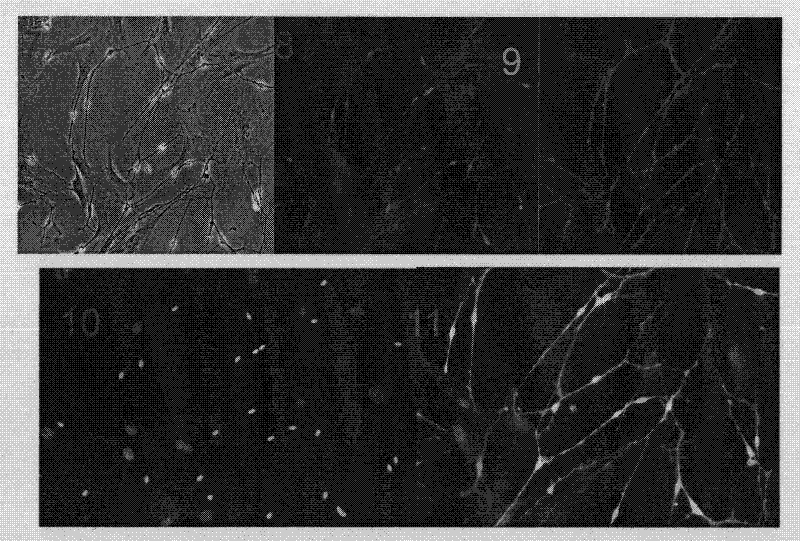
[0049] Example 1 Separation and purification of Schwann cells
[0050] SD mice born at 6 days of dislocation were put to death in 75% alcohol and soaked for 5-10 minutes. Remove both groin fat under aseptic conditions.
[0051] 1. Take the fat of the mouse under aseptic conditions and cut it to 1mm with scissors 3 Size, place it in 3-10 times the amount of DMEM medium to wash, centrifuge and discard the supernatant.
[0052] 2. Digest the nerve fragments with 5-20 times the amount of tissue with a mass-volume ratio of 0.1-0.2% composite collagenase NB4 and 0.05-0.1% dispase mixed enzyme DMEM solution for 30-60 minutes.
[0053] 3. Pipette the suspension obtained in step 2 repeatedly with a pipette for 3 to 5 minutes.
[0054] 4. Centrifuge the suspension obtained in step 3 at 600g for 5-10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and obtain cell pellets.
[0055] 5. Resuspend the cells obtained in step 4 with Schwann cell culture medium (DMEM medium containing 2μM forskolin, 10ng / ml heregulin-...
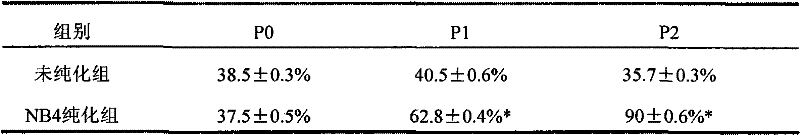
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3 Comparison of digestion results of two digestive enzyme systems
[0065] A) Take primary cells
[0066] 2. 6 C57BL6 mice at 6 days old, after dislocation, put them in 75% alcohol and soak for 5-10 minutes
[0067] 3. Take out the inguinal fat tissue from both sides under aseptic condition and cut it to 1mm with scissors 3 Size, place it in 3-10 times the amount of DMEM medium to wash, centrifuge and discard the supernatant.
[0068] 4. Put the adipose tissue fragments into a centrifuge tube A containing 5ml 2% composite collagenase NB415ml and a centrifuge tube B containing 5ml 2% composite collagenase NB4 and 2ml 0.1% dispaseII respectively.
[0069] 5. Put it in an incubator containing 5% CO2 at 37°C, shake it every five minutes, and digest for about 1.5 hours.
[0070] 6. Centrifuge tube A and tube B at 600g for 5 minutes, collect cells, count and plant them in culture flasks, 0.5 minutes per flask.
[0071] 2) Purification of Schwann cells
[0072] After the primary ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com