Screening and identification method of alcohol dehydrogenase based on NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Diuncleotide) (P) (Phosphate) H (Hydrogen) fluorescence
A technology of alcohol dehydrogenase and identification method, which is applied in the field of screening and identification of alcohol dehydrogenase based on NAD(P)H fluorescence, can solve the problems of high reagent toxicity, cumbersome process, and many reagents, and achieve the interference factors of the reaction Less, simple operation process, high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Excitation and emission wavelengths of coenzymes NADH and NADPH
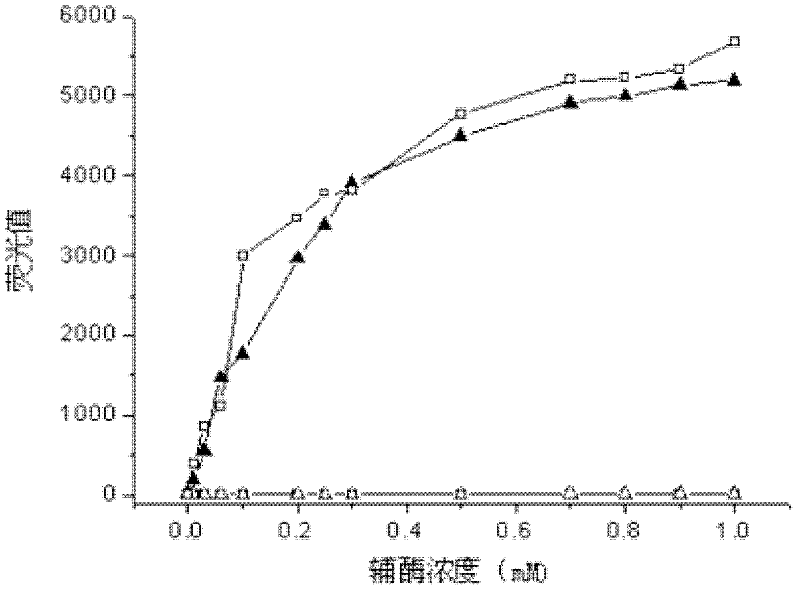
[0033] The reduced coenzyme NADH and NADPH, the oxidized coenzyme NAD + and NADP + Prepare aqueous solutions with different concentration gradients from 0.01 to 1mM respectively, take 300μl and put them into a 96-well microplate, measure the fluorescence intensity at the excitation wavelength of 360nm and emission wavelength of 460nm, the results are shown in figure 1 . It can be seen from the figure that at the excitation wavelength of 360nm and the emission wavelength of 460nm, the reduced coenzyme has fluorescence, while the oxidized coenzyme does not emit fluorescence.
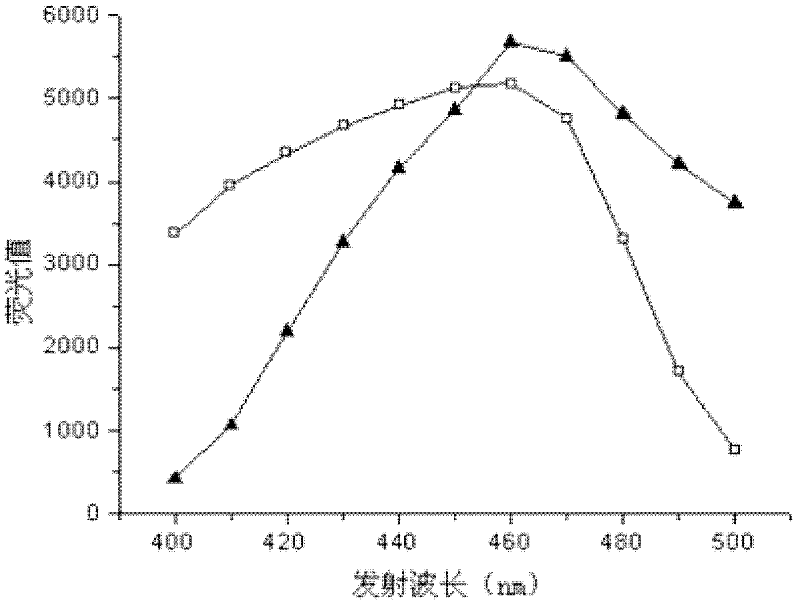
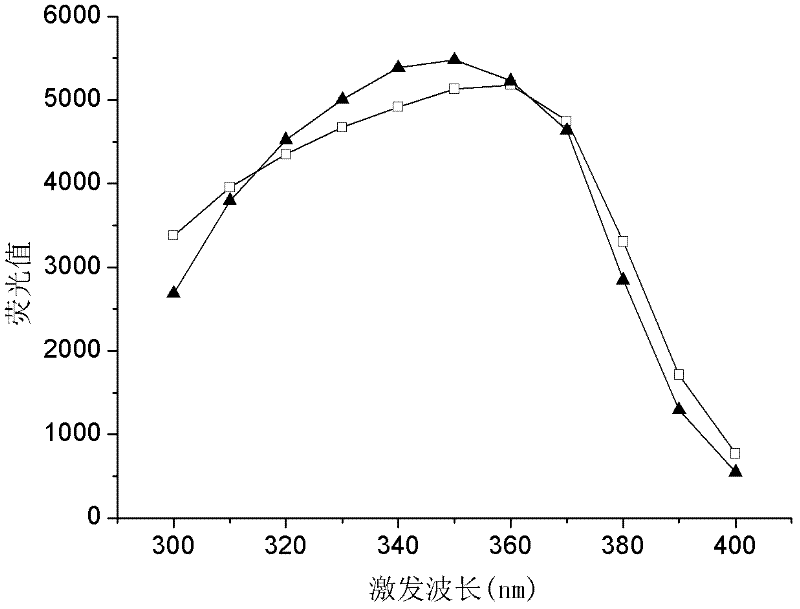
[0034] Prepare 0.5mM NADH and NADPH aqueous solution, set the excitation wavelength to 360nm, measure the fluorescence value in the emission spectrum range of 400-500nm, and obtain the fluorescence spectrum diagram, see figure 2 . Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the optimum emission wavelength of NADH and NADP...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Relationship between temperature, pH, organic solvent, substrate, etc. and NAD(P)H fluorescence
[0036] (1) The relationship between temperature and NAD(P)H fluorescence
[0037] Prepare 0.5mM NAD(P)H aqueous solution, take 300μl and fill it into a 96-well microwell plate, place it overnight in a temperature gradient of 4-70°C for 16h, and seal it with plastic wrap during the period to prevent volatilization from affecting the fluorescence value. The fluorescence values were measured at the optimum wavelength, and the results are shown in Figure 4 . Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the temperature has basically no effect on the fluorescence value of NADH within this range; the autofluorescence of NADPH is weakened at high temperature, but according to Example 1 figure 1 As a result of the analysis, its fluorescence was still significant.
[0038] (2) The relationship between pH and NAD(P)H fluorescence
[0039] Prepare 0.5mM NAD(P)H solution wit...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Using 1-phenylethanol as a substrate for rapid screening of alcohol dehydrogenase-producing bacteria
[0046] Take 150 μl of 1-phenylethanol and spread it on the LB plate, and absorb it for a while, which is the enrichment plate. Weigh 0.5 grams of soil samples (from Hubei, Inner Mongolia, Shandong, etc.), place them in a 2ml centrifuge tube (containing 1ml of sterile water), dilute 1000 times with sterile water, and take 100μl to spread evenly on the enrichment plate. Incubate at 30°C for 48h. Then, colonies with different shapes on the plate were selected and inoculated on the LB slant, and cultured at 30°C for 24h. Take 2 inoculum loops of bacteria from the obtained slant and put them in 60 μl of non-sterile water, and shake to make a bacterial suspension for primary screening. The total volume of the reaction system is 300 μl, including glycine-NaOH buffer solution (total concentration 50 mM) at pH 10.0, 0.5% (V / V) swirling 1-phenylethanol, 1.0 mM NAD ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com