Method for hydrothermally reducing CO2 or CO into methane by using porous nickel catalyst
A catalyst and porous nickel technology, applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve problems such as catalyst bed temperature fluctuations, unfavorable industrial applications, and reduced conversion efficiency, and achieve the effects of solving energy shortages, facilitating reaction temperature, and controlling reaction temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The exhaust gas of coal-fired power plants is CO 2 One of the main sources of emissions. Currently, China's power sector emits 2.7 billion tons of CO2 per year 2 It ranks second in the world after the United States. Applying the present invention to the power sector, the waste CO emitted by it can be 2 The collection is passed into a hydrothermal reactor for treatment. Moreover, the waste heat of the power plant can provide the temperature required for some reactions, so that the energy consumption of hydrothermal treatment of carbon dioxide can be reduced.
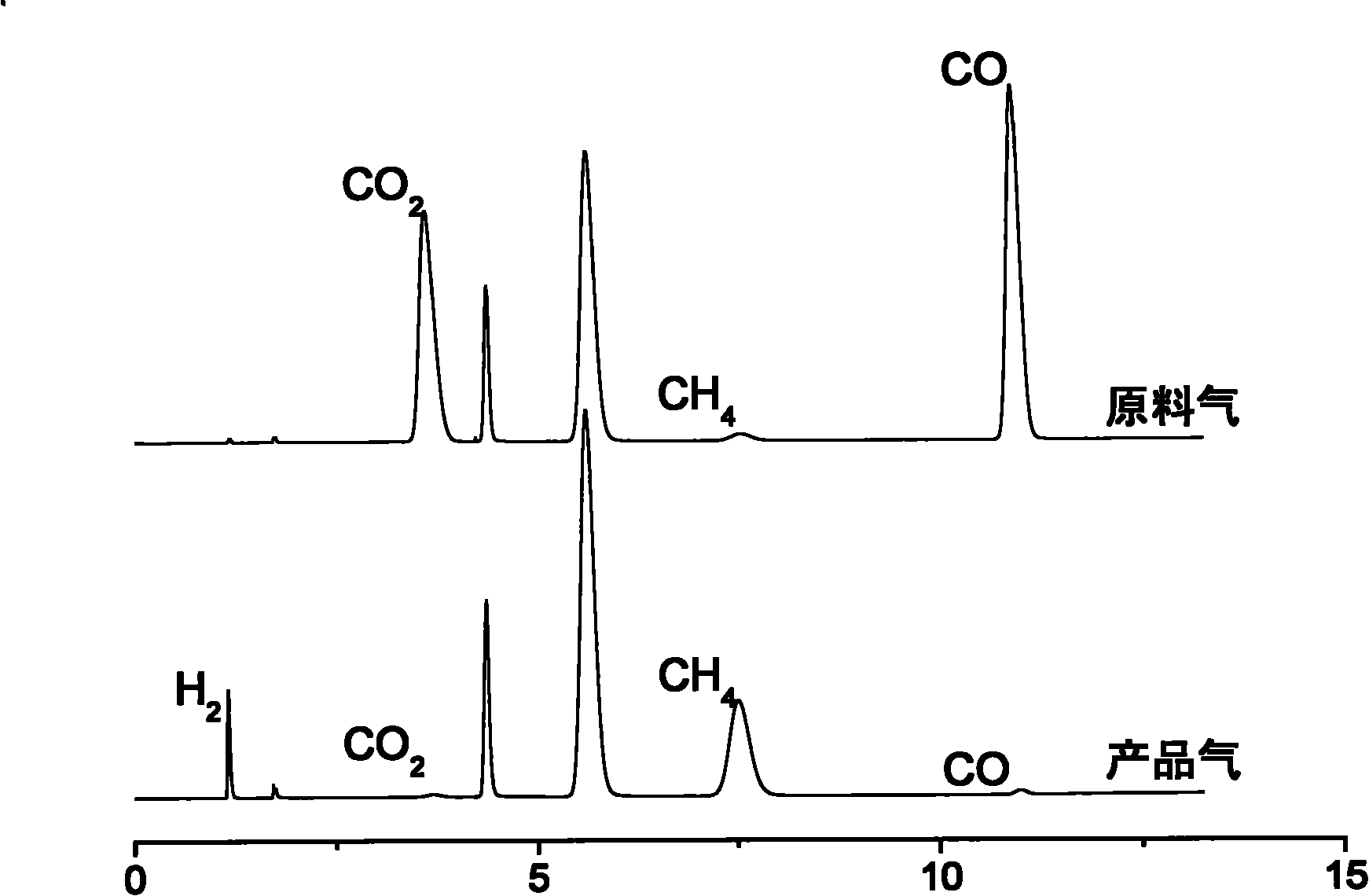
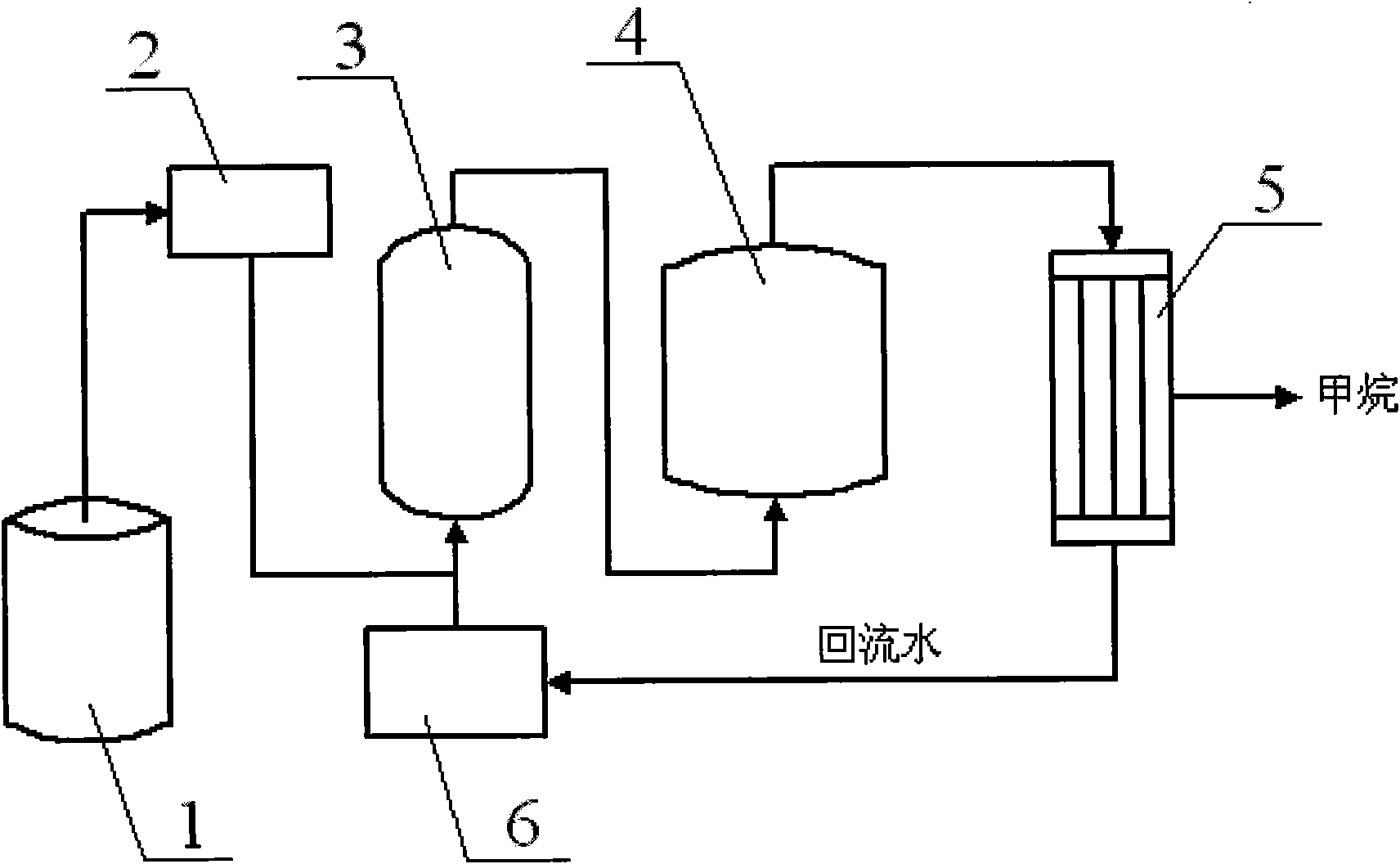
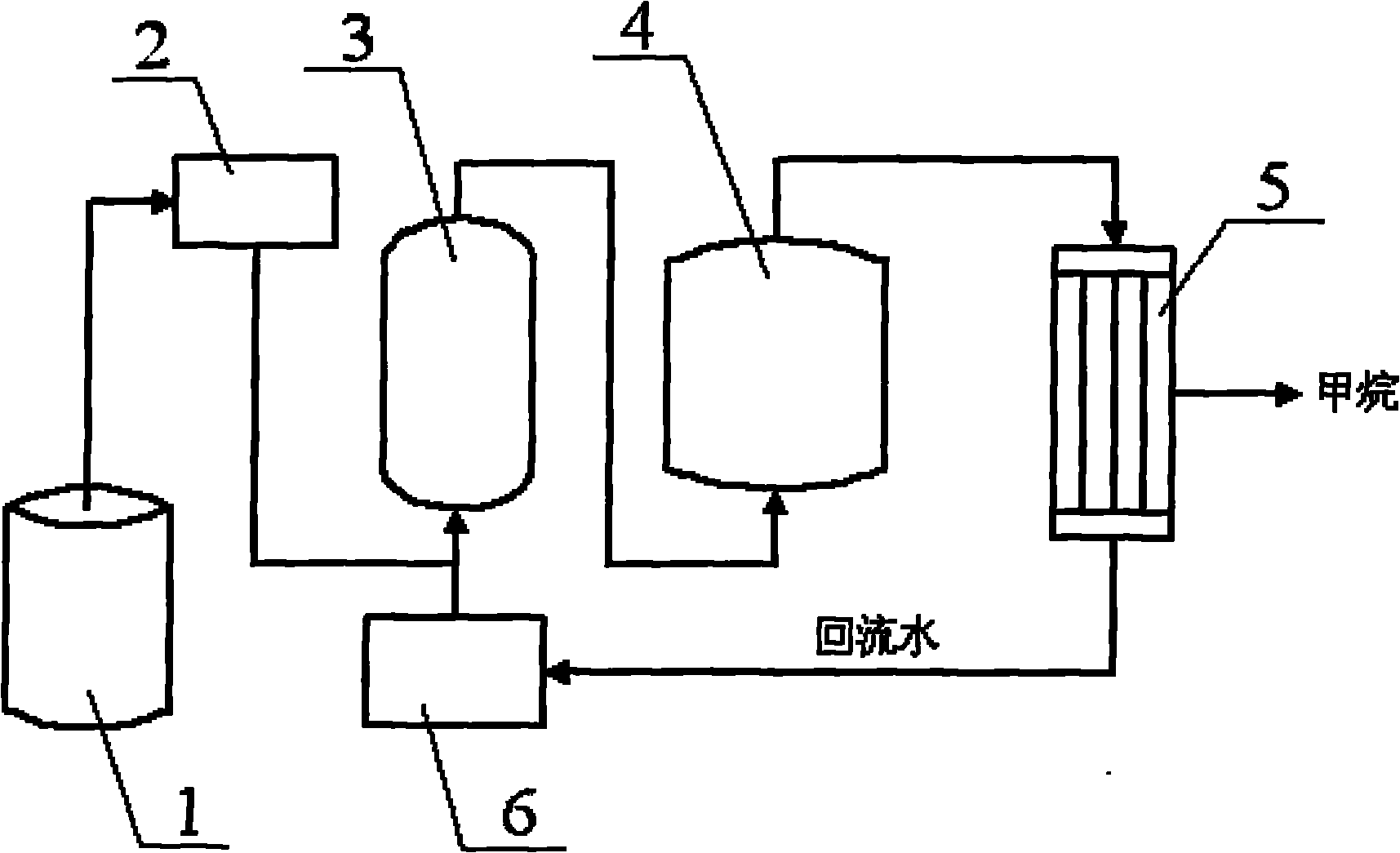
[0025] Coal-fired power plants use appropriate hydrothermal reactors according to requirements, and their industrial production can adopt the process flow shown in the attached figure. The reaction conditions are controlled as follows: the amount of hydrogen added is CO 2 5 times (in molar ratio), the reaction temperature is 300° C., the reaction pressure is 10 MPa, the ratio of catalyst addition to feed gas i...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The average operating efficiency of coal-fired industrial boilers is only 60% to 65%. The annual emission of soot is about 2 million tons, sulfur dioxide is about 7 million tons, and carbon dioxide is nearly 1 billion tons. It is the second largest source of soot pollution after thermal power plants. . In response to this situation, hydrothermal reaction devices can be installed in each coal-fired plant to collect and process the exhaust gas emitted by it.
[0029] Coal-fired industrial boilers use appropriate hydrothermal reactors according to their specifications, and their industrial production can adopt the process flow shown in the attached figure. The reaction conditions are controlled as follows: the amount of hydrogen added is CO 2 5 times (in molar ratio), the reaction temperature is 350° C., the reaction pressure is 10 MPa, the ratio of catalyst addition to feed gas is 1:1 (molar ratio), and the reaction time is 60 minutes.
[0030] Through this reaction, CO...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Emissions of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide from waste incineration plants are increasing, and it has been calculated that most incinerators produce more carbon dioxide per year than thermal power plants. For the large amount of carbon dioxide contained in the flue gas, a hydrothermal treatment equipment can be built on site to collect the discharged waste gas and use it as raw material for hydrothermal conversion. Moreover, the large amount of heat energy brought by incineration can fully provide the temperature required for the reaction, which further reduces the operating cost of hydrothermal treatment of carbon dioxide.
[0033] The waste incineration plant adopts suitable hydrothermal reactors according to the requirements, and its industrial production can adopt the process flow shown in the attached figure. The reaction conditions are controlled as follows: the amount of hydrogen added is CO 2 10 times (in molar ratio), the reaction temperature is 200°C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com