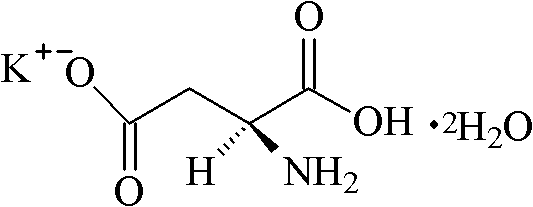
Method for preparing monopotassium L-aspartate dihydrate by separation process
A technology of aspartic acid and chelated potassium, applied in the field of chemistry, can solve the problem of large fixed cost plant and equipment investment, large difference in product moisture, and difficulty in producing stable and uniform potassium L-aspartate hemihydrate. things, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
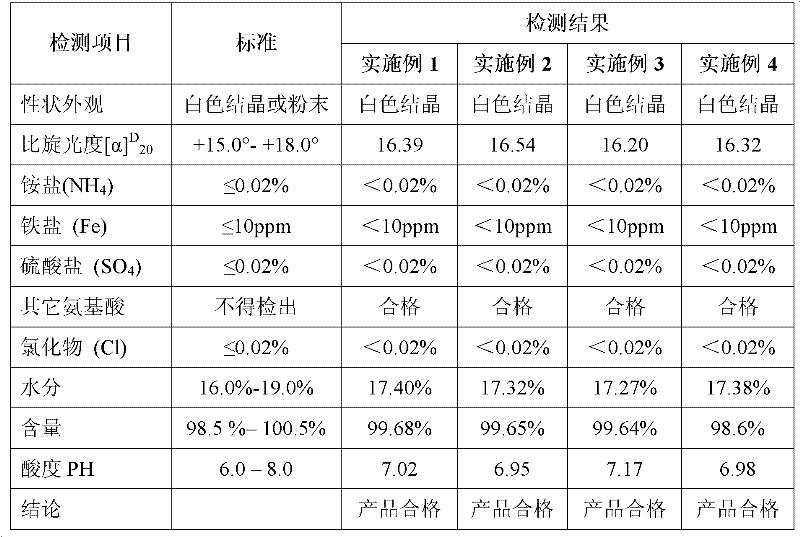
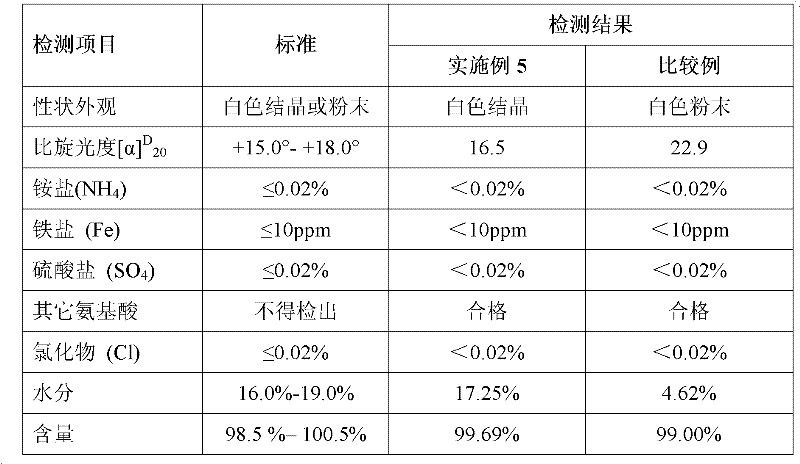
[0027] Add 500ml of deionized water into a 1000ml beaker, heat and stir on a magnetic stirrer, when the temperature rises to 70℃~75℃, add 100g of L-aspartic acid, K 2 CO 3 52g. After the reaction solution was clarified, samples were taken to measure the pH, and the pH of the corrected end point was 6.0-8.0. Add activated carbon 0.01Kg / L, decolorize, press filter, concentrate to 200ml, cool down to 16°C, add 2g of L-aspartic acid chelated potassium dihydrate as seed crystal, stir and cool to crystallize, add 50ml of absolute ethanol to soak for 2 Suction filter after hours. The solid material obtained by suction filtration was put into a single-necked flask, and then poured out after 4 hours of vacuum drying at room temperature and reduced pressure on a rotary evaporator to obtain 125g of finished product, with a yield of 79.61%. The test was qualified. The test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Add 500ml of deionized water into a 1000ml beaker, heat and stir on a magnetic stirrer, when the temperature rises to 75°C, add 100g of L-aspartic acid, K 2 CO 3 52g. After the reaction solution is clarified, take a sample to measure the pH, and correct the end point to pH=6.0-8.0. Add activated carbon 0.01Kg / L, decolorize, filter with suction, concentrate to 200ml, cool down to 16°C, add 3g of seed crystal L-potassium glutamate, stir and cool to crystallize, add 50ml of absolute ethanol to soak for 2 hours, and then filter with suction. The solid material obtained by suction filtration was packed into a single-necked flask, and then poured out after 4 hours of vacuum drying at room temperature and reduced pressure on a rotary evaporator to obtain 132g of finished product, with a yield of 83.54%. The test was qualified, and the test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Add 500ml of deionized water into a 1000ml beaker, heat and stir on a magnetic stirrer, when the temperature rises to 75°C, add 100g of L-aspartic acid, K 2 CO 3 52g. After the reaction solution is clarified, take a sample to measure the pH, and correct the end point to pH=6.0-8.0. Add activated carbon 0.01Kg / L, after decolorization, suction filtration, concentration to 200ml, after cooling down to 16°C, add 4g of seed crystal L-potassium glutamate, stir and cool to crystallize, add 50ml of absolute ethanol to soak for 2 hours and then suction filtration. The solid material obtained by suction filtration was put into a single-necked flask, and then poured out after 4 hours of vacuum drying at room temperature and reduced pressure on a rotary evaporator to obtain 132g of finished product, with a yield of 83.01%. The test was qualified. The test results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com