Particle-containing cell aggregate
A technology of aggregates and particles, applied in the field of cell aggregates, can solve the problems of reduced production capacity of useful substances and weakened cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A stirring propeller blade made of Teflon (registered trademark) was attached to a fixed stirring motor (manufactured by Shinto Scientific Co., Ltd., Sany type motor), and it was fixed together with a 1000 ml round bottom flask. 375ml of olive oil was added to the flask, and 10ml of an alkali-treated gelatin aqueous solution (concentration about 10%) with an isoelectric point of 4.9 was added dropwise while stirring at 37°C and 420rpm to prepare a W / O emulsion. After 10 minutes of stirring, the flask was cooled to 4°C and stirred for 30 minutes. After cooling, 100 ml of acetone was added thereto, stirred for 1 hour, and gelatin hydrogel particles were recovered by centrifugation. The recovered hydrogel particles were washed with acetone and further washed with 2-propanol to obtain uncrosslinked gelatin hydrogel particles. The hydrogel particles were dried and stored at 4°C.
[0040] 500 mg of dried uncrosslinked gelatin hydrogel particles were suspended in 100 ml of a...
Embodiment 2
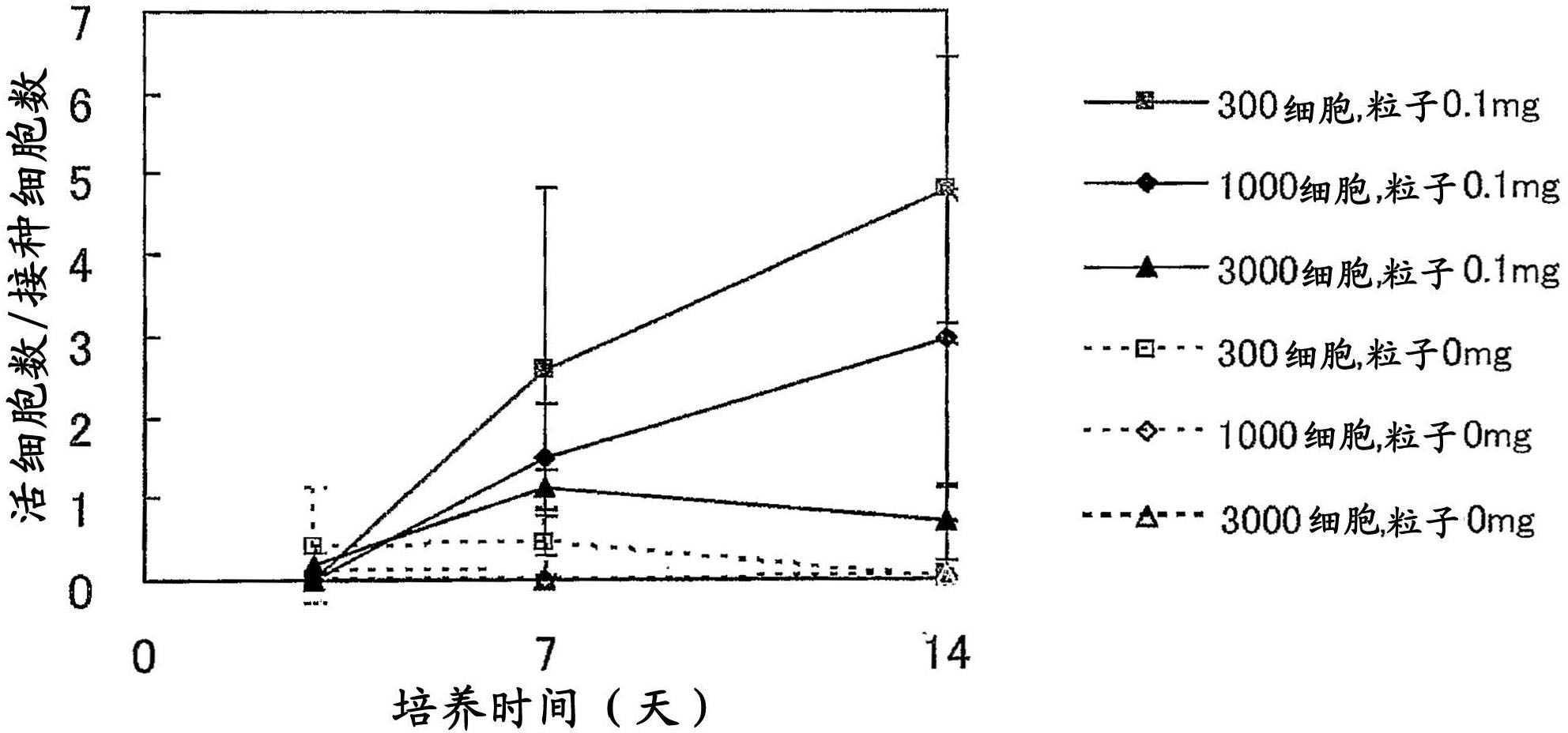
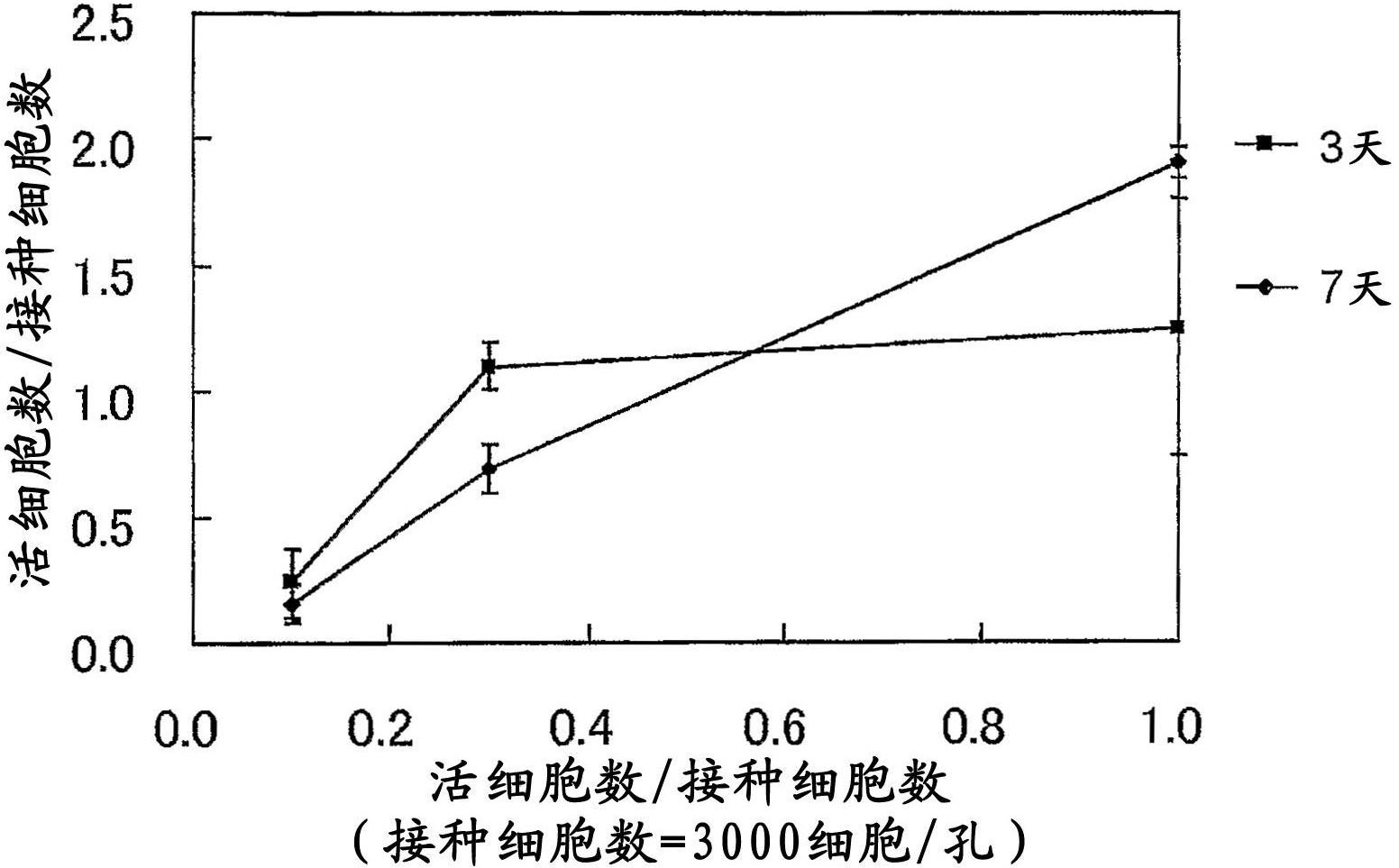
[0044] Cell aggregates were produced in the same manner while changing the ratio of MSCs to the number of particles. As a result, when the number of particles / number of cells was 0.3 or more, the number of living cells increased with the culture time ( figure 2 ). That is, as the particle / cell ratio increases, the cell viability increases. This result is considered to be because the presence of the particles in the cell aggregate improves the diffusion of substances inside and outside the aggregate, thereby improving the nutrition of the cells, the supply of oxygen, and the excretion of waste.
Embodiment 3
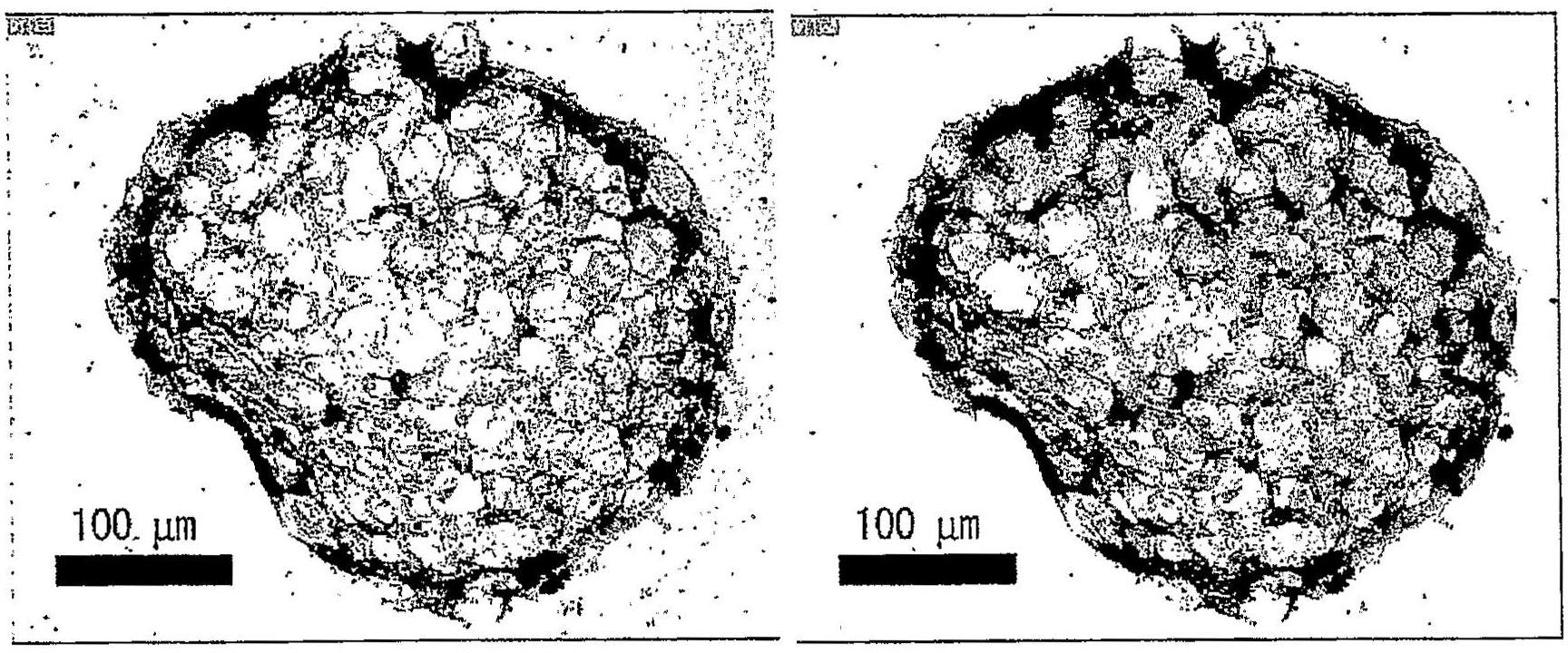
[0046] Similar to Example 2, particle-containing MSC aggregates having a particle number / cell number ratio of 0.5 were produced, and the infiltration of BrdU into the aggregates was studied. On day 6 of cell culture, BrdU was added to the culture medium, and cell aggregates were collected on day 7 to make cryosections. Anti-BrdU antibodies were used to immunostain the largest section through the center of the aggregate. The stained sites indicated that the infiltration of BrdU into the nucleus was high and the cells were proliferating. The results confirmed the infiltration of BrdU into the cells on the surface and inside of the aggregate, indicating that the cells present inside were also proliferating ( image 3 ). In contrast, when cell aggregates were formed using MSC aggregates without particles and cultured under the same conditions, and the infiltration of BruU was studied, the infiltration was confirmed in cells near the surface of the aggregate, but not in the inner...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com