Y55 mark free-cutting steel plate and manufacture method thereof
A manufacturing method and free-cutting technology, applied in the field of medium-thick steel plate manufacturing, can solve problems such as the inability to meet the large demand for free-cutting steel plates, the surface quality of cast slabs and scrap steel plates, and the huge impact on production costs, achieving light oxide segregation and improving metal The effect of low yield and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
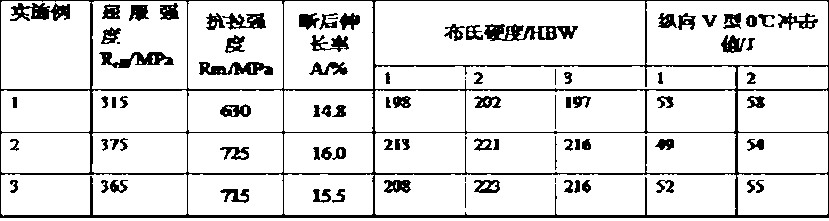
[0020] Example 1: A Y55 brand free-cutting steel plate in this embodiment is composed of the following components in weight percentage: C 0.58%, Mn 1.10%, Si 0.08%, P 0.025%, S 0.050%, Ca 0.0019%, Ti 0.013%, Alt 0.008%, the balance is iron Fe and unavoidable impurities. The thickness of the billet is 420mm, and the thickness of the steel plate after rolling is 115mm.
[0021] The smelting, continuous casting, heating, rolling and stack cooling processes of the present embodiment are as follows:
[0022] 1) Smelting process: Converter decarburization, dephosphorization, no desulfurization, weak deoxidation at the outbound station, no aluminum wire feeding at the argon station, and oxygen content of 30ppm. In order to increase the yield of ferrous sulfide alloy, no lime is added for refining, 450kg of refining slag and 500kg of submerged arc slag are added. The yield of ferrous sulfide alloy smelted this time is 73.4%. Outbound temperature 1550℃;
[0023] 2) Continuous cast...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: A continuous casting slab of this embodiment produces Y55 brand free-cutting steel plate, which is composed of the following components in weight percentage: C 0.50%, Mn 0.9%, Si 0.15%, P 0.045%, S 0.08%, Ca 0.0015% , Ti 0.010%, Alt 0.015%, and the rest is iron Fe and unavoidable impurities. The thickness of the billet is 300mm, and the thickness of the steel plate after rolling is 85mm.
[0028] The smelting, continuous casting, heating, rolling and stack cooling processes of the present embodiment are as follows:
[0029] 1) Smelting process: converter decarburization, dephosphorization, no desulfurization, weak deoxidation at the exit station, no aluminum wire feeding at the argon station, and the oxygen content is 58ppm. No lime is added for refining, 400kg of refining slag is added, and 450kg of submerged arc slag is added. The yield of ferrous sulfide alloy smelted this time is 76.6%. The outbound temperature is 1545°C;
[0030] 2) Continuous cast...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: A kind of continuous casting slab of this embodiment produces Y55 grade free-cutting steel plate, which is composed of the following components in weight percentage: C 0.53%, Mn 0.70%, Si 0.05%, P 0.038%, S 0.15%, Ca 0.0040% , Ti 0.011%, Alt 0.003%, and the rest is iron Fe and unavoidable impurities. The thickness of the billet is 250mm, and the thickness of the steel plate after rolling is 55mm.
[0035] The smelting, continuous casting, heating, rolling and stack cooling processes of the present embodiment are as follows:
[0036]1) Smelting process: converter decarburization, dephosphorization, no desulfurization, weak deoxidation at the exit station, no aluminum wire feeding at the argon station, and oxygen content of 70ppm. No lime is added for refining, 350kg of refining slag is added, and 400kg of submerged arc slag is added. The yield of ferrous sulfide alloy smelted this time is 81.6%. The outbound temperature is 1540°C;
[0037] 2) Continuous ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com