Method for producing low-carbon olefins from methanol and naphtha
A technology for low-carbon olefins and naphtha, which is applied in the petroleum industry, bulk chemical production, hydrocarbon cracking to produce hydrocarbons, etc., can solve the problem of low yield of low-carbon olefins, etc. The effect of low material temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
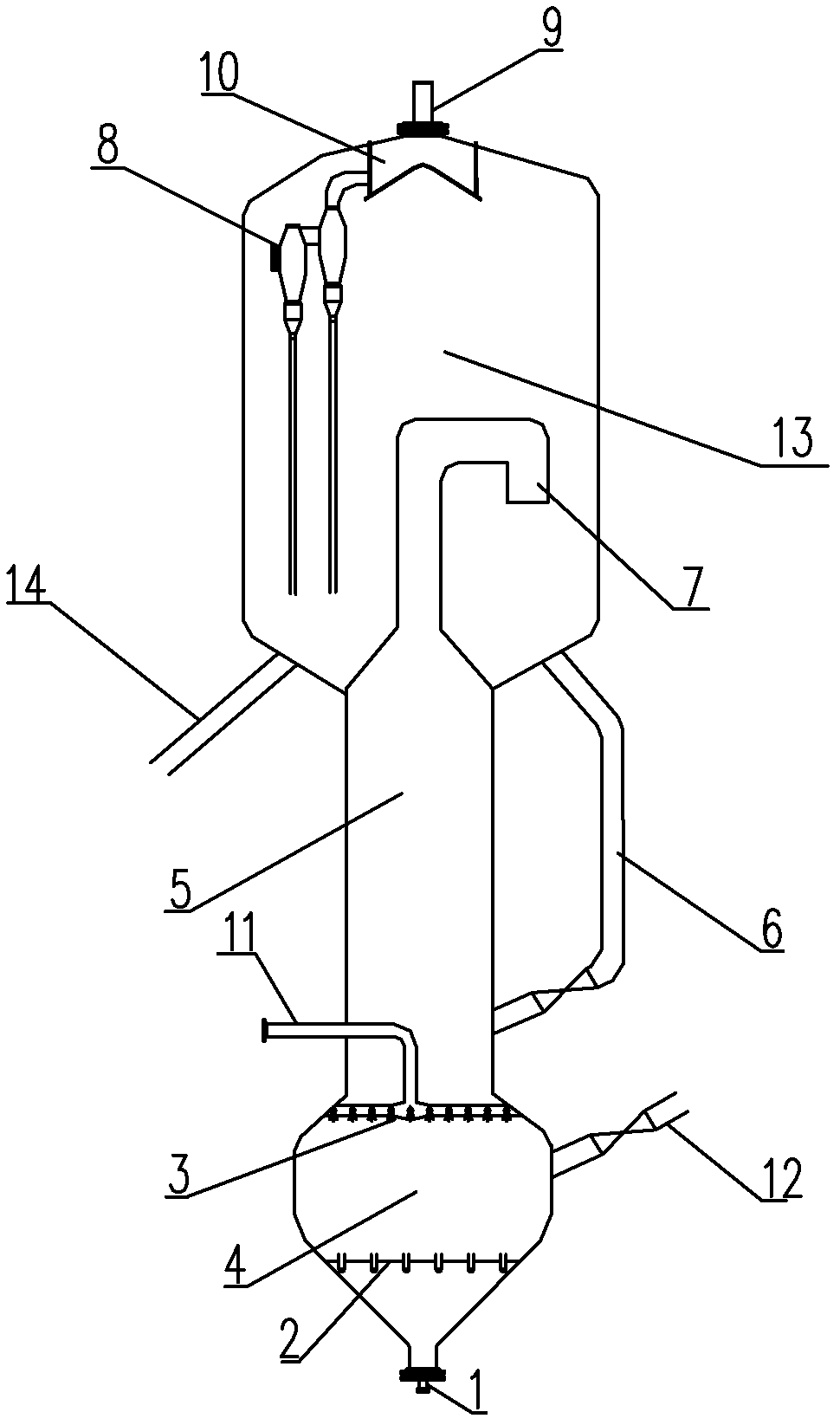
[0019] in such as figure 1 In the shown reaction device, the catalyst is ZSM-5, SiO 2 / Al 2 o 3The molar ratio is 10, naphtha and water vapor enter the first reaction zone with a weight ratio of 1.5:1, contact with the catalyst, and the gas phase stream and catalyst that are generated are mainly methanol After the raw material is contacted, it enters the second reaction zone to generate a product stream including low-carbon olefins, and simultaneously forms a raw catalyst. The raw catalyst is divided into two parts, 40% of the weight enters the regenerator for regeneration, and 60% of the weight returns through the external circulation inclined pipe In the second reaction zone, the regenerated catalyst formed in the regenerator returns to the first reaction zone. Wherein, the methanol entering through the distribution pipe is in countercurrent contact with the gas phase flow formed in the first reaction zone, and the feed temperature of the methanol raw material is 200°C. ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] According to the conditions and steps described in Example 1, the catalyst is ZSM-5, SiO 2 / Al 2 o 3 The molar ratio is 100, naphtha and water vapor enter the first reaction zone with a weight ratio of 0.05:1, contact with the catalyst, and the gas phase stream and the catalyst that enter from the distribution pipe at the outlet end of the first reaction zone are mainly methanol After the raw materials are contacted, they enter the second reaction zone to generate a product stream including low-carbon olefins, and simultaneously form a raw catalyst. The raw catalyst is divided into two parts, 80% of the weight enters the regenerator for regeneration, and 20% of the weight returns through the external circulation inclined pipe In the second reaction zone, the regenerated catalyst formed in the regenerator returns to the first reaction zone. Wherein, the methanol entering through the distribution pipe is in countercurrent contact with the gas phase stream formed in the ...
Embodiment 3
[0025] According to the conditions and steps described in Example 1, the catalyst is ZSM-5, SiO 2 / Al 2 o 3 The molar ratio is 70, naphtha and water vapor enter the first reaction zone with a weight ratio of 0.5:1, and the unborn catalyst is divided into two parts, 50% of the weight enters the regenerator for regeneration, and 50% of the weight returns to the first reaction zone through the external circulation inclined pipe. In the second reaction zone, the feed temperature of methanol raw material is 100°C. The carbon deposition mass fraction of the regenerated catalyst is 0.1%, and the reaction conditions in the first reaction zone are: the reaction temperature is 650° C., the reaction pressure is 0.01 MPa in terms of gauge pressure, and the gas phase velocity is 0.6 m / s; The reaction conditions are as follows: the reaction temperature is 617° C., the reaction pressure is 0.01 MPa in terms of gauge pressure, the gas phase velocity is 1.5 m / s, and the feed weight ratio of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com