Rabdosia rubescens liquid extract and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of rubescens leaf and water extract, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as breast softening, increased risk of breast cancer, increased risk of venous thromboembolic disease, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The preparation of embodiment 1 oridonium leaf water extract
[0024] After washing 21g of dried Radix japonicus leaves with tap water, add 500ml of double distilled water and stir and extract at 80°C for 30 minutes. The clear liquid obtained by filtration was concentrated under reduced pressure at 40° C. to obtain 6.3 g of water extract of Radix radix leaves as a pale yellow solid. Grind into powder for later research use.
Embodiment 2
[0025] The HPLC-diode array fingerprint of embodiment 2 Radix radix leaf water extract
[0026] HPLC: Waters 2695Separations Module;
[0027] Detector: Waters 2996 diode array (PAD);
[0028] Kromasil C 18 Reversed-phase column (5μm, 250mm×4.6mm);
[0029] Guard column (5μm, 10mm×4.6mm);
[0030] Mobile phase: acetonitrile / water (containing 0.05% glacial acetic acid);
[0031] Mobile phase flow rate: 0.3ml / min;
[0032] Injection volume: 50μl;
[0033] Elution method: gradient elution (see Table 1 for the specific gradient)
[0034] Table 1 Gradient table of mobile phase for HPLC-diode array analysis of the water extract of Rubescens japonicus
[0035]
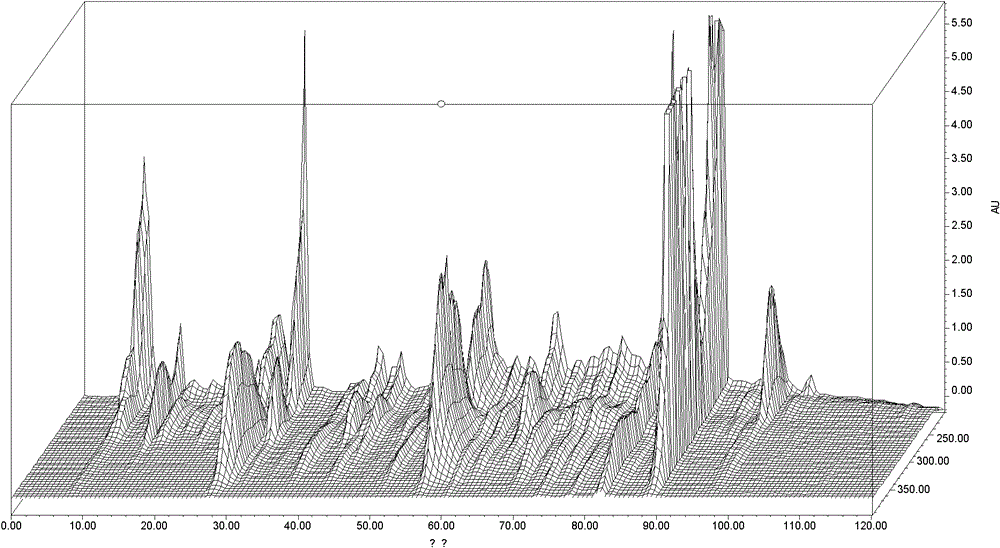
[0036] The 3D map of the chromatogram-ultraviolet absorption spectrum of the water extract of Dong Lingcao: see figure 1 .
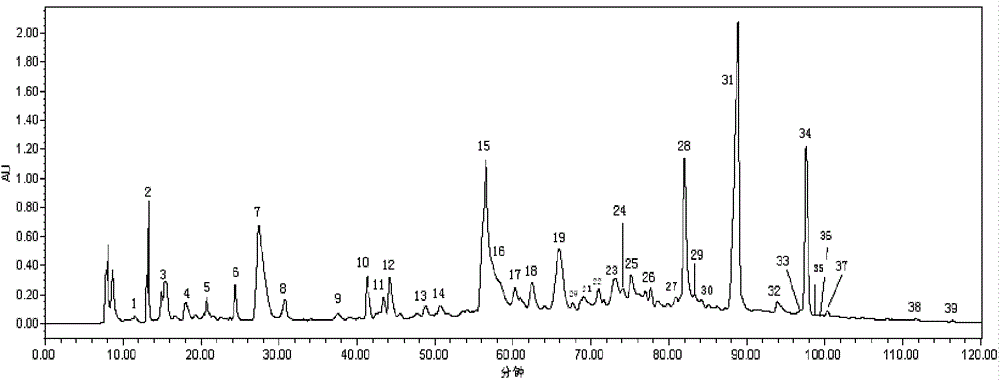
[0037] The HPLC fingerprint of the water extract of Rubescens japonicus under 254nm detection: see figure 2 , 39 peaks were analyzed at one time, and the retention times of 30 peaks are lis...
Embodiment 3
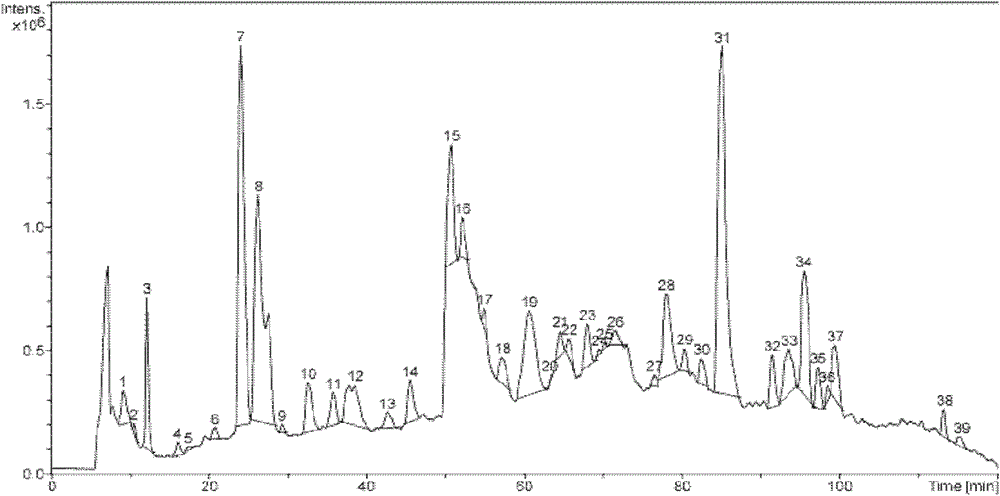
[0040] Example 3 (-)ESI-Q-TOF-MS fingerprints of the water extract of Radix radix leaves
[0041] (-)ESI-Q-TOF-MS: using an optimized small molecule analysis method, the specific parameters are a) Source Type: ESI; b) Ion Polarity: Negative; c) Scan begin: 50m / z; d) Scan begin: 1500m / z; e) Set Capillary: 3500 V; f) Set Nebulizer: 0.8Bar; g) Set Dry Heater: 200℃; h) Set Dry Gas: 8.0ml / min; i) Funnel 1 RF: 300Vpp; j) Funnel 2RF: 300Vpp; k) ISCID Energy: 0eV; l) Hexapole RF: 200Vpp; m) Ion Energy: 5eV; n) Low Mass: 200m / z; o) Collision Energy: 14eV; p) Collision RF: 140Vpp ; q) Transfer Time: 110.8 μS; r) Pre Puls Storage: 8.7 μS; s) Source: 1400v, 2nA; t) Calibrate the mass spectrometer with sodium formate before each analysis.
[0042]Using the HPLC-diode array analysis and the well-explored high-performance liquid chromatography conditions and the system-optimized mass spectrometry conditions, the negative ion mode (-)ESI was used to conduct (-)ESI-Q-TOF-MS on the water extra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com