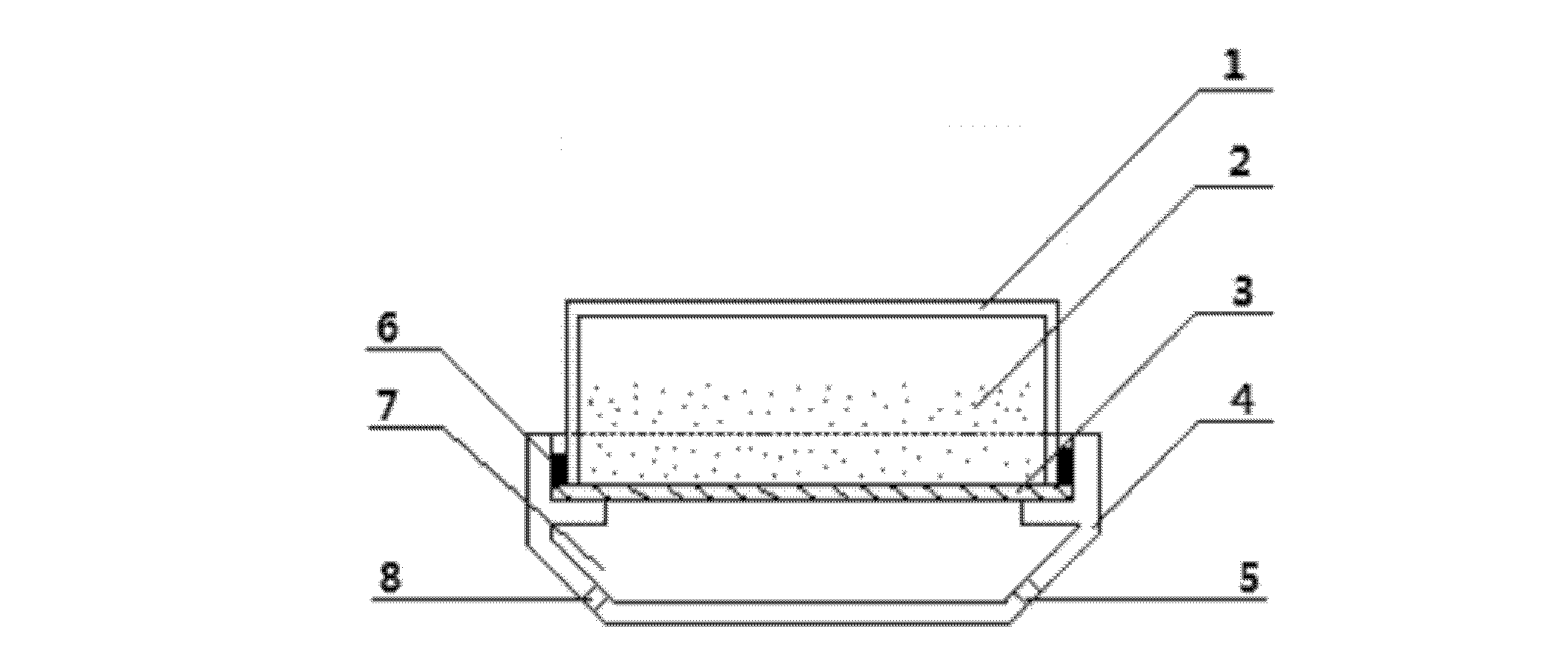
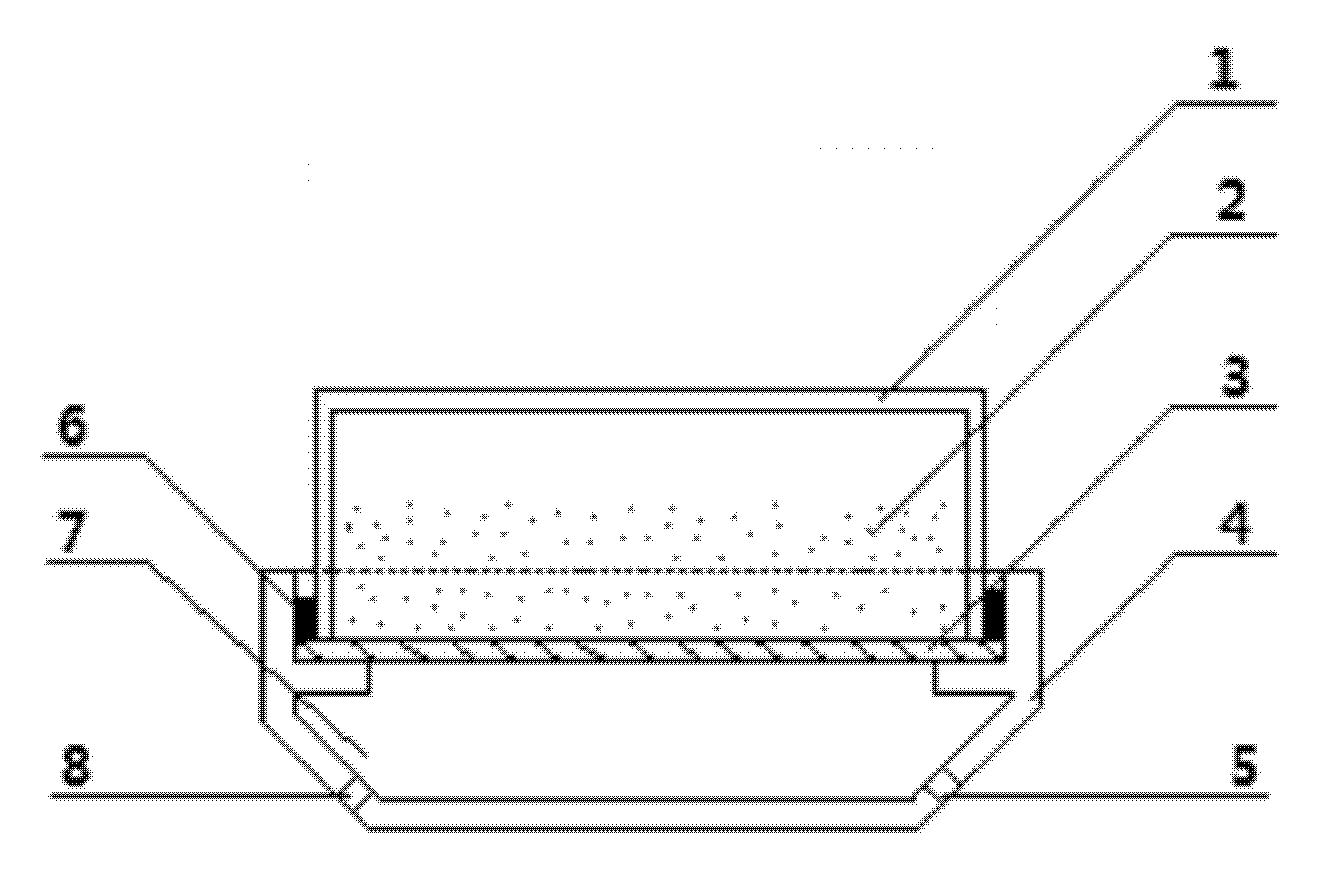
Method and device for preparing functional nanoparticle/bacterial cellulose composite membranes
A technology of bacterial cellulose and functional nanometers, applied in fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of weak adsorption force of functional nanoparticles, and achieve the effects of low cost, good adsorption and short cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1. Prepare seed medium for activating Acetobacter. The composition of the seed medium is: glucose 7.0w / v%, peptone 0.6w / v%, citric acid monohydrate 0.3w / v%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.2w / v%, sodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate 0.3w / v%, yeast extract 0.5w / v%. Control the pH value of the seed medium to 7.0, and sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes.
[0040] 2. Take out the acetogenes stored in the freezer. Heat the inoculation loop on the alcohol lamp, extend the inoculation loop into the inclined surface of the test tube, hook one loop of the strain and insert it into the Erlenmeyer flask containing the seed medium as described in step 1. Seal the Erlenmeyer flask into which the strain was inserted with gauze, put it into a shaker for activation at 30° C. for 24 hours, and the shaker rotates at 160 rpm.
[0041] 3. Prepare a fermentation medium containing iron ferric oxide nanoparticles in a culture vessel for cultivating a functional nanoparticle / bacterial ce...
Embodiment 2
[0046] 1. Prepare seed medium for activating Bacillus aceti. The composition of the seed medium is: glucose 5.0w / v%, peptone 0.4w / v%, citric acid monohydrate 0.1w / v%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.1w / v%, sodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate 0.1w / v%, yeast extract 0.4w / v%. Control the pH of the seed medium to 6.0, and sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes.
[0047] 2. Take out the acetobacteria stored in the freezer. Heat the inoculation loop on the alcohol lamp, extend the inoculation loop into the inclined surface of the test tube, hook one loop of the strain and insert it into the Erlenmeyer flask containing the seed medium as described in step 1. Seal the Erlenmeyer flask into which the strain was inserted with gauze, put it into a shaker for activation at 30° C. for 24 hours, and the shaker rotates at 160 rpm.
[0048] 3. Prepare a fermentation medium containing temperature-induced reversible discoloration microcapsules with gum arabic and gelatin as the wall materia...
Embodiment 3
[0053] 1. According to the cultivation process described in the doctoral dissertation "Preparation and Structural Properties of Bacterial Cellulose / Carbon Nanotube Composite Materials", the seed medium and fermentation medium were prepared for the activation of Acetobacter xylinum and the bacterial fiber of Acetobacter xylinum respectively. prime cultivation.
[0054] 2. In the step of preparing the fermentation medium, add nano-silver particles to the fermentation medium, the particle diameter of which is 60-120nm, and the added mass accounts for 5.0wt% of the total mass of the fermentation medium.
[0055] 3. During cultivation, seal the culture container with an oxygen-permeable silicone membrane and place it upside down on the airtight oxygen chamber, and seal the joint between the culture container and the airtight oxygen chamber with paraffin. After standing for 1 h, oxygen was introduced into the oxygen chamber. Static culture was carried out at 30°C for 14 days.
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturation susceptibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com