Amorphous tellurium-cadmium-mercury/crystalline silicon heterojunction infrared-detector and manufacturing method thereof
An infrared detector, silicon heterojunction technology, applied in final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, semiconductor devices, etc. Reduced weight and good lattice matching performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
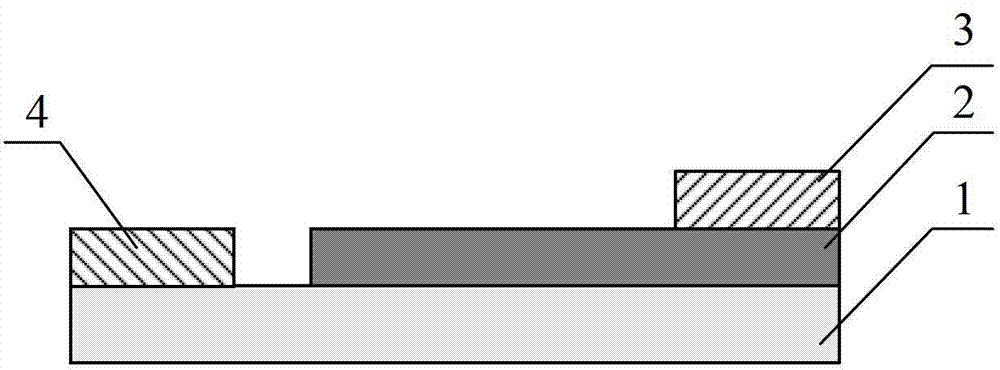
[0031] as attached figure 1 As shown, this figure is an embodiment of the a-HgCdTe / c-Si heterojunction infrared detector described in the present invention. It consists of c-Si substrate 1, a-HgCdTe thin film 2, Cr / Au alloy metal first electrode 3 and Cr / Au alloy metal second electrode 4, wherein the c-Si substrate is n-type crystalline semiconductor material , the c-Si substrate is not only used as the substrate, but also one of the materials that constitute the heterojunction; the a-HgCdTe film is an amorphous semiconductor material that is not intentionally doped, and its thickness is 1-2 μm; the heterojunction consists of a- Composed of HgCdTe film and c-Si substrate, a-HgCdTe film and c-Si substrate have good lattice matching, a-HgCdTe film and c-Si substrate are directly connected; metal first electrode and a-HgCdTe film connected, the metal second electrode is connected to the c-Si substrate.
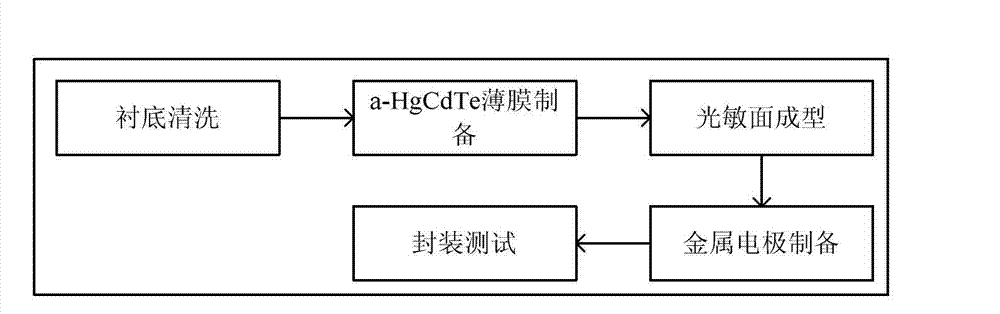
[0032] The preparation process of the a-HgCdTe / c-Si heterojunction infrare...
Embodiment 2
[0041] attached Figure 5What is shown is another embodiment of the a-HgCdTe / c-Si heterojunction infrared detector described in the present invention. The technical feature of this embodiment is that: the metal first electrode 3 and the metal second electrode 4 are ring-shaped electrode structures; The -Si substrate is directly connected, but the a-HgCdTe thin film 2 is not connected to the second metal electrode 4 and is separated; the first metal electrode 3 is located on the a-HgCdTe thin film 2 and is directly connected to it. The rest of the technical features are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0042] The preparation process of the a-HgCdTe / c-Si heterojunction infrared detector of the present embodiment is as follows (such as Figure 8 shown):
[0043] The first step, substrate cleaning: the same as Step 1 in Embodiment 1;
[0044] The second step, preparation of the second metal electrode: preparing a ring-shaped second metal electrode 4 on the upper surface of...
Embodiment 3
[0051] attached Image 6 What is shown is another embodiment of the a-HgCdTe / c-Si heterojunction infrared detector described in the present invention. The technical feature of this embodiment is that the metal first electrode 3 is a circular electrode structure, and the metal second electrode 4 is a circular electrode structure; the c-Si substrate 1 is located on the metal second electrode 4 and is connected to it; a-HgCdTe The thin film 2 is located on the c-Si substrate and connected to it; the metal first electrode 3 is located on the a-HgCdTe thin film 2 and directly connected to it. The rest of the technical features are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0052] The preparation process of the a-HgCdTe / c-Si heterojunction infrared detector of the present embodiment is as follows (such as Figure 8 shown):
[0053] The first step, substrate cleaning: the same as Step 1 in Embodiment 1;
[0054] The second step, preparation of the second metal electrode: prepare a circ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com