Method for manufacturing SnAgCu lead-free solder
A lead-free solder and raw material technology, applied in the direction of welding/cutting media/materials, welding media, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of rough growth interface of reactants, easy generation of tissue defects, unfavorable weld reliability, etc. Versatility, reducing the chance of false soldering, and the effect of grain refinement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
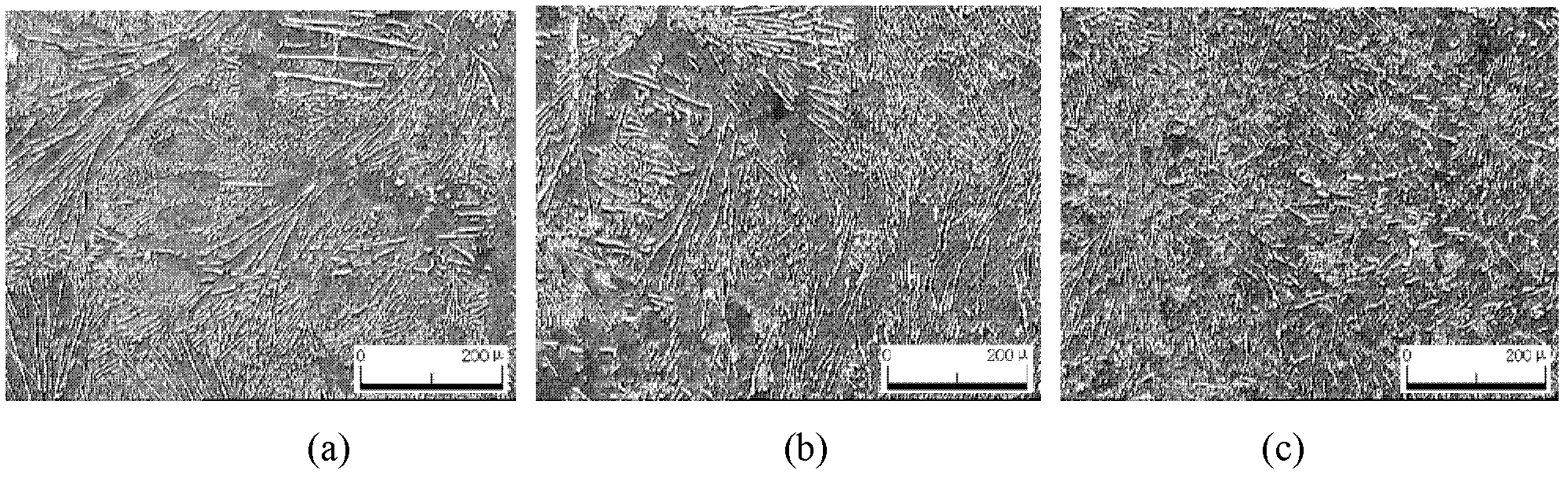
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 are comparative experiments of embodiment 3, not the scope of protection of the present invention.
[0041] Example 1:
[0042] The raw material of SnAgCu series ternary alloy lead-free solder in the present embodiment constitutes by mass percentage:
[0043] Ag3.5%, Cu0.7%, Sn95.8%.
[0044] The present embodiment SnAgCu series ternary alloy lead-free solder is prepared according to the following steps:
[0045] Mix the raw materials according to the ratio and heat up to 500°C for 1 hour under nitrogen protection to obtain an alloy melt to ensure that the alloy is melted and mixed evenly, and then poured into an alloy ingot; finally, the alloy ingot is processed into a solder by mechanical processing . The processing form of solder can be rolling, wire drawing or other conventional mechanical processing methods according to actual requirements, so as to obtain solder in the form of foil, sheet, rod, wire, granule or powder. The solder ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The raw material of SnAgCu series ternary alloy lead-free solder in the present embodiment constitutes by mass percentage:
[0048] Ag3.5%, Cu0.7%, Sn95.8%.
[0049] The present embodiment SnAgCu series ternary alloy lead-free solder is prepared according to the following steps:
[0050] Mix the raw materials according to the ratio and heat up to 500°C for half an hour under nitrogen protection to obtain an alloy melt, then raise the temperature of the alloy melt to 850°C and keep it for 15 minutes; then lower the temperature to 500°C and keep it for 0.5 hours, then cast into an alloy ingot; finally, the alloy ingot is processed into solder by means of mechanical processing. The processing form of solder can be rolling, wire drawing or other conventional mechanical processing methods according to actual requirements, so as to obtain solder in the form of foil, sheet, rod, wire, granule or powder. The solder in this example is in the form of flakes.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The raw material of SnAgCu series ternary alloy lead-free solder in the present embodiment constitutes by mass percentage:
[0053] Ag3.5%, Cu0.7%, Sn95.8%.
[0054] The present embodiment SnAgCu series ternary alloy lead-free solder is prepared according to the following steps:
[0055] Mix the raw materials according to the ratio and heat up to 500°C for half an hour under the protection of nitrogen to obtain an alloy melt, then raise the temperature of the alloy melt to 1050°C for 15 minutes; then lower the temperature to 500°C for 0.5 hours, then cast into an alloy ingot; finally, the alloy ingot is processed into solder by means of mechanical processing. The processing form of solder can be rolling, wire drawing or other conventional mechanical processing methods according to actual requirements, so as to obtain solder in the form of foil, sheet, rod, wire, granule or powder. The solder in this example is in the form of flakes.
[0056] The effect of the present...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com