Plant cell microspheres and use thereof
A plant cell and microsphere technology, applied in plant cell microspheres and its application fields, can solve problems such as environmental pollution, lack of intelligence, high pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of environmental gain, easy expansion and upgrading, and precise technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
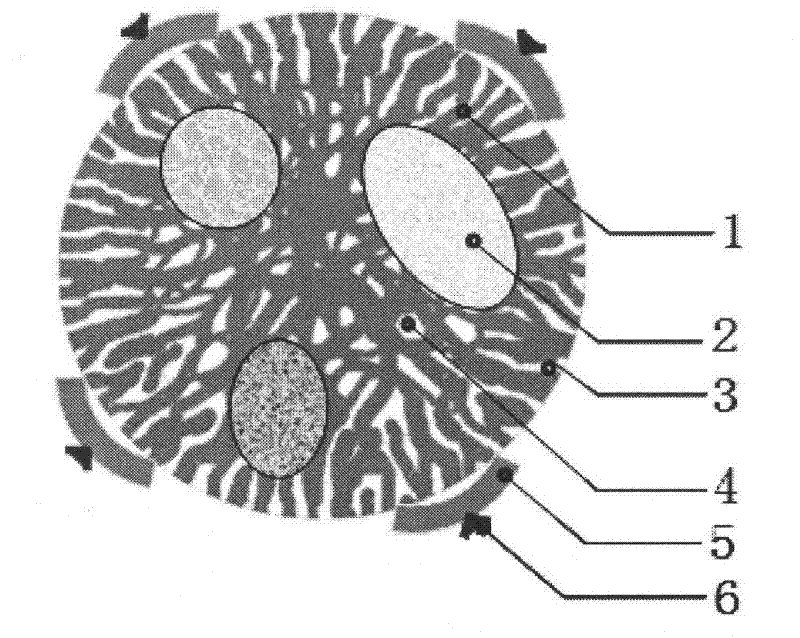
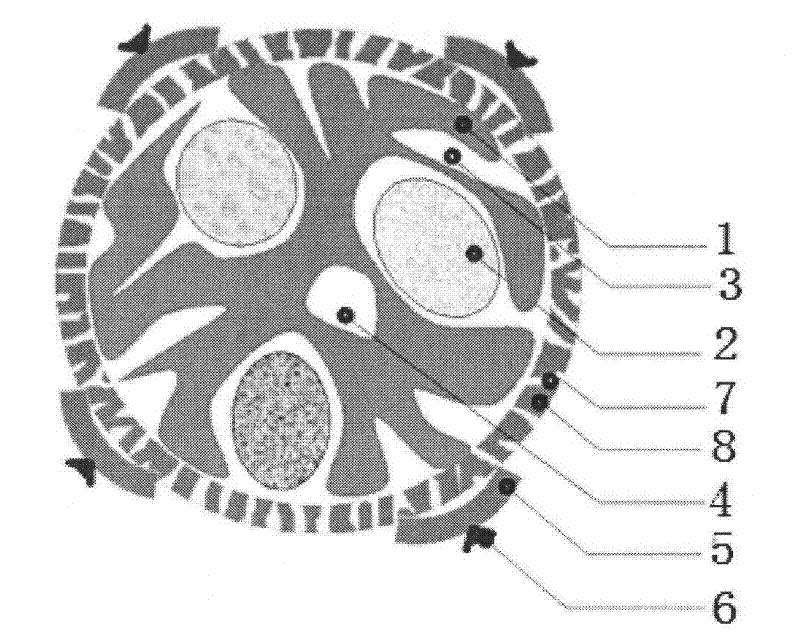
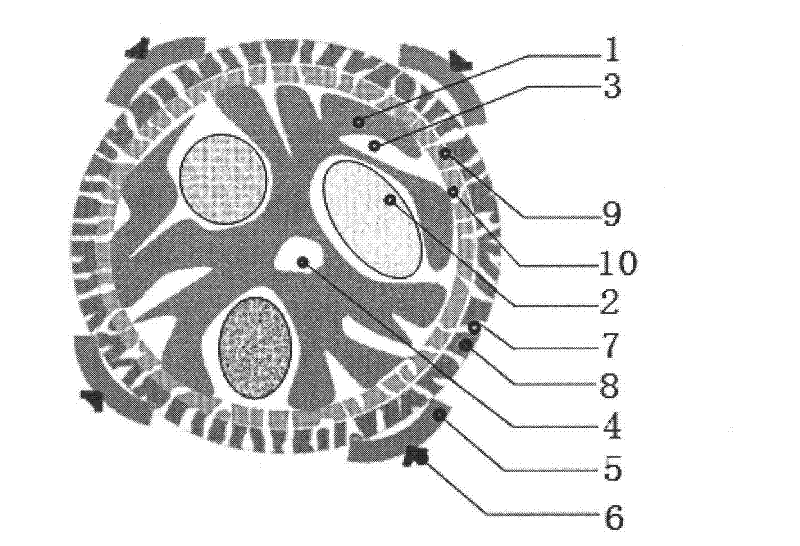
[0047] The plant cell microsphere is a microsphere processed and manufactured on the basis of plant protoplasts, plant cells, plant pollen or pollen, and the plant cell microspheres derived from protoplasts contain a matrix, a matrix channel, a cavity, an inner sphere and an outer part ; Cell-derived plant cell microspheres contain an outer wall, a matrix, a matrix channel, a cavity, an inner sphere and an outer part; a sporopollen-derived plant cell microsphere contains an outer wall, an inner wall, a matrix, a matrix channel, a cavity, an inner sphere and an outer part pieces.
[0048] Plant cell microspheres are produced by prokaryotic or eukaryotic plant cells or sporopollen as raw materials, with plant cells as the main body of the microsphere structure, which can include protoplasts, cell walls (walled microspheres), sporopollenia (sporopollen microspheres or pollen microspheres), all of the internal and external accessories, or a combination of one or more of them.
[...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: plant cell microspheres of protoplast origin:
[0052] Plant cell microsphere protoplast refers to the remaining cell part of plant cells after the cell wall is removed, and its structure includes cell membrane, nucleus (or nuclear region of prokaryotic cells), organelles (or non-membrane-coated functional regions corresponding to prokaryotic cells) , and the cytoplasm. Its structure and components can change its existence and properties through the genetic improvement, modification, mutagenesis, selection of developmental stage, treatment and processing involved in the production process of the plant cell microspheres.
[0053] Prokaryotic or eukaryotic plant cells, especially somatic cells, are used as solid or liquid medium for fermentation, such as: B5, MS, NLN and other medium. Cultivation temperature: 0-80°C. Shaking speed: 1-500rpm. The culture medium contains N, P, K, Fe, Ca and other macroelements, Mn and other trace elements, vitamins and othe...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3: Cell-derived plant cell microspheres:
[0058] Cells of prokaryotic or eukaryotic plants, especially somatic cells, are cultured in solid or liquid medium (for example: B5, MS, NLN, etc.) for fermentation. Cultivation temperature: 0-80°C. Shaking speed: 1-500rpm. The medium contains N, P, K, Fe, Ca and other macroelements, Mn and other trace elements, vitamins and other organic elements and sugar, etc., pH 5-8. The above items, as well as the cultivation conditions such as light time, light intensity and wavelength, are determined according to the requirements of the species and the shape, structure, material composition, function, color and yield of the finished microspheres.
[0059] The suspension cells produced by culture can be separated by centrifugation (100-5000rpm), filtration (50-400 mesh filter), adsorption (organic or inorganic material adsorption, affinity material adsorption, etc.) or electrophoresis separation (corresponding culture medium or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com