Method for isolating protein from food
A protein and protein extract technology, applied in the direction of protein food ingredients, fish protein ingredients, milk protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of high protein content, high cost of wastewater treatment, low yield, etc., and achieve low process cost , increase yield, improve the effect of separation yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
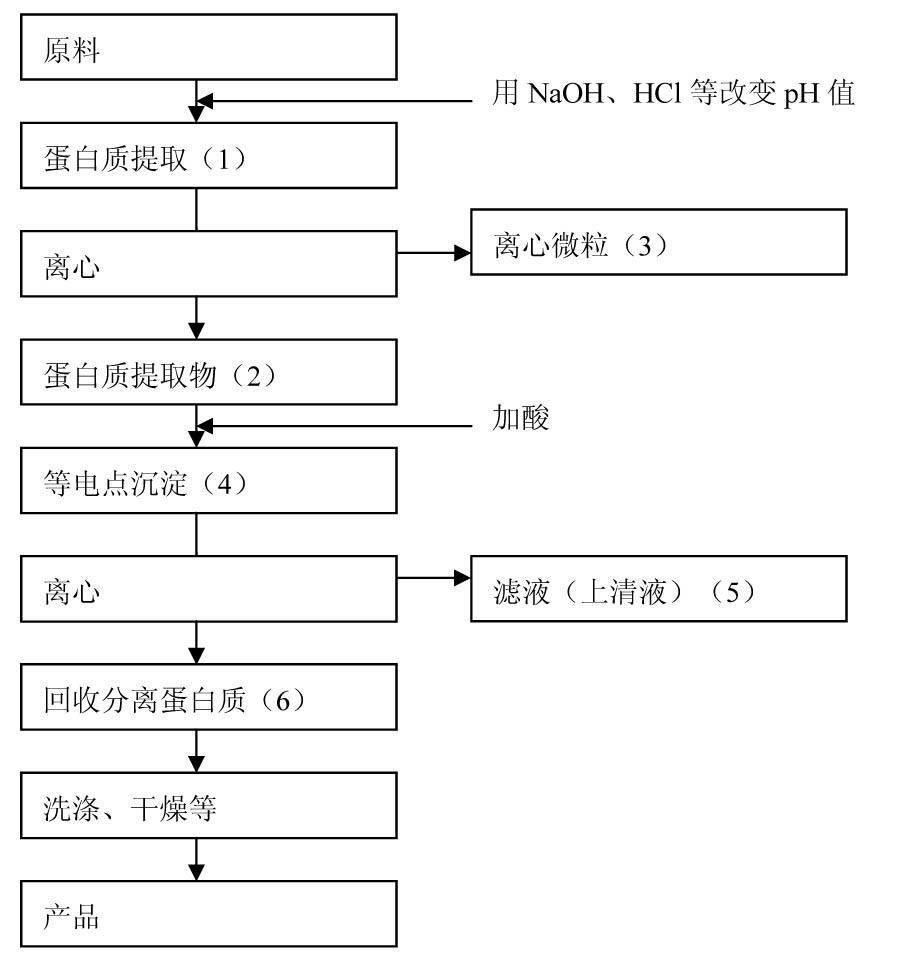
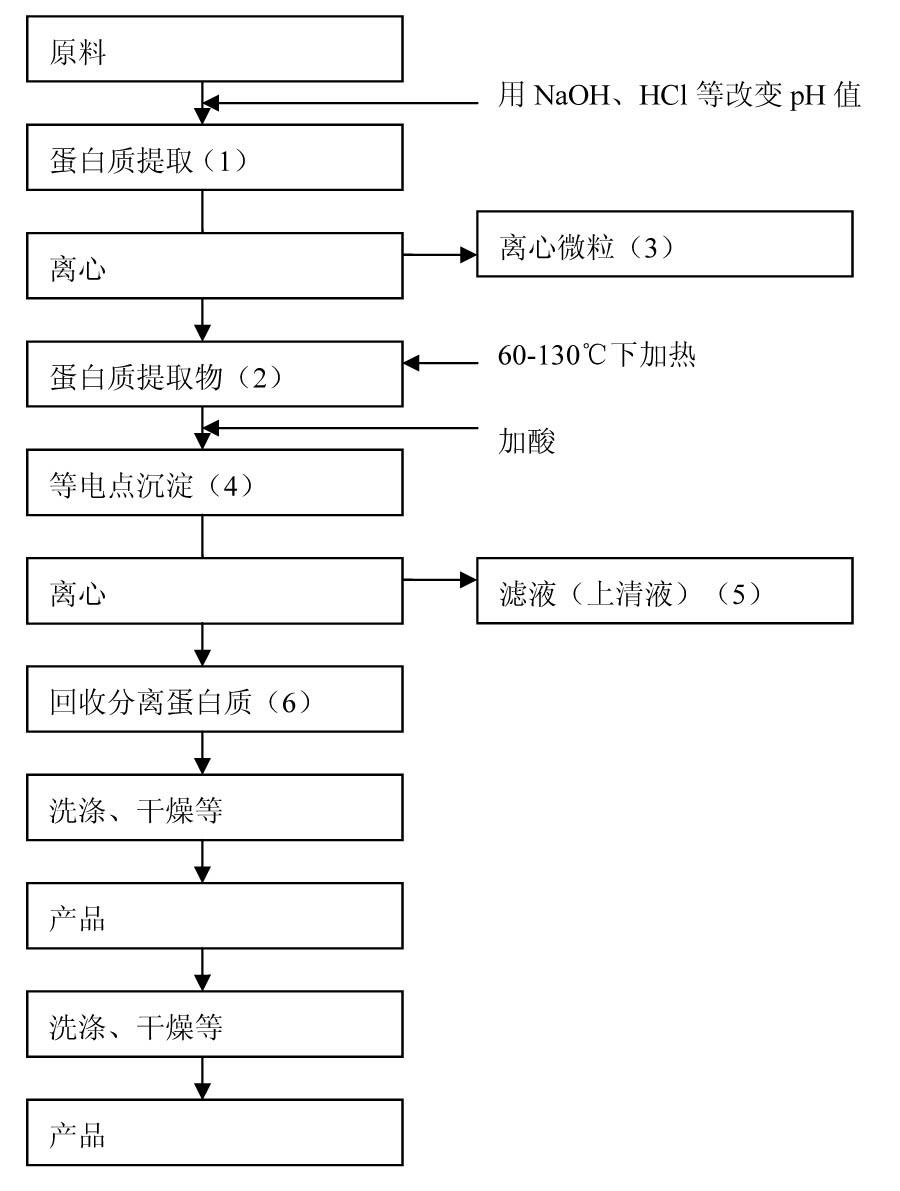
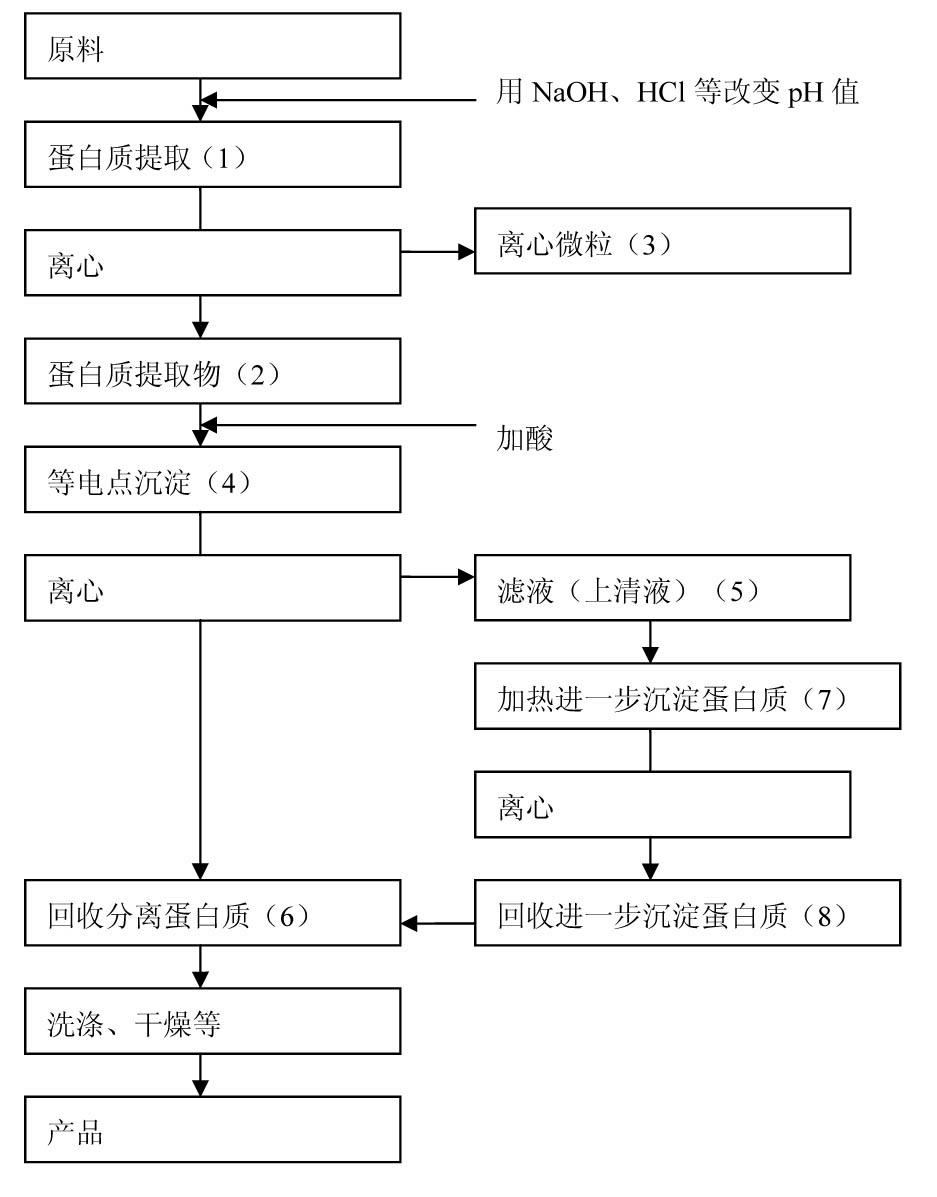
Image
Examples
example 1
[0050] Example 1: Isolation of protein from rice bran by isoelectric precipitation and heating
[0051] The protein was separated by isoelectric point precipitation, and 5000g defatted rice bran (crude protein content: 990g) was used as raw material. Protein was extracted by adding 5 times water to 5000 g of defatted rice bran, maintaining the pH at 9 and stirring at 30 °C for 1 hour. Therefore, the protein extract obtained by centrifugation was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes to separate the supernatant and the microparticles. The supernatant was extracted and then the proteins in the supernatant were precipitated while maintaining the pH at 4 and stirring for 30 minutes (acid precipitation process). In addition, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes. Centrifuge microparticles (white protein coagulum) were produced by the process described above (protein coagulum A), and the remaining centrifuge supernatant (protein filtrate) was heated to 60-145°C. Heat while sti...
example 2
[0056] Example 2: Isolation of protein from soybeans by isoelectric precipitation and heating
[0057] The protein was separated by isoelectric point precipitation method, and 5000g defatted soybean (crude protein content: 990g) was used as raw material. Protein was extracted by adding 10 times water to 5000 g of defatted soybeans, keeping the pH at 9 and stirring at 30°C for 1 hour. Therefore, the protein extract obtained by centrifugation was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes to separate the supernatant and the microparticles. The supernatant was extracted for use, and then the protein in the supernatant was precipitated while maintaining the pH at 4 and stirring for 30 minutes (acid precipitation process). The protein solution turned white at pH 4 and was centrifuged again at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes. Centrifuge microparticles (white protein coagulum) were produced by the process described above (protein coagulum A), and the remaining centrifuge supernatant was heat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com