Photoelectric chemical analysis method adopting molecular imprinting functionalization modified electrode
A technology of molecular imprinting and electrode modification, which is applied in the fields of electrochemical variables of materials, material analysis by electromagnetic means, and material analysis, etc., can solve problems such as poor selectivity, maintain stability, and the method is simple and feasible, and avoids photoelectrochemical oxidation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
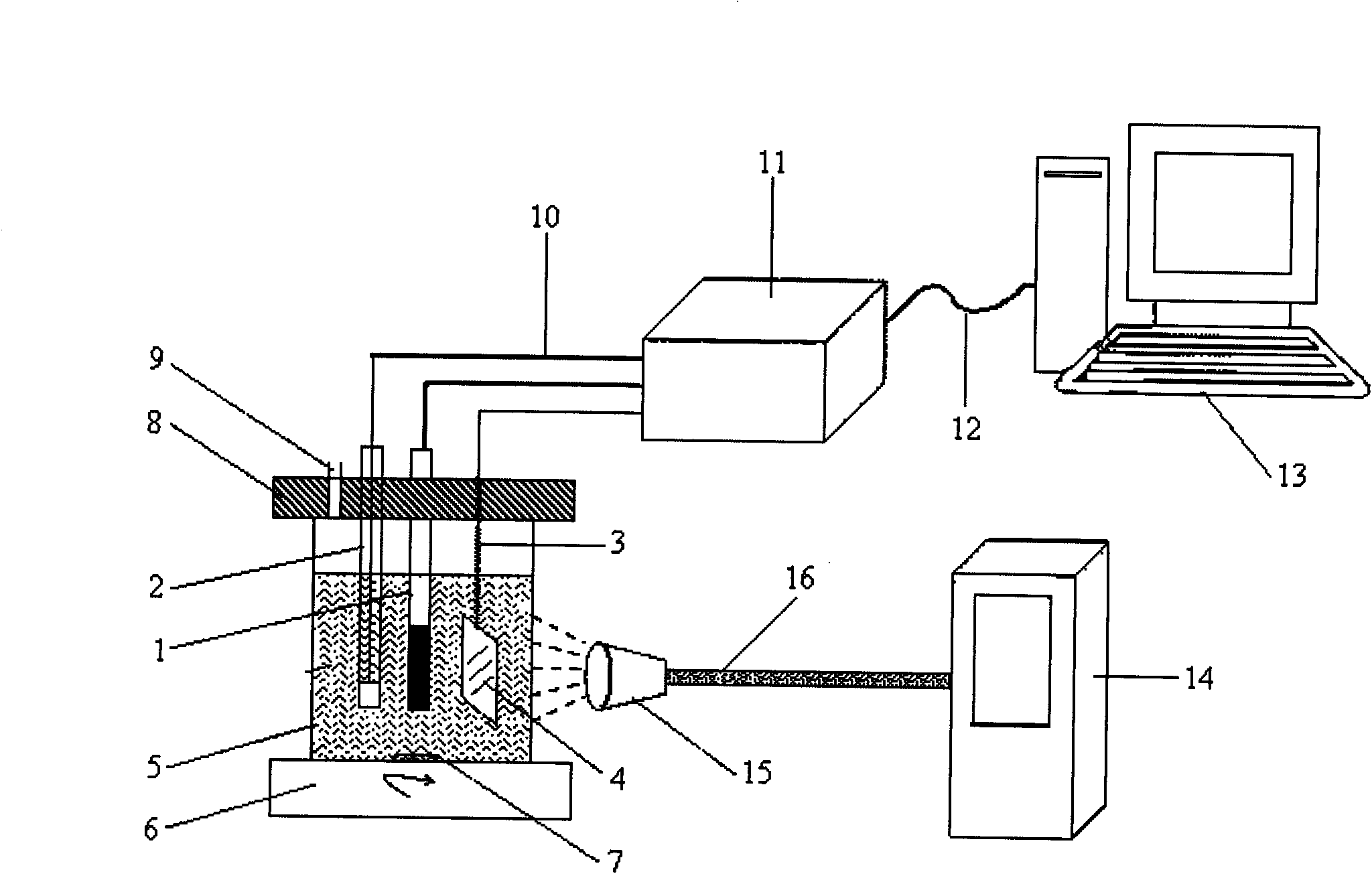
[0022] TiO used in the present invention 2 The NTs electrode is referred to in the literature by Maggie Paulose et al. (Anodic Growth of Highly Ordered TiO 2 Nanotube Arrays to 134nm in Length, Maggie Paulose, Karthik Shankar et al, J.Phys.Chem.B, 2006, 110, 16179-16184) reported in the anodic oxidation method prepared, and carried out corresponding improvements, specifically with The ground and polished Ti plate is used as the anode, and the Pt sheet is used as the cathode. The 0.27M HF aqueous solution is used as the electrolyte, and the pre-oxidation is carried out for 1h in a two-electrode system, the electrode distance is 1cm, and the voltage is 20V. After pre-oxidation, in the same system, use 0.27M NH 4 The ethylene glycol solution of F is the electrolyte, and the anodic oxidation is continued for 2 hours. TiO obtained by anodic oxidation 2 NTs were sintered at 500 °C in an oxygen atmosphere with a heating rate of 1 °C / min.
[0023] TiO prepared by the above method...
Embodiment 2
[0025] A series of 2,4-D standard solutions with different concentrations were prepared by using 0.1M PBS buffer solution with pH 7. First, use the hint figure 1 The photoelectrochemical analysis device shown in , with 0.1M PBS buffer at pH 7 as electrolyte 4, and TiO modified with molecularly imprinted polypyrrole film 2 NTs is the working electrode 1, which is scanned by cyclic voltammetry to obtain a stable voltammetry curve, the scanning potential is -0.2-0.2V (Vs.SCE), and the scanning rate is 50mV / s. Rinse the scanned electrode carefully with distilled water, then replace it with a certain concentration of 2,4-D solution as electrolyte 4, turn on the stirrer, and stir for 10 minutes to make 2,4-D rapidly selectivity on the surface of the working electrode Enrichment. Turn off the stirrer, let it stand still, turn on the ultraviolet light source 14, set the applied potential of 0.2V (Vs.SCE), use the electrochemical analyzer 11 to measure the photocurrent by using the i...
Embodiment 3
[0027] First, prepare the used working electrode in 0.2M Na 2 HP 4 The solution was oxidized at a constant potential of 1.3V (Vs.SCE) for 20min to achieve surface renewal and regeneration, and then cyclically scanned in 0.1M PBS buffer with pH 7 to obtain a stable voltammetry curve. Wash the electrode carefully and use it as working electrode 1 to contain a certain concentration of 2,4-D or 2,4-D and 100 times the concentration of 2,4-D interfering substances, such as acetamiprid, atrazine or baicao The mixed solution of dryness is electrolyte 4, and its pH value is adjusted with 0.1M PBS buffer solution of pH=7. in gesture figure 1 In the photoelectrochemical analysis system shown in , the test conditions set in Example 2 were used to measure the photocurrent of the solution, and the concentration of 2,4-D in the actual solution was calculated according to the working curve drawn in Example 2. The results showed that other small molecular interferers with 100 times the con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com