Method for preparing carbon-coated nanometer molybdenum dioxide material
A technology of molybdenum dioxide and carbon coating, which is applied in the preparation/purification of carbon, vanadium oxide, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of limited performance, unfavorable rapid carrier transport, etc., and achieve raw materials that are easily available, environmentally friendly, Simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
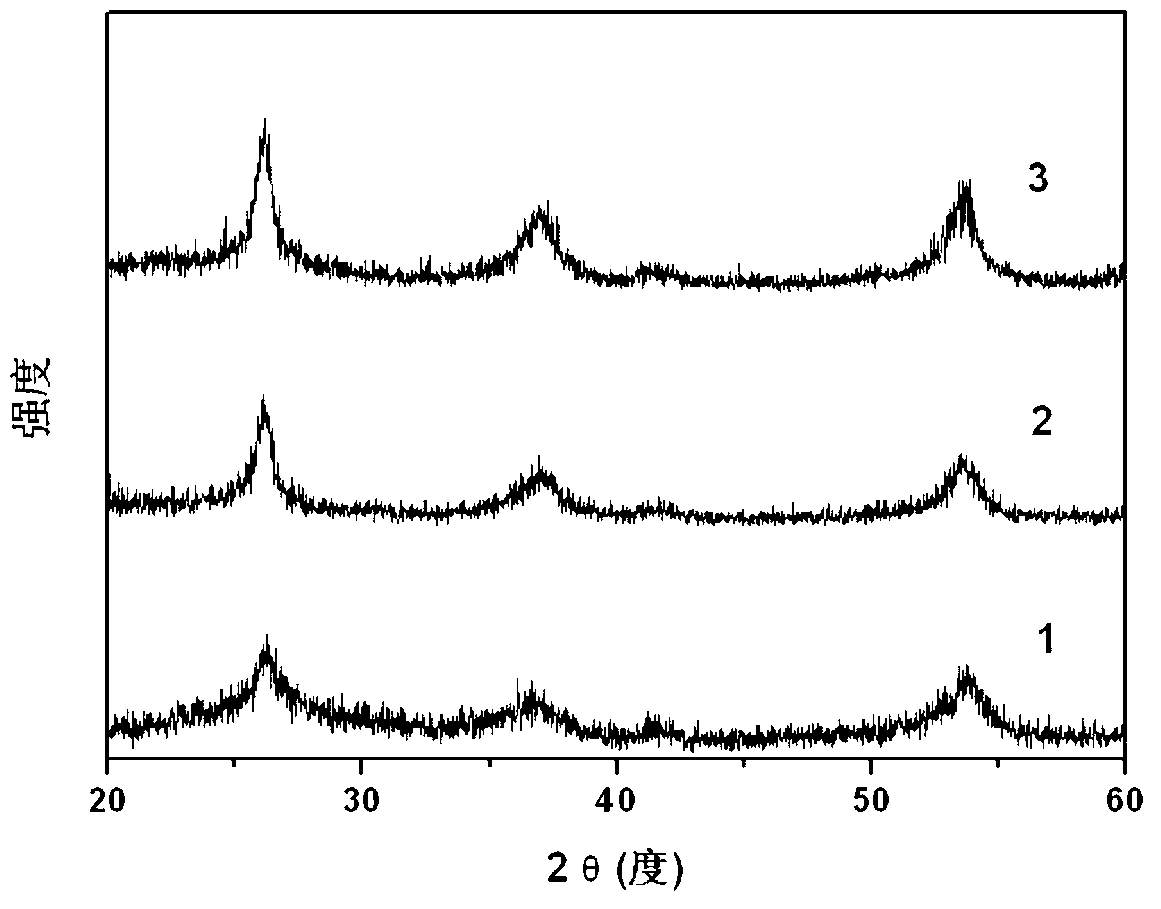
[0020] Add 1.0g fructose and 1.1g sodium molybdate (Na 2 MoO 4 ), forming a mixture (the number of moles of reducing sugar with Mo 6+ The molar ratio of molarity is 1:1, and the mass ratio of the sum of the mass of sugar and molybdenum precursor to the solvent is 1:19); the mixture is put into a reaction kettle, and crystallized at a heating temperature of 160°C; the crystallization After 4 hours of curing time, the reaction kettle was cooled to room temperature to obtain a crystallized product; the crystallized product was washed with water, and then centrifuged to obtain a carbon-coated nanomolybdenum dioxide material. Its XRD diffraction pattern is shown in figure 2 As shown in 1, the peak position and peak intensity of the diffraction peak are consistent with the JCPDS card (32-0671) of the XRD diffraction peak database, and it can be seen that the prepared MoO is a monoclinic structure 2 product.
Embodiment 2
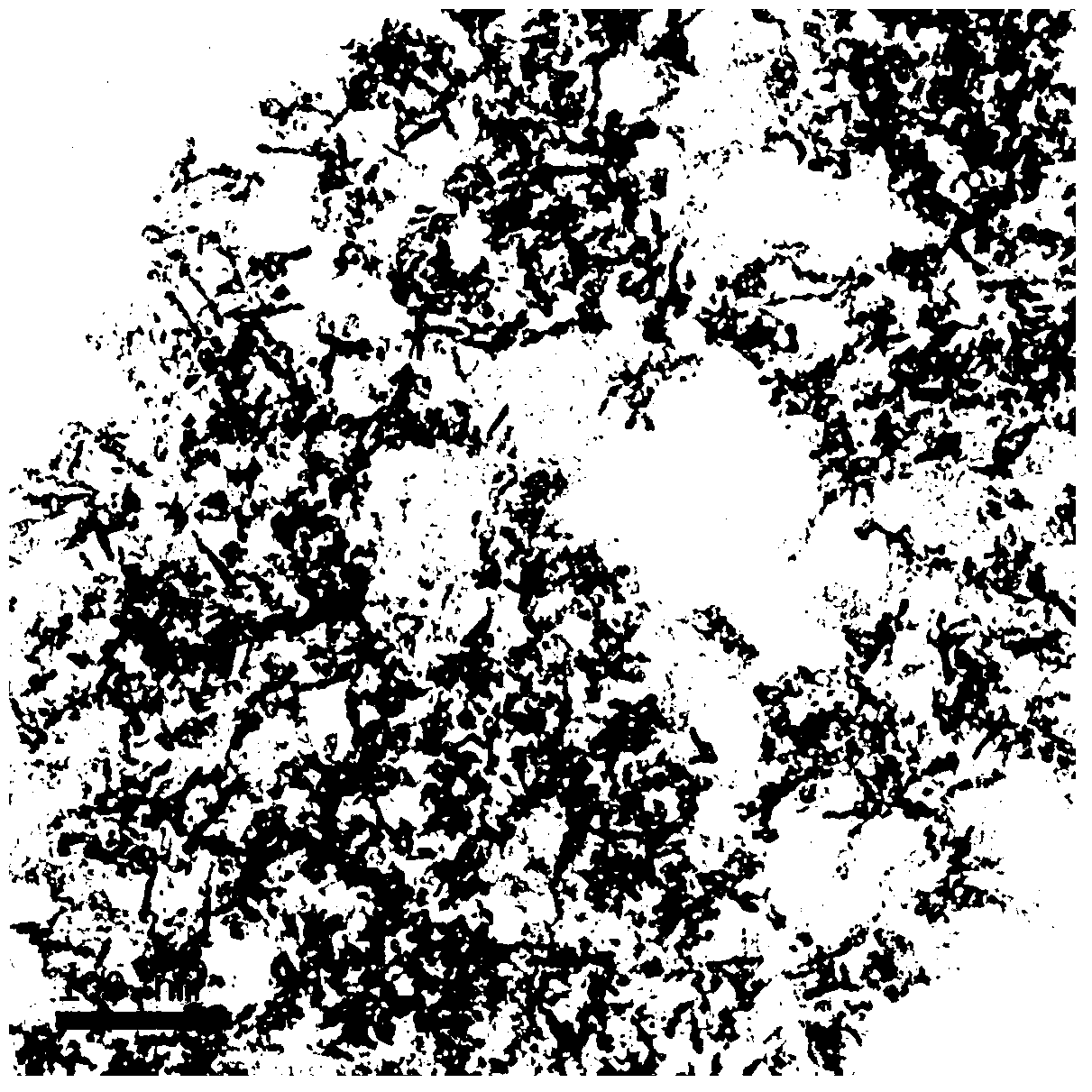
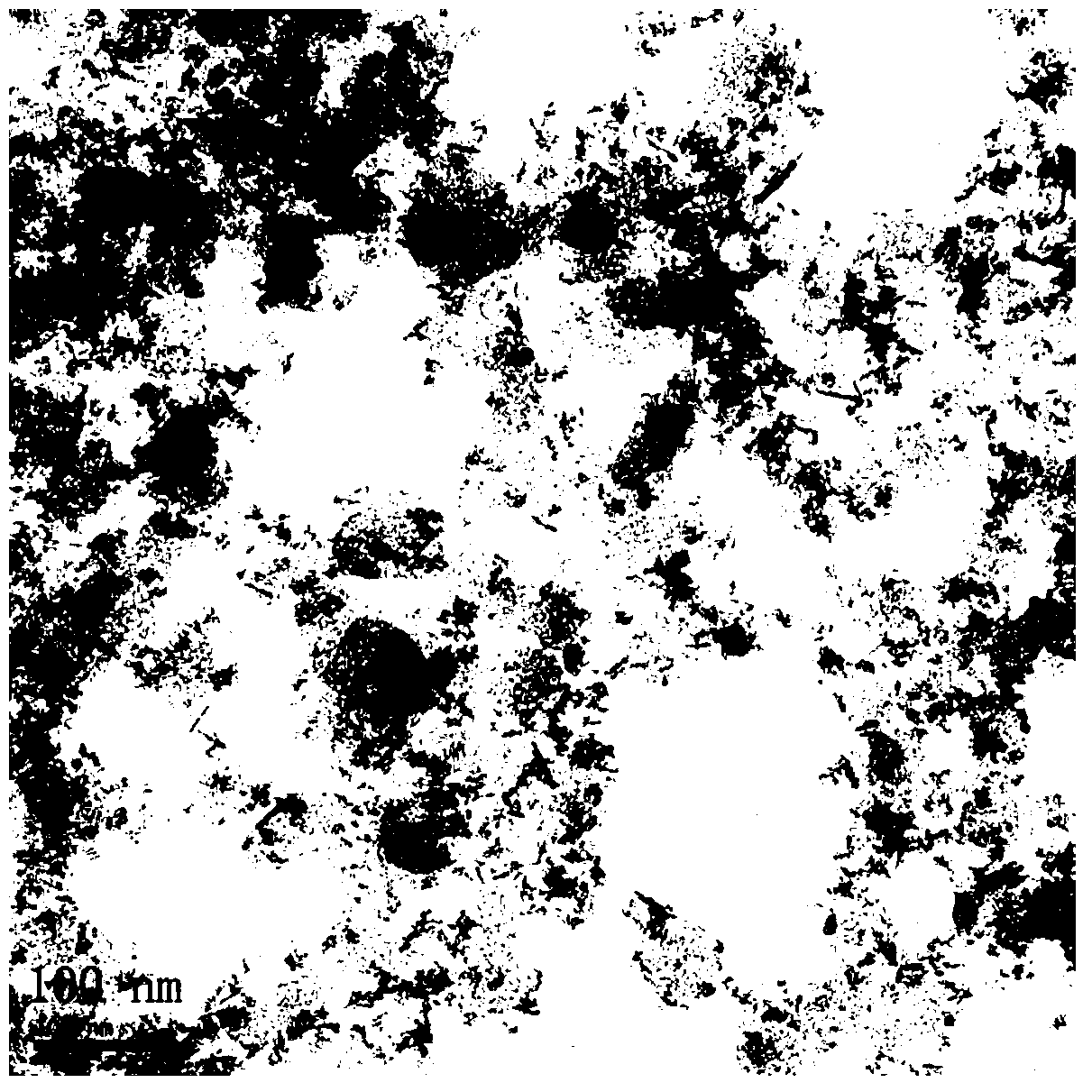
[0022] Add 0.5g glucose and 0.4g molybdenum trioxide (MoO 3 2H 2 O), forming a mixture (the number of moles of reducing sugar and Mo 6+ The molar ratio of molarity is 1.25:1, and the mass ratio of the sum of the mass of sugar and molybdenum precursor to the solvent is 1:17.5); the mixture is put into a reaction kettle and crystallized at a heating temperature of 160°C; the crystallization After a heating time of 12 hours, the reaction kettle was cooled to room temperature to obtain a crystallized product; the crystallized product was washed with water, and then centrifuged to obtain a carbon-coated nano molybdenum dioxide material. Its XRD diffraction pattern is shown in figure 2 As shown in 3, the peak position and peak intensity of the diffraction peak are consistent with the JCPDS card (32-0671) of the XRD diffraction peak database, and it can be seen that the prepared MoO is a monoclinic structure 2 product; its TEM photo is shown in figure 1 As shown, it can be seen ...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Add 2.8g maltose and 1.2g ammonium molybdate ((NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O), forming a mixture (the number of moles of reducing sugar and Mo 6+ The molar ratio of molarity is 1.20:1, the mass ratio of the sum of the mass of sugar and molybdenum precursor to the solvent is 1:12); put the mixture into the reaction kettle, and crystallize at a heating temperature of 160°C; crystallization After 22 hours of curing time, the reaction kettle was cooled to room temperature to obtain a crystallized product; the crystallized product was washed with water, and then centrifuged to obtain a carbon-coated nano molybdenum dioxide material. Its XRD diffraction pattern is shown in figure 2 As shown in 3, the peak position and peak intensity of the diffraction peak are consistent with the JCPDS card (32-0671) of the XRD diffraction peak database, and it can be seen that the prepared MoO is a monoclinic structure 2 product.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com