Method for extracting natural fibre from herbaceous plants
A herbal and natural fiber technology, applied in fiber raw material processing, textile and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption, large consumption of alkali, and insufficient utilization, and achieve the effect of low energy consumption and high pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment one is raw material with rice straw
[0020] 1. Material preparation
[0021] Straw, after the rice is harvested, air-dried to dry (water content less than 10%), the blue straw must be air-dried and then turned into light brown (or light yellow-brown); cut the raw materials that have been air-dried and removed the blue color to 2cm long The broken joints are crushed into thick filaments by a hammer-type pitting machine for later use.
[0022] 2. Start anaerobic fermentation.
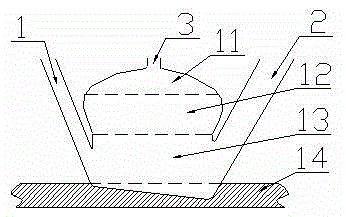
[0023] Put the net bag 8 in the "slag" outlet 2 of the fermentation tank in advance, and insert the insert plate 6, and put 100 mesh / cm from the feed inlet 1 2 The biogas slurry of the old biogas digester after sieving (or the pond field activated sludge slurry with an appropriate amount of water), the biogas slurry and activated sludge are rich in anaerobic bacteria. At the same time, add 4 times the volume of the old biogas tank biogas slurry prepared fermentation raw materials ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2 Taking wheat straw as raw material
[0034] 1. Dry the wheat stalks after harvesting to dryness (less than 10% moisture), and the green wheat stalks must turn off-white after drying.
[0035] 2. Cut the air-dried wheat straw into 2cm-long pieces, impregnate it with clarified fresh saturated lime water (material: lime water = 1:5 parts by weight) for 24 hours, then take it out and dry it in the air (with 10% water content) Below), it is crushed into thick strips by a hammer-type pitting machine.
[0036] 3. Carry out the same operations as in the steps 1-7 of Example 1 with the wheat straw prepared. Among them, 2 to 3 steps get 98 kg of dry fiber and 4 m of combustible gas. 3 , add 256 kg of wheat straw in 4 steps and prepare 256 kg of combustible gas in the process 3 , 5 steps to get 102 kg of dry fiber.
[0037] Present embodiment obtains 198 kilograms of natural fibers altogether twice, combustible gas 9m 3 (The water content of each fiber is the s...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment Three With asparagus as raw material
[0039] 1. Dry the harvested Asparagus in the sun until it is dry (9% water content), and the cyan Asparagus should be dried until it turns off-white.
[0040] 2. Cut the air-dried Asparagus japonica into 2cm-long pieces, and crush them into thick filaments through a hammer-type pitting machine, which is used as a material for the fermentation of Asparagus japonica.
[0041] 3. Carry out the same operations as in the steps 1 to 7 of Example 1 with Asparagus grass. Among them, 120 kg of dry fiber and 5 m of combustible gas are obtained in steps 2 to 3 3 , 4 steps plus 260 kg of asparagus preparations, the process yields 5.8m of combustible gas 3 , 5 steps to get 130 kg of dry fiber.
[0042] Present embodiment obtains 245 kilograms of natural fibers altogether twice, combustible gas 10.8m 3 (The water content of each fiber is the same as in Example 1).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com