Phosphogypsum composite pretreatment technique
A phosphogypsum and pretreatment technology, applied in the field of renewable resources and environmental protection, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of phosphogypsum and achieve significant economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] raw material source
[0019] Phosphogypsum slag—the discharge port produced by Guangxi Luzhai Fertilizer Co., Ltd. Phosphogypsum slag contains about 30% acidic water, 15% solid impurities, and 35% SO 3 , 70% CaSO 4 2H 2 O, pH=2, the particles are uneven and grayish black.
[0020] Industrial wastewater—wastewater from a phosphate rock ball mill workshop in a fertilizer factory.
[0021] Alkaline calcium-enhancing fluid—a slurry made of lime produced by surrounding lime factories, with a pH value of about 12.
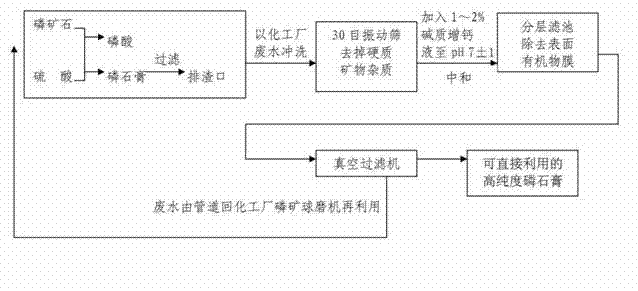
[0022] process flow
[0023] Take phosphogypsum slag directly from the slag outlet of the chemical enterprise, discharge it into a 30-mesh vibrating screen, and wash the phosphogypsum slag with industrial wastewater to remove about 10% of the hard mineral impurities with coarser particle sizes. The phosphorus obtained after washing The gypsum slurry is added to the phosphogypsum mass of 2% alkaline calcium solution to adjust the pH value to 7 ± 1, and then se...
Embodiment 2
[0025] raw material source
[0026] Phosphogypsum slag——with embodiment 1.
[0027] Industrial wastewater—wastewater from a phosphoric acid washing process in a chemical fertilizer plant.
[0028] Alkaline calcium-increasing liquid——It is made by diluting and stirring calcium carbide slag discharged from caustic soda production in Liuzhou Chemical Plant, and its pH value is about 14.
[0029] process flow
[0030] Add 1% alkaline calcium-enhancing solution to adjust the pH value to 7±1, and refer to Example 1 for others.
Embodiment 3
[0032] raw material source
[0033] Phosphogypsum slag——with embodiment 1.
[0034] Industrial wastewater—wastewater from a phosphate rock ball mill workshop in a fertilizer factory.
[0035] Alkaline calcium-increasing liquid——It is made by diluting and stirring the calcium-increasing alkali slag discharged from Guangxi Fengtang Paper Industry, and its pH value is about 13. process flow
[0036] Add 1.5% alkaline calcium-increasing solution to adjust the pH value to 7±1, and refer to Example 1 for others.
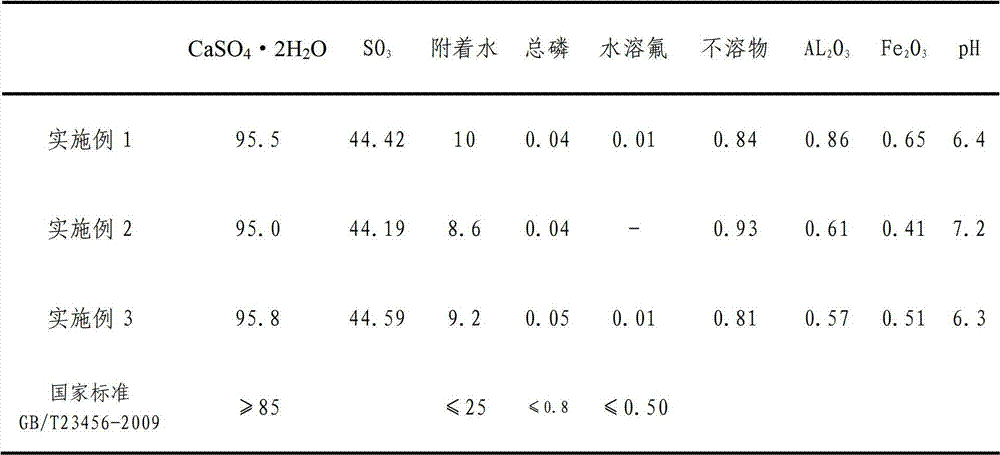
[0037] After testing, the high-purity phosphogypsum of Examples 1 to 3 contains less than 10% water, pH 7±1, SO 3 Up to 43% or more, CaSO 4 2H 2 The O content is more than 90%, the soluble phosphorus is less than 0.01%, the total phosphorus is less than 0.05%, and the impurities are less than 1%. See Table 1 for details.
[0038] Components and properties of table 1 embodiment 1 to 3 high-purity phosphogypsum
[0039]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com