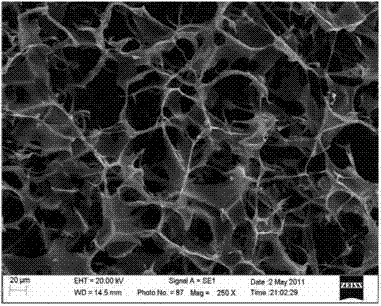
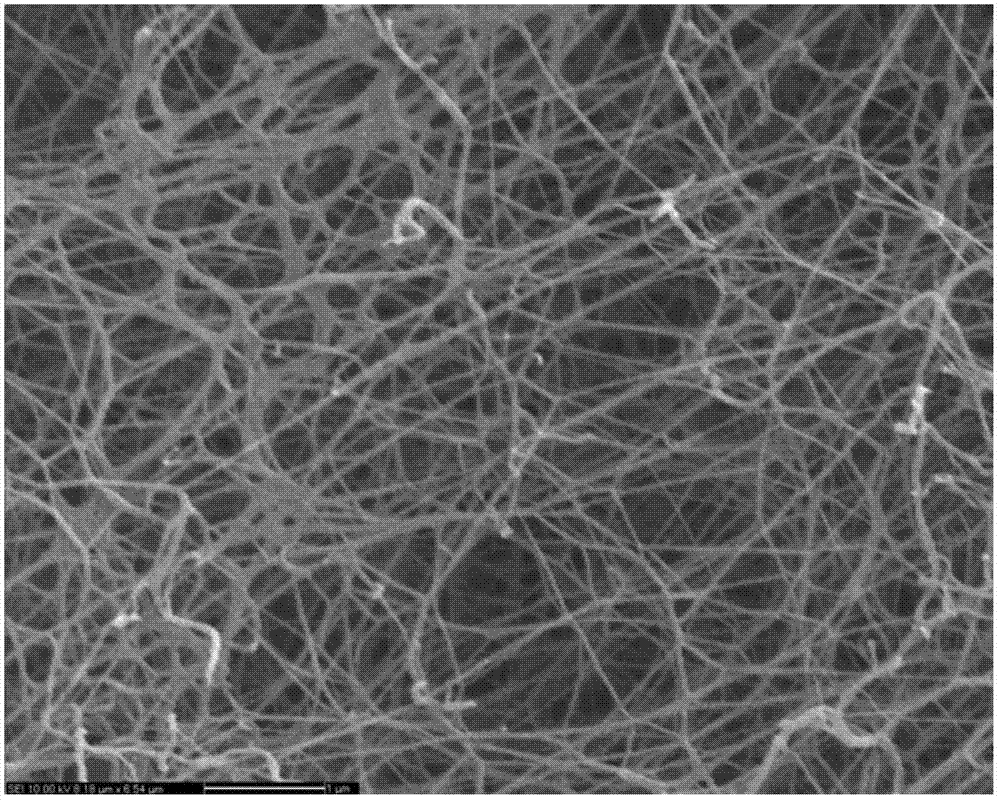
Preparation method of polysaccharide-nanometer bacterial cellulose composite wound dressing
A nano-bacteria, wound dressing technology, applied in medical science, bandages, absorbent pads, etc., can solve the problems of water permeability, ventilation or drainage, poor moisture absorption effect, etc., achieve excellent biocompatibility, promote healing, and reduce the effect of infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The commercially available nano-bacteria cellulose film made by Acetobacter xylinum is cut into a nano-bacteria cellulose film with a diameter of 15mm, and the steps are as follows:
[0034] Step 1, pretreatment and purification of nano bacterial cellulose membrane
[0035] Take the nano-bacterial cellulose and wash it with clean water several times to remove the culture medium and impurities on the surface of the membrane. Then soak the membrane in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, boil at 80°C for 75min, and wash out the bacteria and residual culture medium in the nano-bacterial cellulose membrane. Then soak the nano-bacterial cellulose membrane in 0.05mol / L NaOH solution, boil it at 80°C for 60 minutes, and then rinse it with distilled water several times; then sterilize it with ultraviolet rays to meet the sterilization requirements of the process (the subsequent process requires aseptic operation); Soak the nano-bacterial cellulose film after the above disinfection with dis...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The commercially available nano-bacterial cellulose film prepared by Acetobacter xylinum was cut into a 10×10 cm nano-bacterial cellulose sample.
[0046] Step 1, pretreatment and purification of nano bacterial cellulose membrane
[0047] Take the nano-bacterial cellulose and wash it with clean water several times to remove the culture medium and impurities on the surface of the membrane. Then soak the membrane in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, boil at 85°C for 75min, and wash out the bacteria and residual culture medium in the nano-bacterial cellulose membrane. Then soak the nano-bacterial cellulose membrane in 0.05mol / L NaOH solution, boil it at 85°C for 60 minutes, and then rinse it with distilled water several times; then sterilize it with ultraviolet rays to meet the sterilization requirements of the process (the subsequent process requires aseptic operation); Soak the nano-bacterial cellulose film after the above-mentioned disinfection with distilled water for 4 times, ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The commercially available nano-bacterial cellulose film prepared by Acetobacter xylinum was cut into a 10×10 cm nano-bacterial cellulose sample.
[0058] Step 1, pretreatment and purification of nano bacterial cellulose membrane
[0059] Take the nano-bacterial cellulose and wash it with clean water several times to remove the culture medium and impurities on the surface of the membrane. Then soak the membrane in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, boil it at 90°C for 75 minutes, and wash out the bacterial cells and residual medium in the nano-bacterial cellulose membrane. Then soak the nano-bacterial cellulose membrane in 0.05mol / L NaOH solution, boil it at 90°C for 60 minutes, and then rinse it with distilled water several times; then sterilize it with ultraviolet rays to meet the sterilization requirements of the process (the subsequent process requires aseptic operation); Soak the nano-bacterial cellulose film after the above-mentioned disinfection with distilled water for 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com