Paramagnetic particle method for extracting residual DNAs (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acids) from recombinant protein product
A technology of recombinant protein and magnetic bead method, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problem of low DNA recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
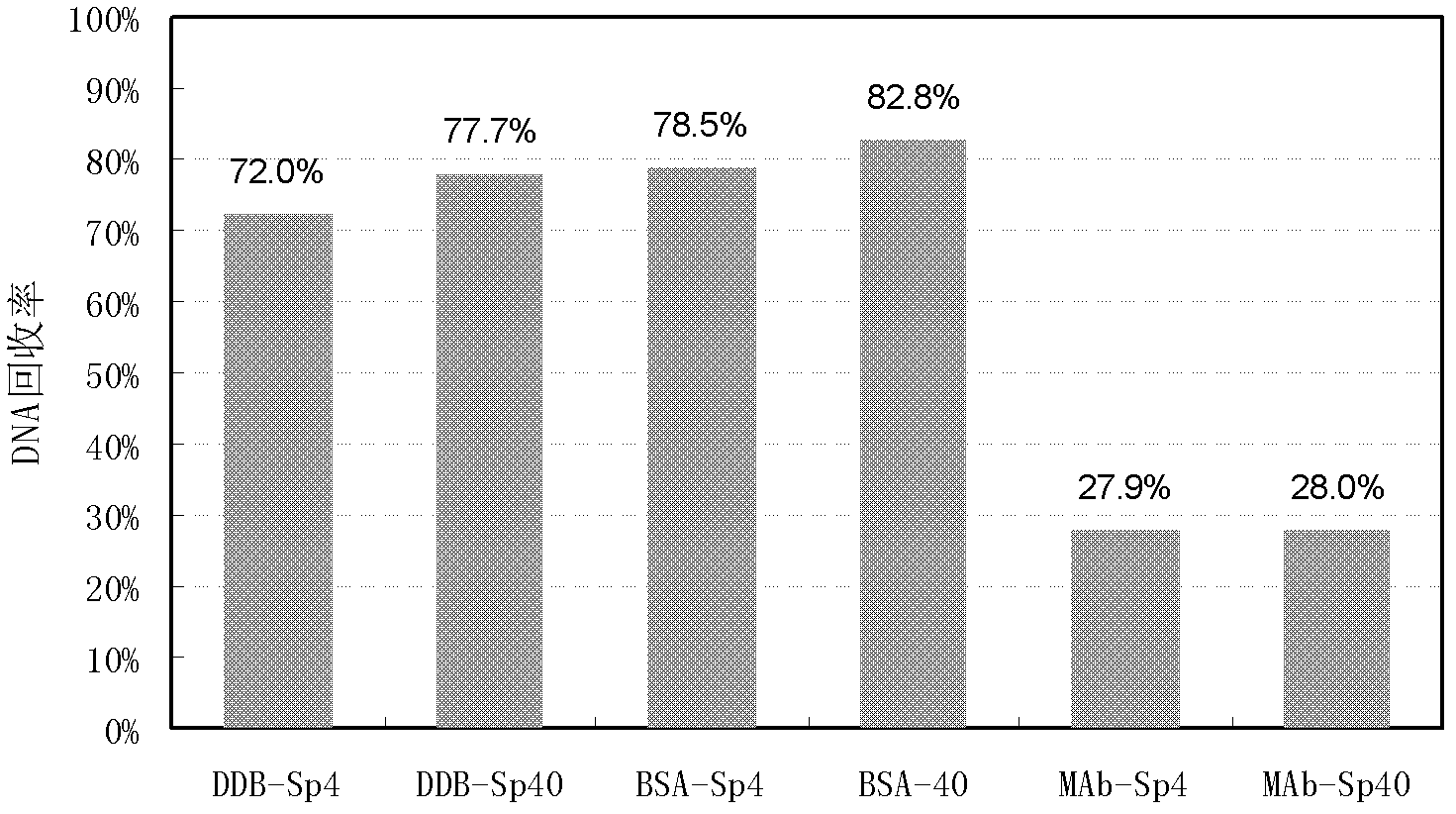
[0031] Example 1 Using conventional conditions to extract the DNA in blank buffer, BSA (bovine serum albumin) solution and antibody 1 stock solution
[0032] The blank buffer (DDB), BSA solution (44mg / ml) and antibody 1 stock solution (44mg / ml) were used as samples, and CHO DNA was added to them, DNA extraction and PCR quantification were performed using conventional methods, and the DNA recovery rate was calculated. Taking a single sample as an example, the steps are described as follows:
[0033] 1) Sample treatment: take nine 2ml DNA low-adsorption centrifuge tubes, add 100μl sample each, adjust the NaCl concentration to about 0.5M, and adjust the pH to 7-8, add 4pg CHO DNA to 3 sample tubes, and 3 samples 40 pg of CHO DNA was added to the tube.
[0034] 2) Digestion: Add 70 μl of proteinase K solution (3 mg / ml, ie 1×PK) to the sample tube, and incubate at 56° C. for 30 minutes.
[0035] 3) DNA binding: After enzyme digestion, add 360 μl freshly prepared lysate, 30 μl mag...
Embodiment 2
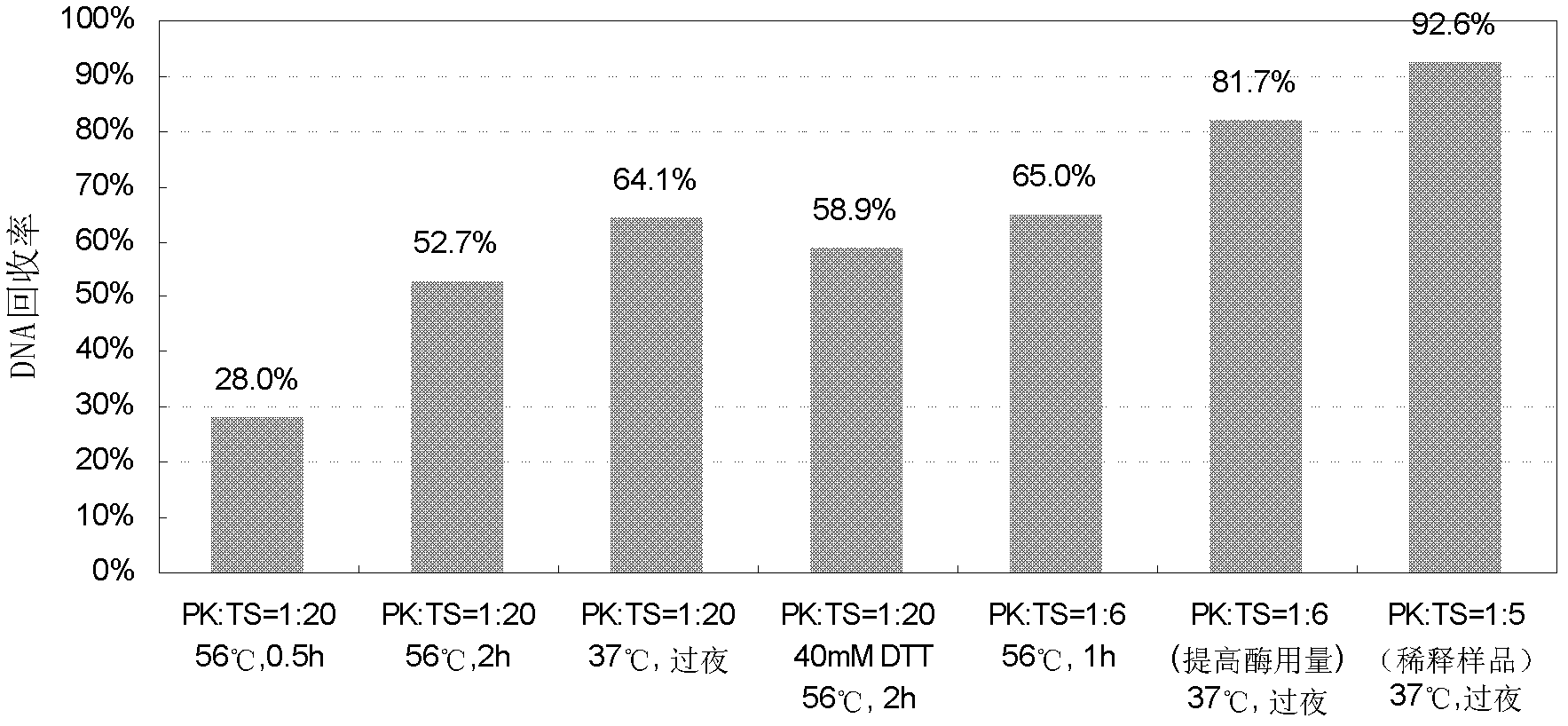
[0040] Example 2 Optimizing Enzyme Cutting Conditions
[0041] Taking the stock solution of Antibody 1 (44mg / ml) as the sample, the cleaning steps and DNA elution conditions of the conventional method were improved, and on this basis, the effects of different digestion conditions on the DNA recovery rate were compared. Proceed as follows:
[0042] 1) Sample treatment and enzyme digestion: See Table 1 for sample treatment and enzyme digestion conditions.
[0043] A. Take 100μl sample in a 2ml DNA low-adsorption centrifuge tube, adjust the NaCl concentration to about 0.5M, adjust the pH to 7-8, record it as TS, and add 3.9pg CHO DNA to each 100μl sample above, as a recovery rate sample, Denoted as TS-Sp. Three replicates were made each, and TS and TS-Sp samples were used for experiments No. 1-6.
[0044] B. First dilute the sample 4 times with PBS, take 100 μl of the sample diluent in a 2ml DNA low-adsorption centrifuge tube, adjust the NaCl concentration to about 0.5M, adjus...
Embodiment 3
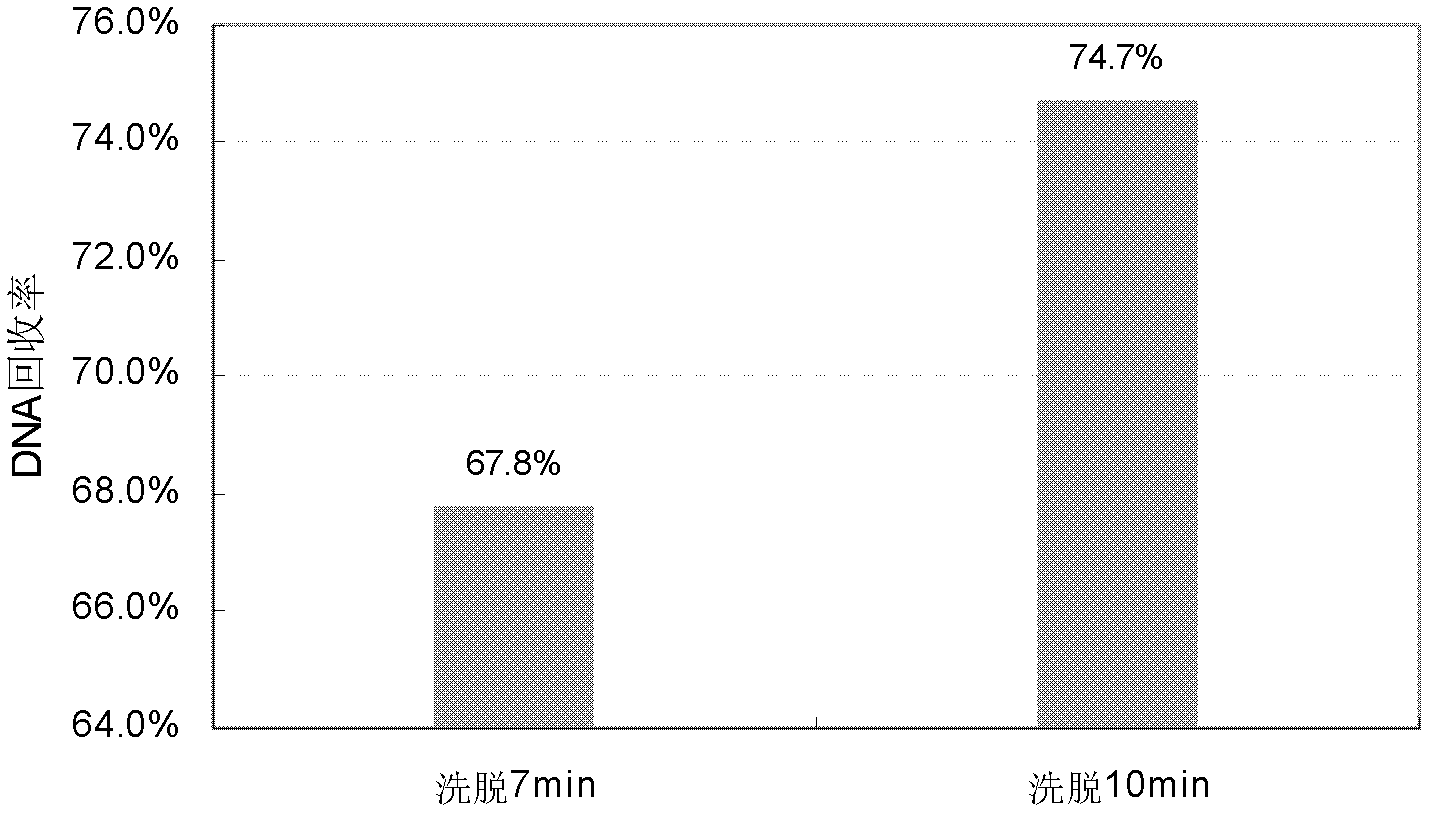
[0053] Embodiment 3 optimizes elution time
[0054] Taking the stock solution of Antibody 1 (44mg / ml) as the sample, the cleaning steps and enzyme digestion conditions of the conventional method were improved, and on this basis, the effects of different elution times on the DNA recovery rate were compared. Proceed as follows:
[0055] 1) Sample preparation: first dilute the sample 4 times with PBS, take 100 μl of the sample diluent in a 2ml DNA low-adsorption centrifuge tube, adjust the NaCl concentration to about 0.5M, adjust the pH to 7-8, and record it as PC. Due to the dilution of the initial sample, the amount of DNA added in the sample used for the sample recovery rate should be reduced accordingly, and 0.9 pg of CHO DNA was added to every 100 μl of the sample dilution, which was recorded as PC-Sp0.9. Each of PC and PC-Sp0.9 had 6 repetitions.
[0056] 2) Digestion: add 70 μl proteinase K solution to the sample tube), and incubate overnight at 37°C.
[0057] 3) DNA bi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com