Edible fungus compost, production method thereof and edible fungus culture process
A production process and edible fungus technology, applied in the field of edible fungi cultivation material and its production process, can solve the problems of unfavorable sustainable development of edible fungus industry, slow decomposition of cellulose and lignin, deterioration of edible fungi reproduction environment, etc., and achieve good promotion Application potential, high biotransformation rate, and improved economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
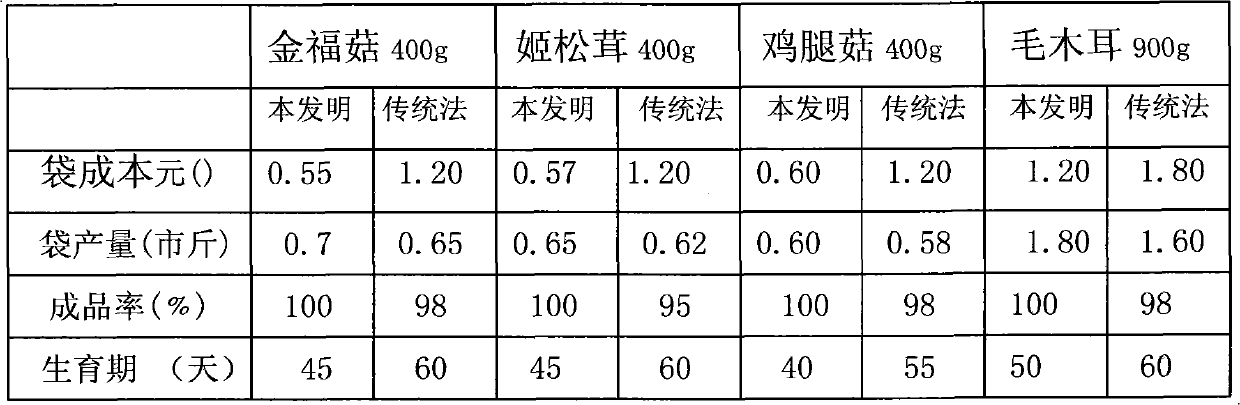
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] A cultivation material for edible fungi, which comprises 80 parts of leftover waste (bacteria chaff) after harvesting edible fungi, 5 parts of cotton seed hulls, 5 parts of bran, 3 parts of corn flour, 1.2 parts of gypsum powder, 4 parts of quicklime, 5 parts calcium peroxide 1.5. 0.3 parts of Zhumectin.
Embodiment 2
[0054] A cultivation material for edible fungi, which comprises 75 parts of leftover waste (bacteria chaff) after harvesting edible fungi, 10 parts of cottonseed hulls, 8 parts of bran, 3.5 parts of corn flour, 1.3 parts of gypsum powder, 1 part of quicklime, 0.8 part of calcium peroxide. 0.4 parts of Zhumectin.
Embodiment 3
[0056] A cultivation material for edible fungi, which comprises 70 parts of leftover waste (bacteria chaff) after harvesting edible fungi, 15 parts of cottonseed hulls, 7 parts of bran, 3 parts of corn flour, 1 part of gypsum powder, 3 parts of quicklime, 0.5 part of calcium peroxide. 0.5 parts of Zhumectin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com