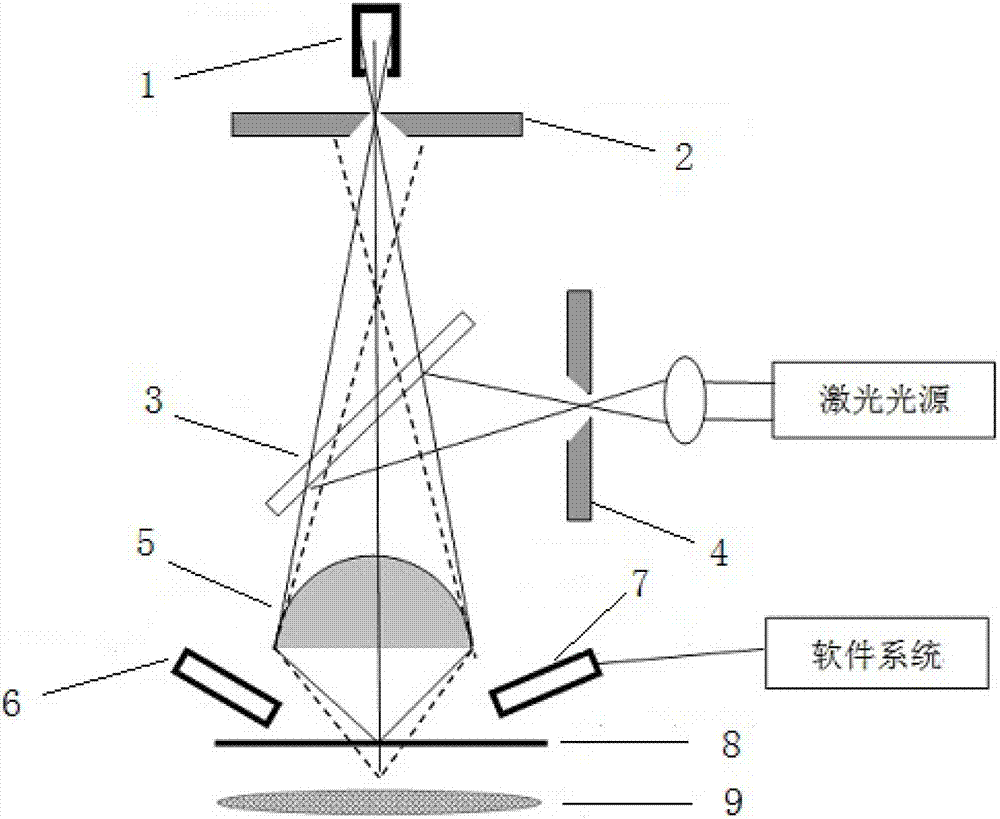
Confocal laser scanning microscope
A confocal microscope and laser scanning technology, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve problems such as impossible, inability to judge the type of phase, inability to visually observe the distribution of tiny impurities or doped phases, etc., to promote development Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
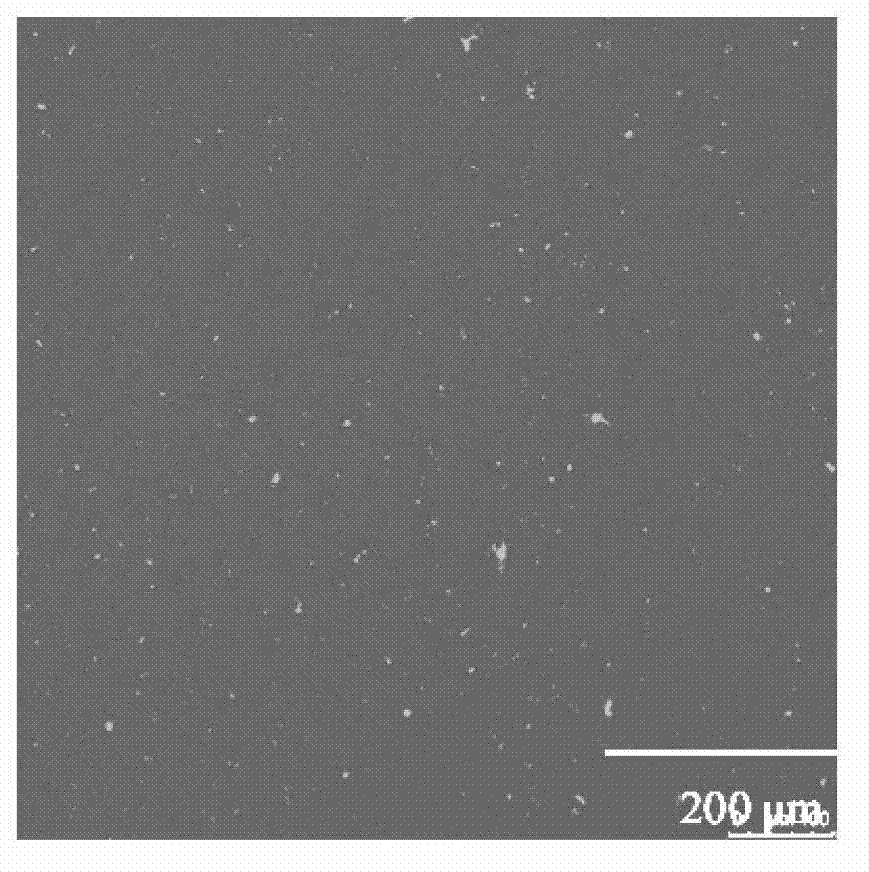
[0021] Bright-field microscopic imaging of pure copper calcium titanate thin films prepared on silicon substrates was carried out by laser scanning confocal microscopy. From figure 2 It can be seen that the inorganic thin film prepared on the opaque substrate can be well imaged, and the thin film is dense and uniform in a wide range, containing a small amount of impurities.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Bright-field microscopic imaging of ZnO-doped copper calcium titanate thin films prepared on silicon substrates was carried out by laser scanning confocal microscopy. From image 3 It can be seen that the laser scanning confocal microscope has a high resolution for material characterization, the tiny cracks in the film are clearly discernible, and the impurity phase in the film can be easily identified through the difference between light and dark.
Embodiment 3
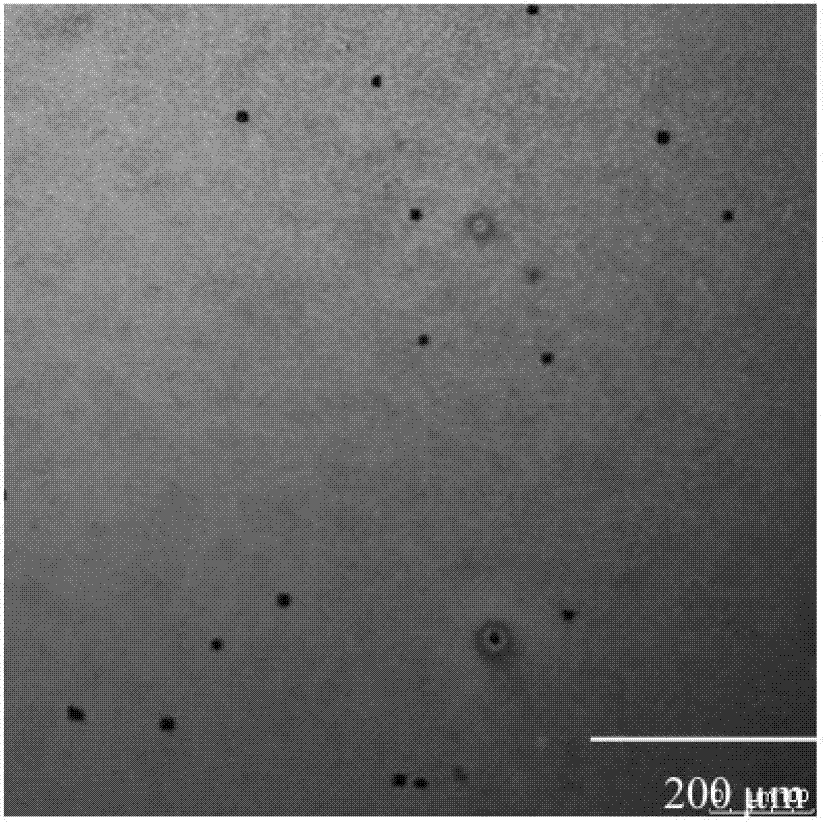
[0025] Using a 380 nm laser as the light source, the pure copper calcium titanate film and the ZnO-doped copper calcium titanate film were imaged by laser scanning confocal microscope. From Figure 4 and Figure 5 It can be seen that there are no fluorescent bright spots in the pure copper calcium titanate film, but blue fluorescent bright spots of ZnO are found in the ZnO-doped copper calcium titanate thin film. In a large field of view, the doped ZnO and the parent phase copper calcium titanate can be clearly distinguished, and the distribution, migration direction and growth process of ZnO in the parent phase are clear at a glance.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com