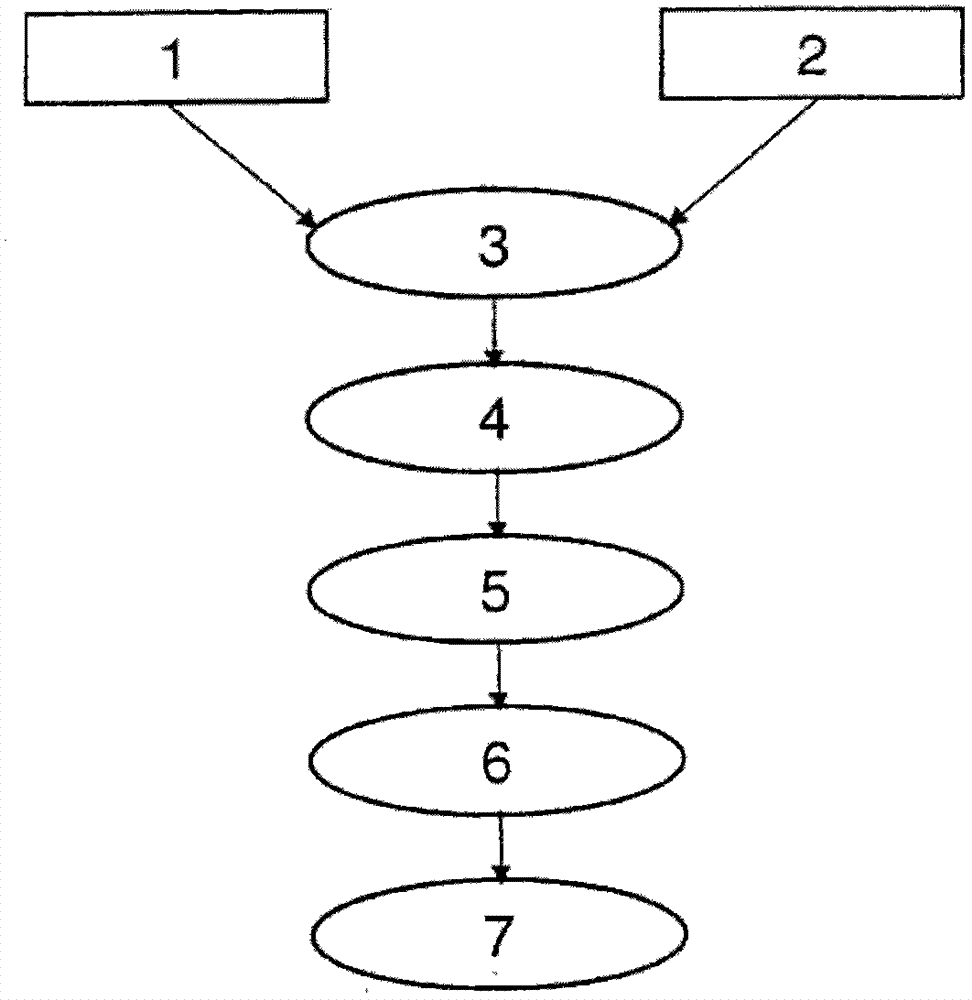
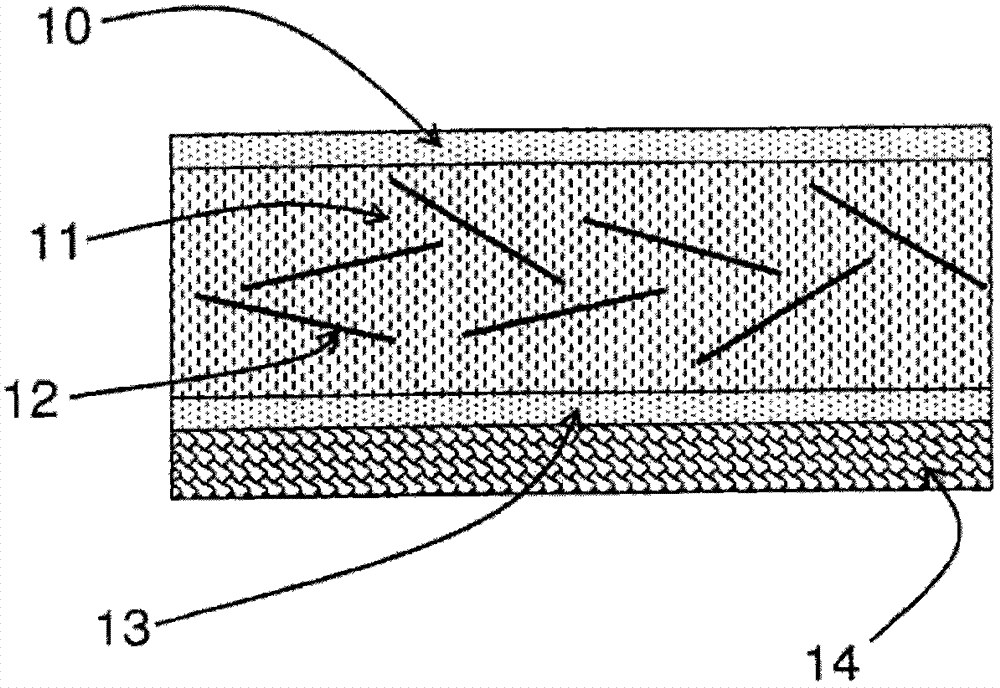
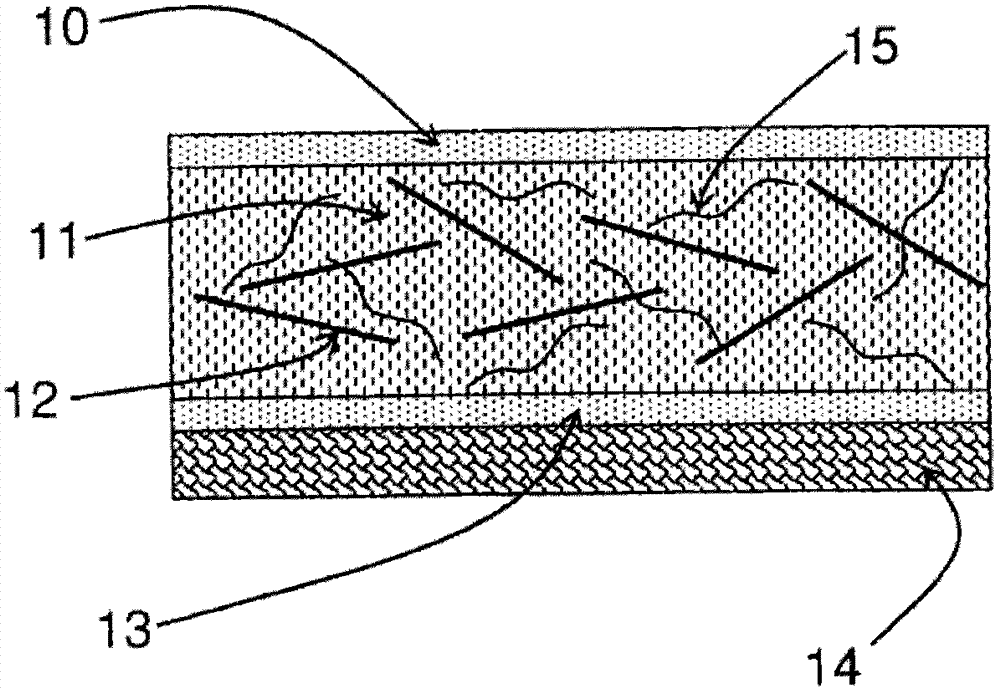
Piezoelectric and/or pyroelectric composite solid material, method for obtaining same and use of such a material
A technology of thermoelectric materials and hybrid materials, applied in material selection for piezoelectric devices or electrostrictive devices, manufacturing/assembly of piezoelectric/electrostrictive devices, piezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devices, etc. direction, which can solve the problems of mechanical properties, mechanical properties, and the inability of the matrix to maintain the original ductility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] Example 1: Preparation of barium titanate nanowires with high shape factor
[0123] Electrodeposit an aqueous solution of barium titanate in the pores of an alumina filter membrane (PAA, Porous Anodised Alumina, Whatmann, 6809-5022 or 6809-5002) to synthesize BaTiO 3 For nanowires, the aluminum oxide filter membrane has a thickness of 50 μm and a porosity of 200 nm. In the presence of 3.27 mL of ethylene glycol (Ref. 324558, Sigma-Aldrich, Lyon, France) and 2 L of water, 3 g of barium acetate (Ref. 255912, Sigma-Aldrich, Lyon, France) and 3.3 g of iso Titanium propoxide (Ref. 377996, Sigma-Aldrich, Lyon, France) was dissolved in 20.16 mL of glacial acetic acid (Ref. A9967, Sigma-Aldrich, Lyon, France), thereby forming a barium titanate sol. The final pH of the prepared barium titanate sol was 5. The filter membrane was positioned in the barium titanate sol such that one of its major surfaces came into sealing contact with the surface of the aluminum plate prior to sil...
Embodiment 2
[0126] Embodiment 2: the preparation of the barium titanate nanotube of high shape factor
[0127] Barium titanate BaTiO was prepared as described in Example 1 3Sol. The barium titanate sol was placed on one of the main surfaces of an alumina filter membrane (PAA) having a thickness of 50 μm and a porosity of 200 nm, thereby forming the inside of the pores of the filter membrane. Surface coating. The porous membrane was dried in air at 100 °C, and then nanotube BaTiO 3 The heat treatment step of annealing is performed at a temperature of about 600° C. in the ambient environment. The alkaline reaction of the porous membrane was initiated as described in Example 1, followed by washing to form BaTiO in an organic solvent such as N,N-dimethylacetamide 3 suspension of nanotubes.
Embodiment 3
[0128] Example 3: Preparation of BaTiO dispersed in a polyamide thermoplastic dielectric matrix 11 3 Piezoelectric and / or thermoelectric hybrid materials made of nanowires
[0129] 250 mg of BaTiO with a shape factor of 25 as described in Example 1 3 The nanowires were dispersed in 20 mL of N,N-dimethylacetamide. The dispersion is carried out in an ultrasonic bath with a frequency of about 20kHz, and the dispersion power is about 500W. On the other hand, 250 mg of polyamide 11 (PA11, Rilsan polyamide 11, ARKEMA, USA) was dissolved in 20 mL of N,N-dimethylacetamide. Mix well by sonicating. After evaporating N,N-dimethylacetamide and thermoforming, a hybrid composite film with a thickness of 150 μm was obtained, in which linear nanoparticles BaTiO 3 The loading in the polyamide dielectric matrix 11 is 12% by volume.
[0130] In a variant, the hybrid composite film is placed in sheet form on the surface of the substrate in ambient conditions or is formed by heat treatment on...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com