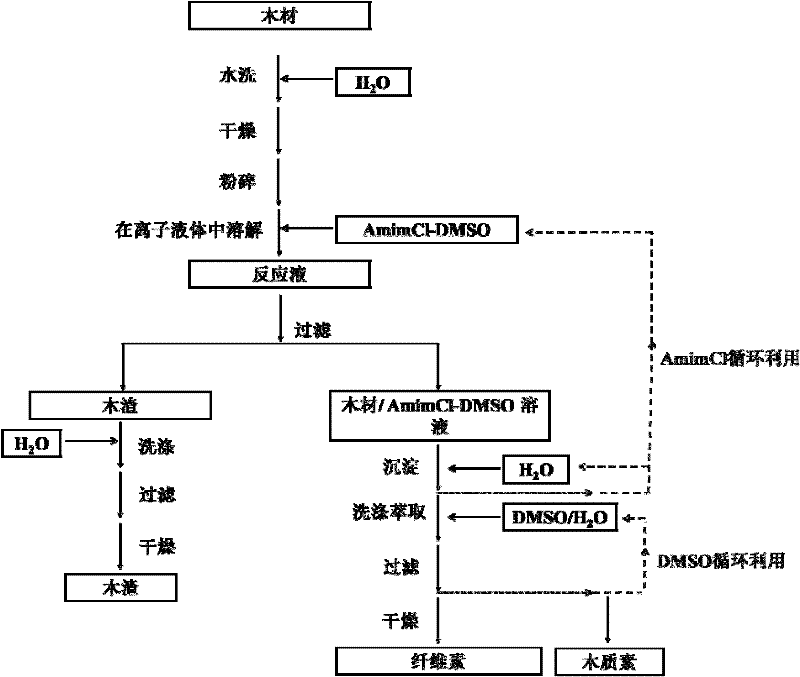
Method for separating cellulose and lignin from plant fiber raw material by utilizing ion liquid
An ionic liquid and plant fiber technology, which is applied in fiber raw material processing, textile and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of low solubility of plant raw materials, inability to obtain effects, low extraction rate of lignin and cellulose, etc., and achieve strong industrial application prospects. , The effect of low production cost and shortened processing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
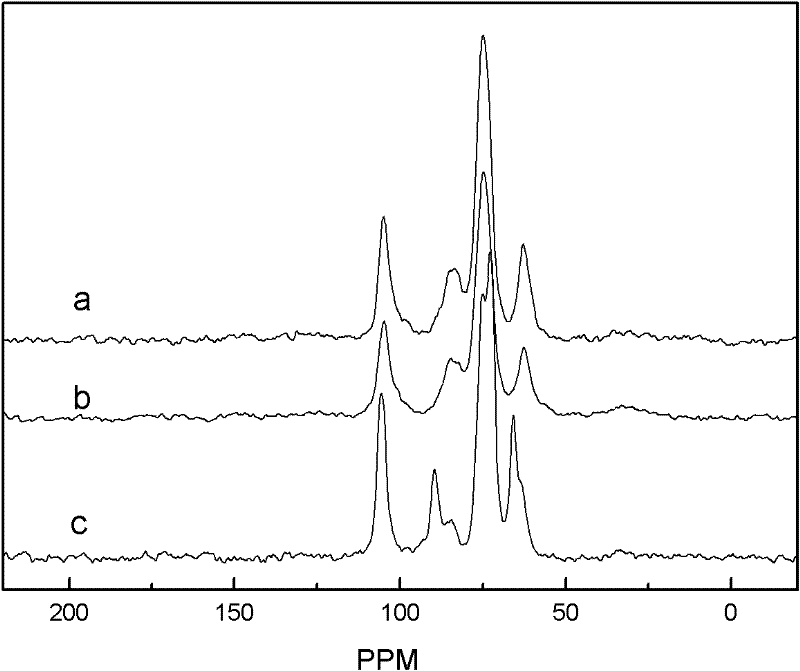
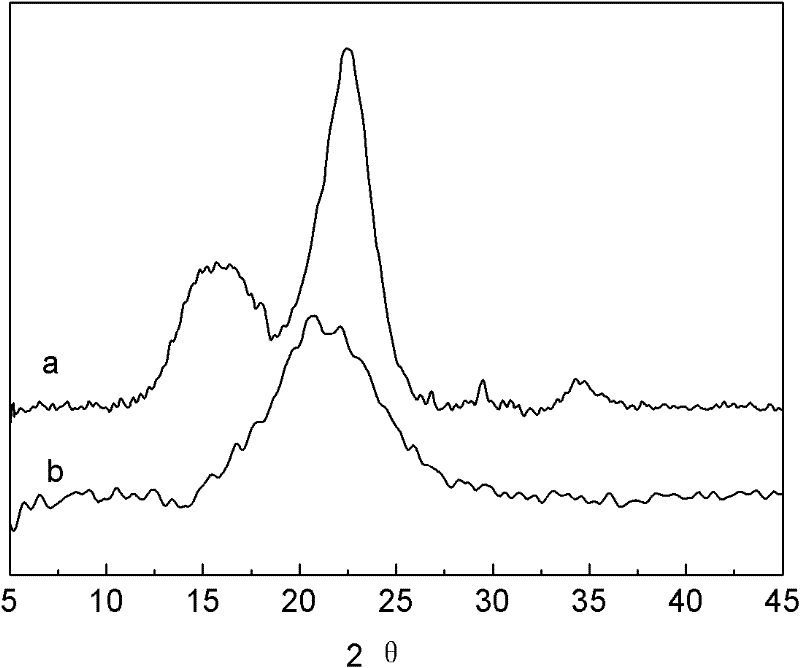
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Weigh about 0.5 g of pine sawdust, 50.0 g of a mixed solution of ionic liquid 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (AmimCl) and DMSO (mass ratio 6:1), put them into a round bottom flask, and heat with microwave to 110°C with vigorous mechanical stirring for 2 hours. After the reaction is finished, use a 300-mesh stainless steel filter to filter and separate, and add water to the filtrate to separate out cellulose and lignin. The mixture was washed 8 times with DMSO / water solution (1:1v), filtered and separated with 200-mesh nylon filter cloth to obtain pine wood cellulose and washing liquid containing lignin. Put pine wood cellulose into a vacuum drying oven and dry at 60°C for 24 hours to obtain cellulose products; recover DMSO / water from the washing liquid by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure to obtain DMSO / water, and separate lignin products at the same time. After testing, the dissolution rate of raw materials in ionic liquid is 36%, the purity of cellulose...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Weigh about 0.5 g of pine sawdust, 50.0 g of a mixed solution of ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (EmimAc) and DMSO (mass ratio 9:1), put them into a round-bottomed flask, and microwave to 100°C with vigorous mechanical stirring for 2 hours. After the reaction is over, use a 400-mesh stainless steel filter screen to filter and separate. The post-treatment of the reaction mixture and the recovery of the ionic liquid are basically the same as in Example 1. The nylon filter cloth is 300 mesh. After testing, the dissolution rate of the raw material in the ionic liquid is 35%, the cellulose purity in the extract is 83%, the cellulose extraction rate can reach 59%, and the lignin purity is 80%.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Weigh about 1.5 g of pine sawdust, 50.0 g of a mixed solution (mass ratio 5:1) of ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BmimCl) and DMSO, put them into a round bottom flask, and heat to 100 ° C, strong mechanical stirring for 3h. After the reaction, use a 280-mesh stainless steel filter to filter and separate. The post-treatment of the reaction mixture and the recovery of the ionic liquid are basically the same as in Example 1. The nylon filter cloth is 280 mesh. After testing, the dissolution rate of the raw material in the ionic liquid is The purity of cellulose in the extract is 85%, the extraction rate of cellulose can reach 62%, and the purity of lignin is 80%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com