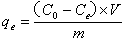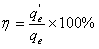Preparation method of cellulose adsorbent for adsorbing heavy metal cations
A technology for adsorbing heavy metals and cellulose, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of wide sources, mild catalytic reaction conditions and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
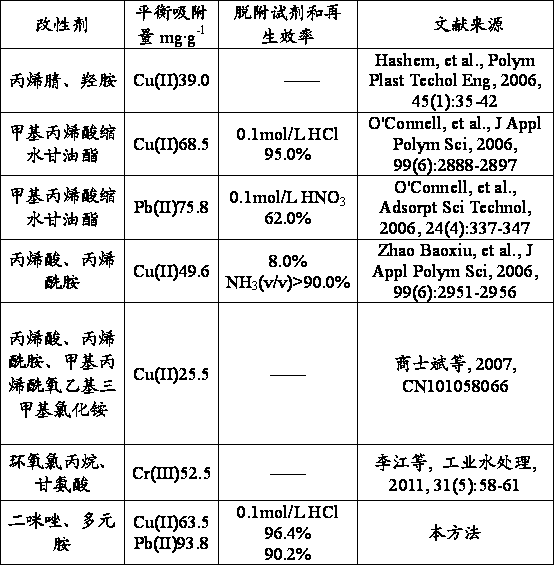
[0026] The present invention discloses a method for preparing a cellulose adsorbent for adsorbing heavy metal cations. The cellulose is a natural renewable and environmentally compatible cellulose. The specific preparation steps include:
[0027] Step 1. After crushing the cellulose to a particle size of less than 80 mesh, soak it in 15% sodium hydroxide solution at 60°C for 2 hours; the cellulose is microcrystalline cellulose, quantitative filter paper or cellulose ester; the hydroxide The dosage of sodium solution is 20~50 times of the mass of cellulose.
[0028] Step 2, adding dimethyl sulfoxide, using azeotropic distillation to remove excess water to obtain cellulose sol; wherein the mass of dimethyl sulfoxide added is 5 to 20 times the mass of cellulose; and azeotropic The entrainer for rectification is isobutanol, and the mass of the entrainer is 5 to 10 times that of dimethyl sulfoxide.
[0029] Step 3. In the presence of nitrogen medium, react the sol with diimidazole...
Embodiment 1
[0040] (1) Weigh 2g of quantitative filter paper, break it to a particle size of 80-100 mesh, put it in a 250mL three-neck flask, add 40g of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass percentage of 15%, stir and swell at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a fiber slurry 24g.
[0041] (2) Weigh 10 g of dimethyl sulfoxide and 80 g of isobutanol in a flask, stir evenly, heat and distill, and remove the water at a distillation temperature of 89.5°C to obtain cellulose sol.
[0042] (3) Infuse high-purity nitrogen gas into the three-neck flask, weigh 150 mg of 1,1'-oxalyldiimidazole and add it to the flask. After activation at 50°C for 2 hours, add 10 mL of isobutanol, stir and filter immediately, and add to the filtrate 60mg of ethylenediamine was added to it, and the reaction was carried out at 60°C for 2h.
[0043] (4) The product was reflux washed with toluene for 12 hours, filtered, and the filter cake was vacuum-dried at 50°C for 12 hours to obtain the cellulose adsorbent. The obtained ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Weigh 2g of microcrystalline cellulose, crush it to a particle size of 200 mesh, put it in a 250mL three-necked flask, add 50g of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass percentage of 18%, stir and swell at 60°C for 2h to obtain a fiber slurry 32g.
[0046] (2) Weigh 20 g of dimethyl sulfoxide and 110 g of isobutanol in a flask, stir evenly, heat and distill, and remove the water at a distillation temperature of 89.5°C to obtain cellulose sol.
[0047] (3) Infuse high-purity nitrogen gas into the three-necked flask, weigh 100 mg of 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole and add it to the flask. After activation at 50°C for 2 hours, add 10 mL of isobutanol, stir and filter immediately, and add 120 mg of melamine was reacted at 60°C for 2h.
[0048] (4) The product was reflux washed with toluene for 12 hours, filtered, and the filter cake was vacuum-dried at 50°C for 12 hours to obtain the cellulose adsorbent. The obtained product is to Cr 3+ The adsorption capacity is 57.7 mg·g ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com