Method and implementation device for driving nonmetal flayer with laser
A laser-driven, non-metallic technology, used in laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient space debris ground simulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
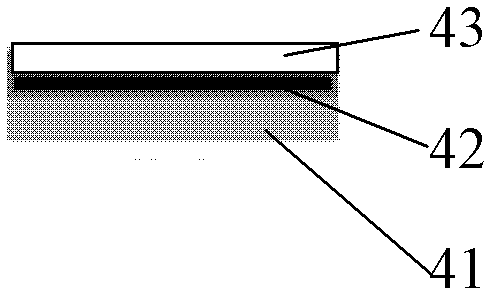
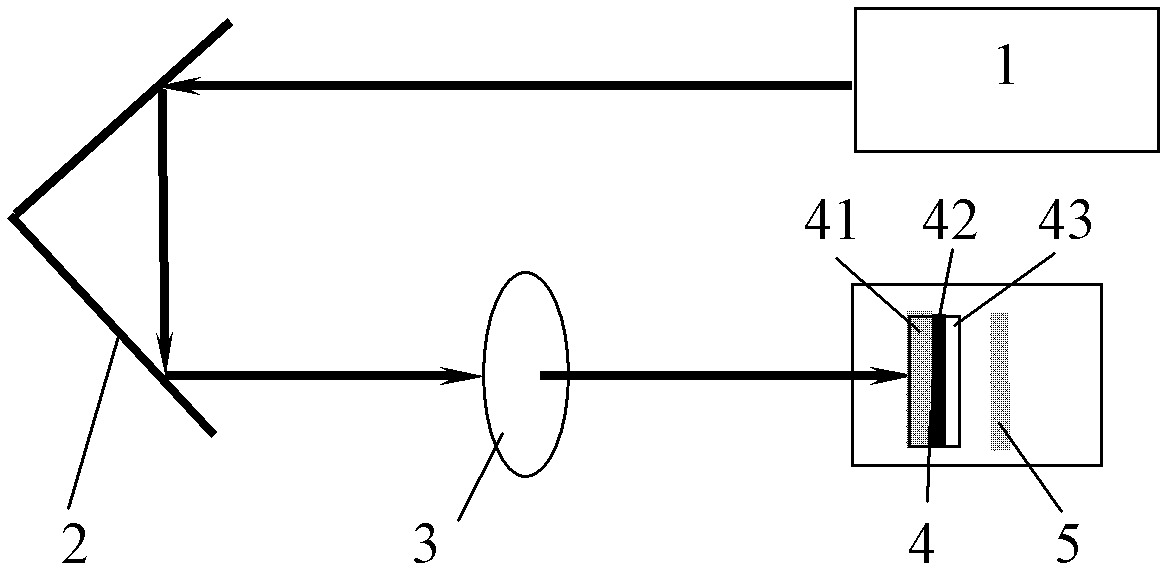
[0028] Preparation of composite flyer target 4:
[0029] First, a silica sol is prepared. Using orthoethyl silicate (TEOS) and γ-(methylpropanoyloxy)propyltrimethoxysilane (MEMO) as precursors, absolute ethanol (EtOH) as solvent, hydrochloric acid (HCl) as catalyst, N , N-dimethylformamide is a film-forming accelerator (DCCA). Mix TEOS, MEMO and EtOH evenly, and after 5 min, add H 2 The mixture of O and HCl is slowly added dropwise, and an appropriate amount of DCCA is added at the same time. The molar ratio of the components in the final solution is TEOS / MEMO / EtOH / H 2 O / HCl is 1 / (0-1.0) / 16 / 6 / 0.03. After the addition, fully stir at room temperature for 40 minutes to obtain a silica sol, seal the obtained sol and naturally age it for 24 hours before coating. Secondly, the quartz glass with a diameter of 40 mm and a thickness of 3 mm was ultrasonically cleaned with deionized water and absolute ethanol for 10 minutes to remove residual organic pollutants on the surface of the...
experiment example 2
[0034] The difference between Experimental Example 2 and Experimental Example 1 is that the laser energy is 300mJ, the trigger frequency is 1Hz, and the laser pulse width is 6ns.
experiment example 3
[0036] The difference between this experimental example 3 and experimental example 1 is that a titanium plate is used as the impact target, the pulsed laser is incident on the quartz glass / carbon layer / silicon dioxide film layer, and the transitional carbon layer on the surface of the quartz glass is ablated and then evaporated instantly. , Gasification and ionization to form plasma, the plasma breaks the silicon dioxide film and is driven by high-speed impact on the titanium plate to form damage. In the experiment, the laser energy is 360mJ, the trigger mode is single trigger, and the laser pulse width is 6ns.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com