Dual-wavelength differential temperature measuring system based on optical-fiber radiation attenuation temperature dependency
A technology of temperature dependence and temperature measurement, applied in thermometers, measuring devices, measuring heat, etc., can solve the problems of small temperature variation in F-P cavity length, complicated F-P manufacturing process, and limited sensing temperature range, etc., to achieve suppression of optical fiber bending, Low cost, simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be further described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
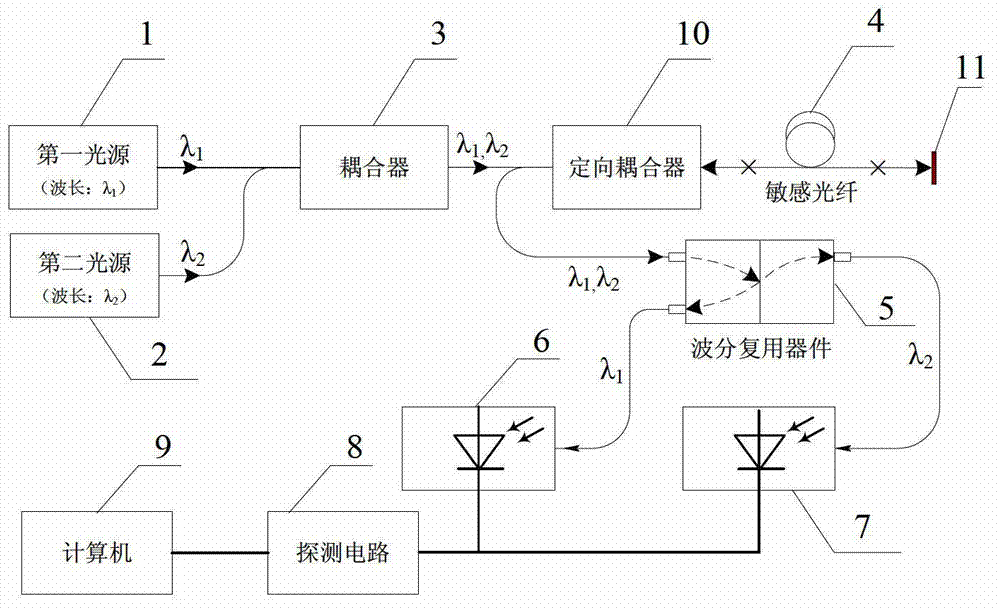
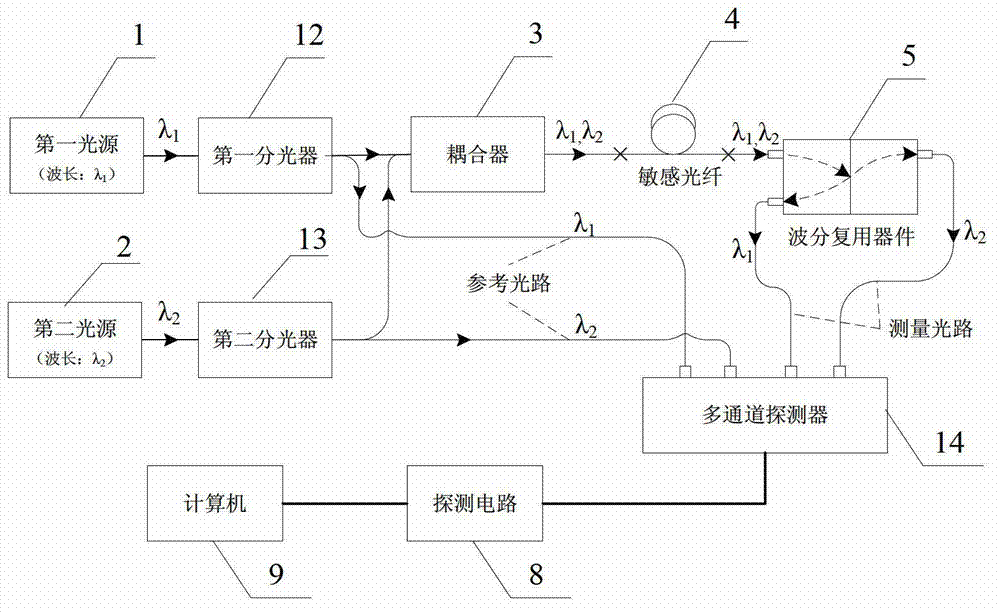
[0030] The invention is a dual-wavelength differential temperature measurement system based on the temperature dependence of optical fiber radiation-induced attenuation, and has three schemes.
[0031] The first option:
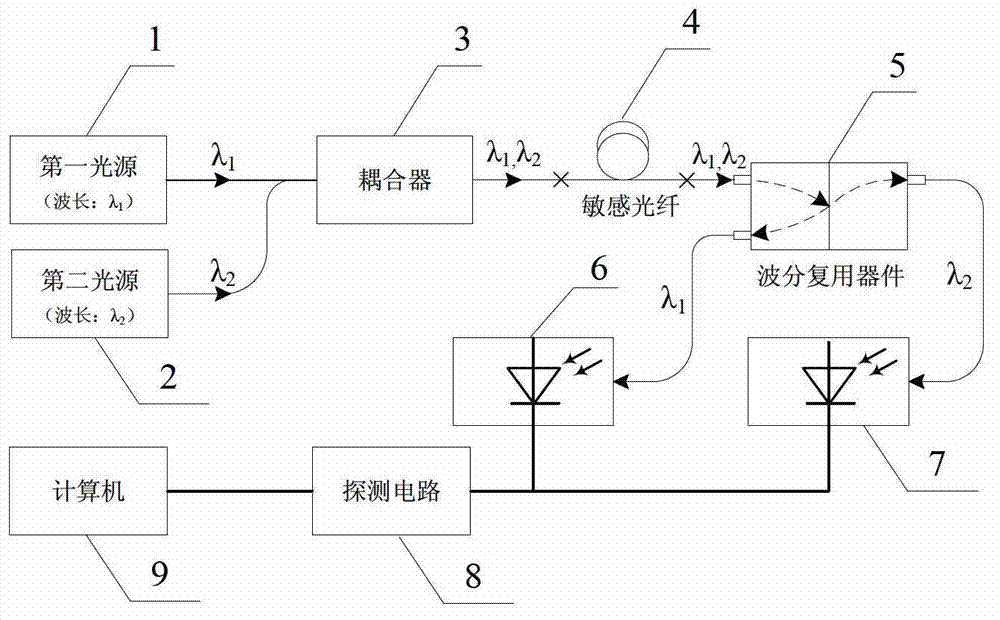
[0032] The first option, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a first light source 1 and a second light source 2 for providing two different wavelength bands of light waves, a coupler 3 for coupling light, a sensitive optical fiber 4 for sensitive temperature changes, and a waveband for separating two wavelengths of light. A demultiplexing device 5, a first detector 6 and a second detector 7 for detecting two-way optical signals, a detection circuit 8 for processing the detected optical signals, and a computer 9 for signal processing and display.
[0033] The first light source 1 emits λ 1 wavelength band, the second light sourc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com