Photo-reduction method for carrying out degradation on organic halides by using carboxylic acids or carboxylates
An organic halide, carboxylate technology, applied in the field of environmental pollutant treatment, can solve the problems of long reaction time, low degradation efficiency, large power consumption, etc. wide effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
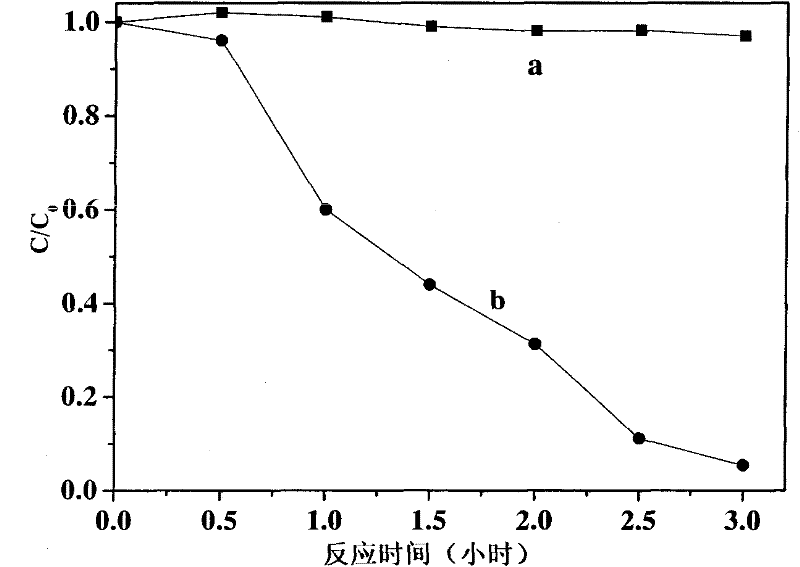
[0028] First add 5 ml of 0.001mM decabromodiphenyl ether dimethyl sulfoxide solution into the glass reactor, then add 0.0001M (NH 4 ) 2 C 2 o 4 Aqueous solution, the reactor mouth is sealed, feed argon or nitrogen 15 minutes, make reaction carry out under anaerobic condition; Magnetic stirring makes decabromodiphenyl ether dimethyl sulfoxide solution and (NH 4 ) 2 C 2 o 4 The aqueous solution is mixed evenly, the artificial light source used is a 300W xenon lamp, equipped with a 420nm cut-off filter, the light source is turned on, and irradiated with visible light for 180 minutes. In the light reaction, the oxalate ion and decabromodiphenyl ether form an ion-pair complex due to the halogen bond, and the ion-pair complex is excited by visible light to undergo electron transfer, and the decabromodiphenyl ether gets the electron of oxalate and is reduced Degradation, dehalogenation to generate low halogenated products. See the reaction result figure 1 , did not join (NH ...
Embodiment 2
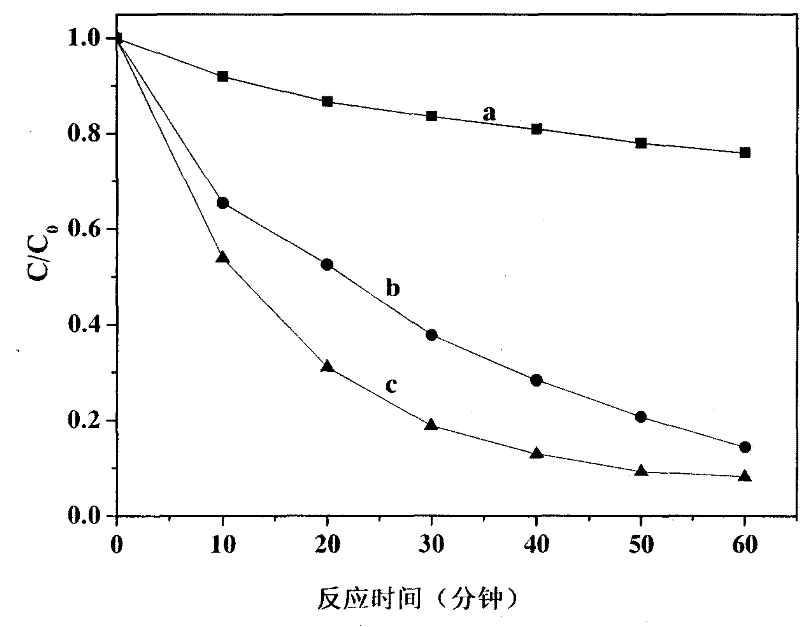
[0031] Add 5 ml of 0.01mM decabromodiphenyl ether methanol solution to the reactor first, then add 0.001M H 2 C 2 o 4 Aqueous solution, seal the reactor mouth, feed argon or nitrogen for 15 minutes, so that the reaction is carried out under anaerobic conditions; magnetic stirring makes decabromodiphenyl ether methanol solution and H 2 C 2 o 4 The aqueous solution is mixed evenly. The artificial light source used is a 300W xenon lamp, equipped with a 420nm cut-off filter, turned on the light source, and irradiated with visible light for 60 minutes. The oxalate ion and decabromodiphenyl ether used form an ion-pair complex due to halogen bonds. The ion-pair complex is excited by visible light to undergo electron transfer, the decabromodiphenyl ether obtains the electrons of oxalate, undergoes reductive degradation, and dehalogenates to generate low-halogenated products. See the reaction result figure 2 , oxalic acid can lead to degradation reactions.
[0032] figure 2 Th...
Embodiment 3
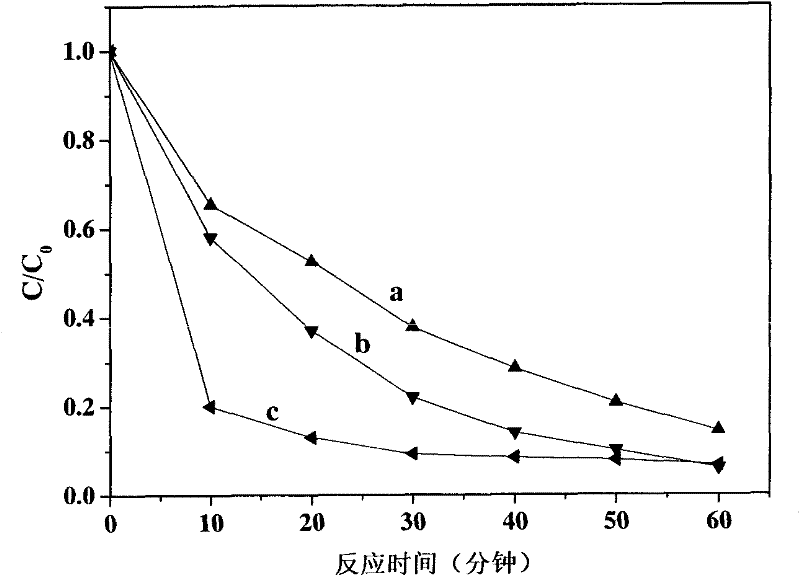
[0034] Add 5 ml of 0.01mM decabromodiphenyl ether methanol solution to the two glass reactors, and then add 0.001M K 2 C 2 o 4 Aqueous solution, 0.001M (NH 4 ) 2 C 2 o 4 Aqueous solution, seal the two reactor ports, respectively pass through argon or nitrogen for 15 minutes, so that the reaction is carried out under anaerobic conditions; magnetic stirring makes decabromodiphenyl ether methanol solution and K 2 C 2 o 4 aqueous solution, decabromodiphenyl ether methanol solution and (NH 4 ) 2 C 2 o 4 The aqueous solution is mixed evenly, the artificial light source used is a 300W xenon lamp, equipped with a 420nm cut-off filter, the light source is turned on, and the visible light is irradiated for 60 minutes, and the oxalate ion used and the decabromodiphenyl ether form ion-pair complexation due to the halogen bond. The ion-pair complex is excited by visible light to undergo electron transfer, and decabromodiphenyl ether obtains electrons from oxalate for reduction a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com