A process for preparing n-type solar cells by co-diffusion of boron and phosphorus
A solar cell and co-diffusion technology, which is applied in the field of preparing n-type solar cells by co-diffusion of boron and phosphorus, can solve the problems of cumbersome preparation process, many process influencing factors, and no profit advantage, and achieve the effect of improving performance and reducing impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
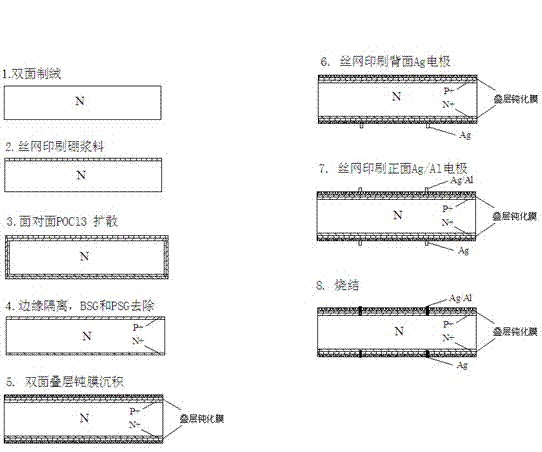
[0022] Such as figure 1 Shown: A process for preparing n-type solar cells by co-diffusion of boron and phosphorus, including the following steps:
[0023] 1. Use n-type silicon wafers with a minority carrier lifetime greater than 50μs and a resistivity of 0.5~15.0Ωcm to remove the damaged layer and texture on the surface of the silicon wafer by chemical etching;
[0024] 2. Print boron paste on the front side of the silicon wafer, and dry it at 100~500°C for 5~30min;
[0025] 3. The active layer is inserted into a quartz boat face to face for high-temperature diffusion; first diffuse at 880-1100°C for 10-60min, then cool down to 800-950°C, and then introduce POCl 3 source for phosphorus diffusion for 10~60min;
[0026] 4. Plasma for edge isolation;
[0027] 5. Chemical corrosion cleaning to remove printing paste, phosphosilicate glass and borosilicate glass, and drying;
[0028] 6. Double-sided passivation, the passivation method is: thermal oxygen passivation plus S...
Embodiment 2
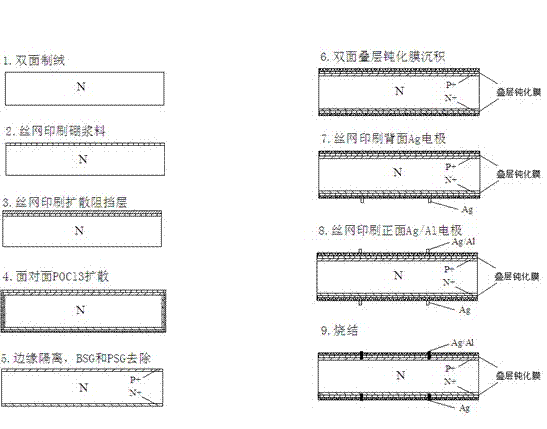
[0032] Such as figure 2 Shown: A process for preparing n-type solar cells by co-diffusion of boron and phosphorus, including the following steps:
[0033] 1. Use n-type silicon wafers with a minority carrier lifetime greater than 50μs and a resistivity of 0.5~15.0Ωcm to remove the damaged layer and texture on the surface of the silicon wafer by chemical etching;
[0034] 2. Print boron paste on the front side of the silicon wafer, and dry it at 100~500°C for 5~30min;
[0035] 3. Print another barrier layer on the front to cover the boron source, and dry at 100-500°C for 5-30 minutes;
[0036] 4. The active layer is inserted into a quartz boat face to face for high-temperature diffusion; first diffuse at 880-1100°C for 10-60min, then cool down to 800-950°C, and then introduce POCl 3 source for phosphorus diffusion for 10~60min;
[0037] 5. Plasma for edge isolation;
[0038] 6. Chemical corrosion cleaning to remove printing paste, phosphosilicate glass and borosilica...
Embodiment 3
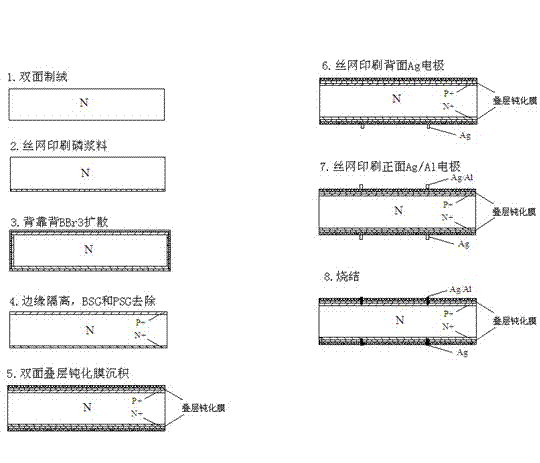
[0043] Such as image 3 Shown: A process for preparing n-type solar cells by co-diffusion of boron and phosphorus, including the following steps:
[0044] 1. Use n-type silicon wafers with a minority carrier lifetime greater than 50μs and a resistivity of 0.5~15.0Ωcm to remove the damaged layer and texture on the surface of the silicon wafer by chemical etching;
[0045] 2. Print phosphorous paste on the back of the silicon wafer, and dry it at 100-500°C for 5-30 minutes;
[0046] 3. The active layer is inserted into the quartz boat back to back for high temperature diffusion, and the BBr is passed through at a temperature of 880~1100°C 3 Source for boron diffusion for 10~60min;
[0047] 4. Plasma for edge isolation;
[0048] 5. Chemical corrosion cleaning to remove printing paste, phosphosilicate glass and borosilicate glass, and drying;
[0049] 6. Double-sided passivation, the passivation method is: thermal oxygen passivation plus SiN film deposited on both sides,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com