Resistant starch content measuring method for rice
A determination method and technology of resistant starch, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve problems affecting the accuracy of determination results, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
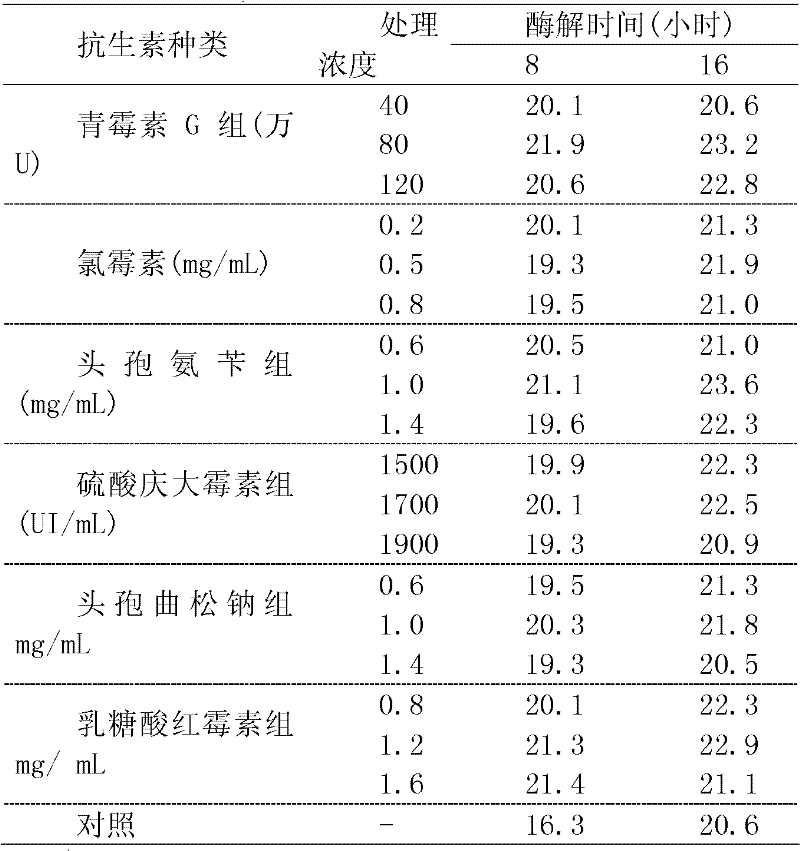
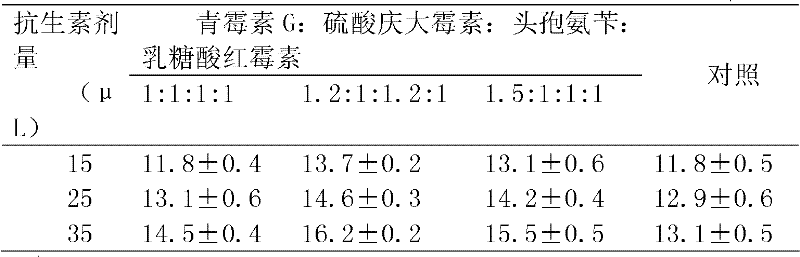
[0011] A. The effect of antibiotics on the hydrolysis of slow-digesting starch. It can be seen from Table 1 that in the hydrolysis system of α-amylase at 37°C, the glucose concentration in the hydrolyzate of the treatment and the control group showed an increasing trend with the prolongation of the hydrolysis time. The response time of the treatment group was higher than 8 hours in 16 hours. Under the same hydrolysis time, the glucose content in the hydrolyzate of the antibiotic group was significantly higher than that of the control group. At the same time, it was found that after 16 hours of hydrolysis reaction, the glucose content of the hydrolyzed solution of the cephalexin group was the highest, followed by the penicillin G group, the third highest was the erythromycin lactobionate group, and the glucose content of the gentamicin sulfate group was the lowest. In addition, different doses of antibiotic concentrations have significant differences in the glucose content of ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Technical scheme of the present invention is:
[0024] A. There are 6 treatments and controls in the experiment. The test set penicillin group (diluted to 0.48mg / mL), gentamicin sulfate group (diluted to 1600UI / mL), cephalexin group (diluted to 1.0mg / mL), erythromycin lactobionate group (diluted to 0.1mg / mL), ceftriaxone sodium group (diluted to 1.0mg / mL), chloramphenicol (diluted to 0.5mg / mL) group with 6 treatments and distilled water as a control. Accurately weigh 0.1000g of rice flour (Jiangtangdao No. 1) passed through a 100-mesh sieve, add 40mg of α-amylase (Sigma A-3176), and then add 4mL of sodium maleate buffer solution (0.1mol / L, pH6.0) , add 10 μL 3300UI / mL amyloglucosidase (AGM) to treat it into 4 mL of starch hydrolysis mixture, add 35 μL of 6 kinds of antibiotics to the reaction system, and add 35 μL of distilled water to the starch hydrolysis mixture as a control. Glucose content was detected at 37°C at the 8th hour and 16th hour of enzymatic digestion...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com