Application of GmPGIP3 protein and coding gene thereof to cultivation of plant for resisting root rot and full rot
A technique for coding genes and transgenic plants, which is applied in the field of application of GmPGIP3 protein and its coding genes in cultivating plants resistant to root rot and take-all disease, and can solve the problems of unreliable selection of single plants, difficulties in identification and selection of resistance, Problems such as the lack of germplasm resources of wheat with high resistance to root rot
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1. Obtaining GmPGIP3 Gene Transformed Plant
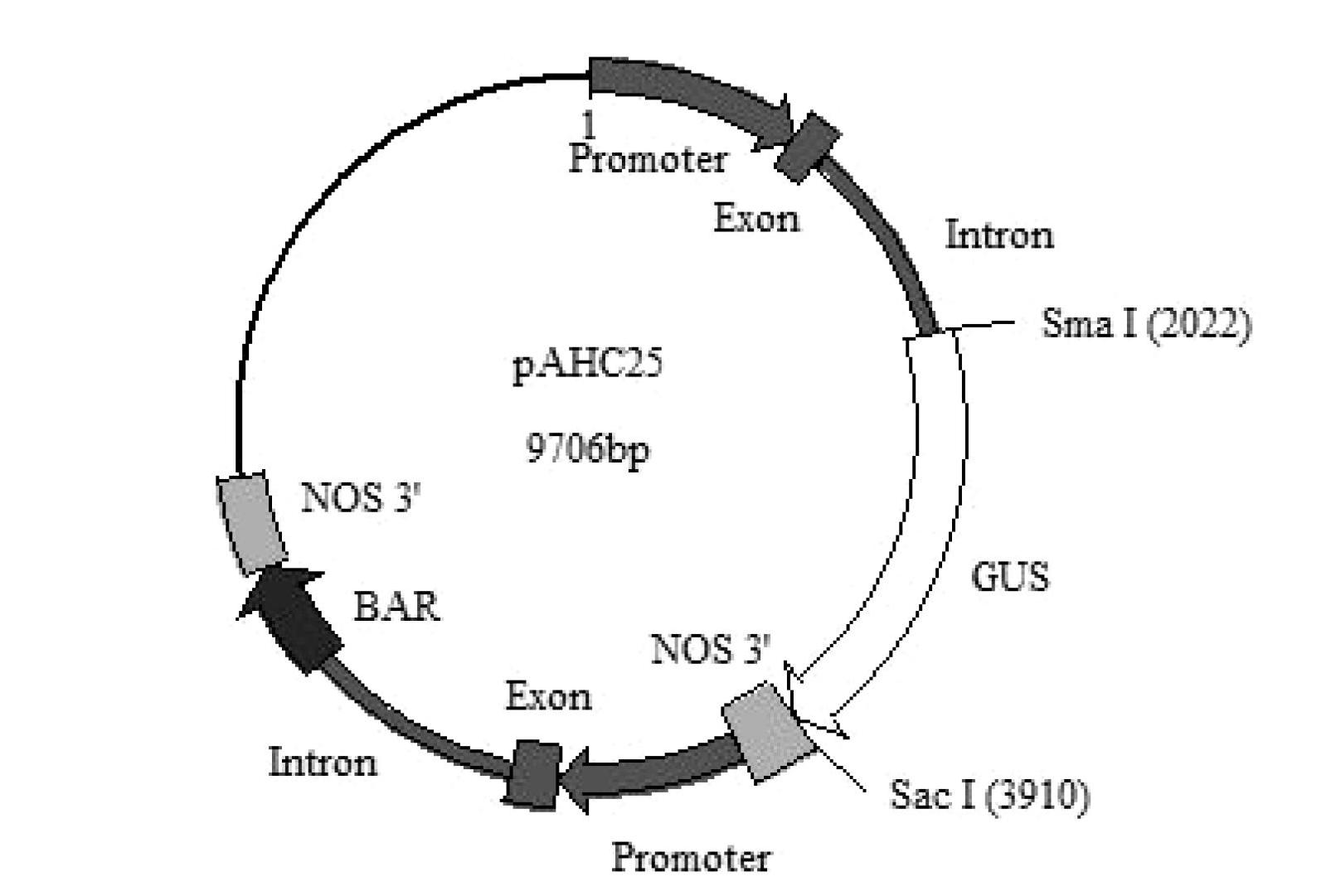
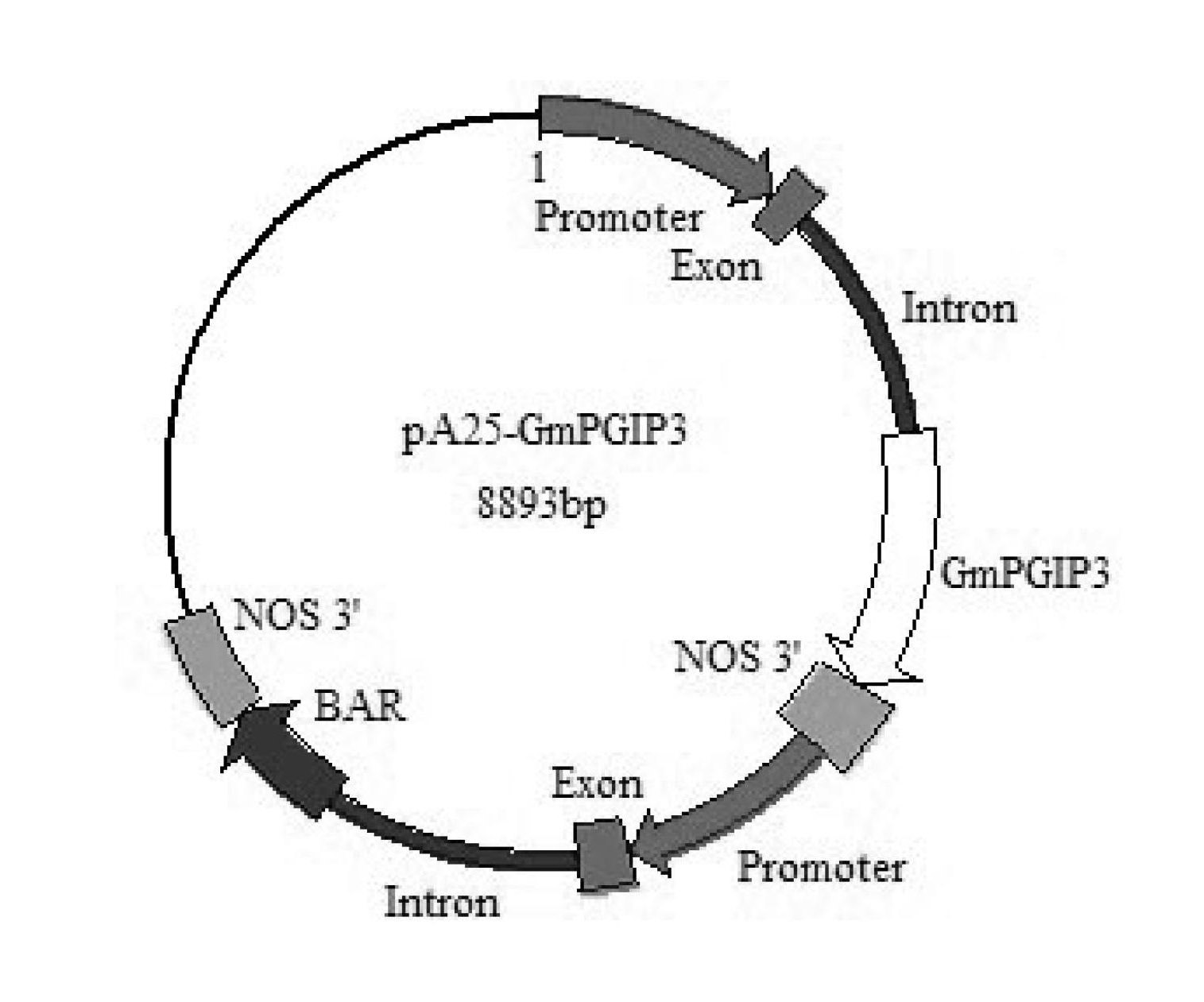
[0030] 1. Construction of recombinant expression vector
[0031] 1. Design a pair of primers based on the cDNA sequence of GmPGIP3 gene as follows:
[0032] GmPGIP3-F: 5′-ATGTCAAAGTTAAGCATTCT-3′;
[0033] GmPGIP3-R: 5'-TTAAGTGCATGGTGGAAGAG-3'.
[0034] 2. Extract total RNA from the leaves of Zhonghuang 13 in soybean variety and reverse transcribed into cDNA.
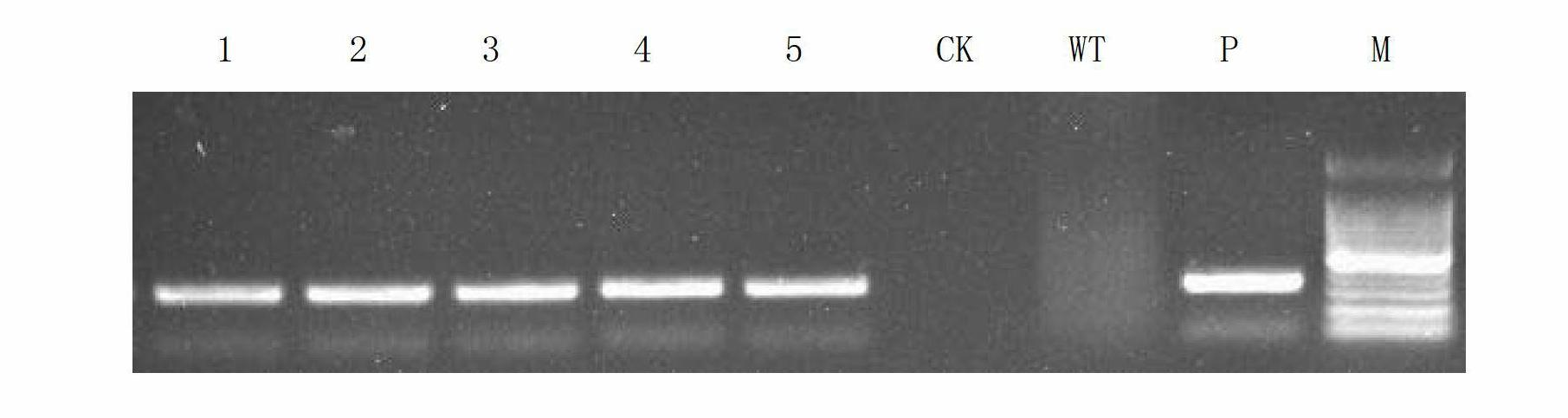
[0035] 3. Using the cDNA of step 2 as a template, a primer pair consisting of GmPGIP3-F and GmPGIP3-R is used for PCR amplification to obtain a PCR amplification product. The sequencing result of the PCR amplified product is shown in sequence 2 of the sequence table.
[0036] 4. Using the PCR amplified product of step 3 as a template, a primer pair consisting of GmPGIP3-SMAF and GmPGIP3-SACR is used for PCR amplification to obtain a PCR amplified product.
[0037] GmPGIP3-SMAF:5′-AT CCCGGG ATGTCAAAGTTAAGCATTCT-3';
[0038] GmPGIP3-SACR:5′-GT GAGCTC TTAAGTGCATGGTGGAAGAG...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Example 2: Identification of Root Rot Resistance of Transgenic Plants with GmPGIP3 Gene
[0085] The T of the GmPGIP3 transgenic wheat obtained in Example 1 2 Generation plants (10 plants per line), T of the GmPGIP3 transgenic wheat obtained in Example 1 1 Generation plants (20 plants per line), the T of the empty carrier wheat obtained in Example 1 2 Generation plants (10 plants per line), the empty carrier wheat obtained in Example 1 T 1 Progeny plants (20 plants per line) and Yangmai 18 (WT) (20 plants) were identified as follows:
[0086] During the wheat tillering period, insert a toothpick full of wheat root rot pathogenic bacteria and a grain of wheat kernel full of wheat root rot pathogenic bacteria into the 1-2 leaf sheaths at the base of the wheat. Try to keep the leaf sheath in a natural state of holding stems; spray water for 5-7 days after inoculation, and investigate the condition during the wax maturity period.
[0087] According to the 0-4 grade standard, the d...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Example 3. Identification of resistance to total erosion of GmPGIP3 transgenic plants
[0100] The T of the GmPGIP3 transgenic wheat obtained in Example 1 2 Seed generation (20 grains per plant), T of the empty carrier wheat obtained in Example 1 2 Generation seeds (20 seeds per plant) and Yangmai 18 (WT) seeds (20 seeds) were identified as follows:
[0101] After sterilizing and accelerating the germination of the seeds, they are moved to the flowerpots that have been put into the wheat rot disease pathogenic bacteria cake (one flowerpot for each seed, and the substrate is a mixture of 1 mass of river sand and 2 mass of nutrient soil), After cultivating for 3 weeks, take pictures and identify the following indicators: measure the total root length and black (diseased) root length of a single plant, calculate the percentage of black root area to the total root area (percentage of diseased roots), and make the total erosion serious The degree is divided into five levels (0-4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com