Method for extracting chlorogenic acid from Lonicera japonica leaves activated under catalysis of enzyme
A honeysuckle leaf, catalytic activation technology, applied in organic chemistry, separation/purification of carboxylic acid esters, etc., can solve the problem of chlorogenic acid extraction and purification process instability, affecting the economic development value of chlorogenic acid products, and increasing production energy consumption. and cost issues, to achieve the effect of ensuring extraction energy efficiency and product quality, reducing environmental treatment costs, and low production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The specific steps of a method for extracting chlorogenic acid by enzymatically activating honeysuckle leaves are as follows:
[0022] (1) Raw material pretreatment
[0023] Wash the honeysuckle leaves, dry them, place them in an oven, bake them in an oven at 100°C for 60 minutes, take them out, crush them with a pulverizer, and pass through a 60-mesh molecular sieve to obtain honeysuckle leaves with a particle size of less than 60 mesh. Subpackage, spare.
[0024] (2) Enzymolysis reaction
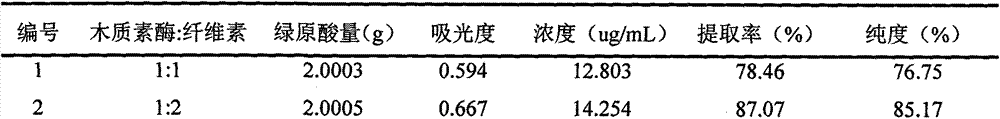
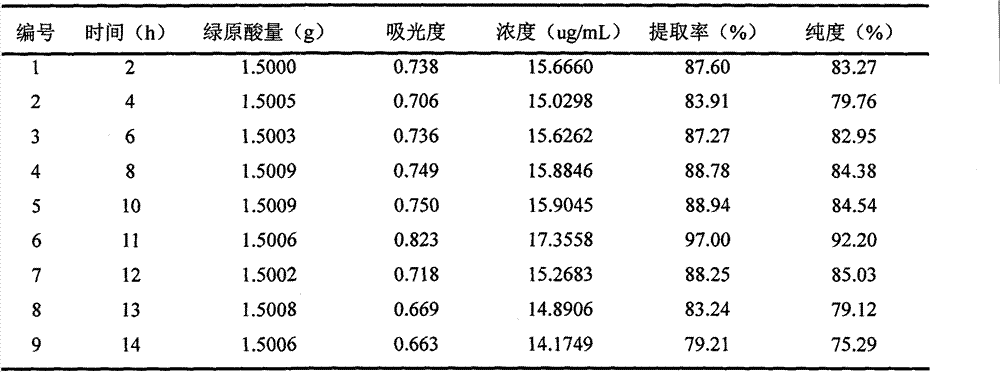
[0025] After the step (1) is completed, the mass of the honeysuckle leaf solid waste pretreated in the step (1): the mass of the enzyme: the volume ratio of water is 1:0.1:25. The enzyme is ligninase: cellulase with a mass ratio of 1:2. In the raw material pretreated in step (1), add compound enzyme and water, stir evenly, then use sulfuric acid solution to adjust the pH value of the system to 4, and then place the mixed solution after adjusting the pH value in a shaker, After p...
Embodiment 2
[0031] A method for extracting chlorogenic acid by enzymatically activating honeysuckle leaves, same as in Example 1, wherein:
[0032] In step (1), the mesh number of honeysuckle leaves selected is 160 mesh, the oven temperature is 110° C., and the drying time is 30 minutes.
[0033] In step (2), the mass of honeysuckle leaf solid waste: the mass of enzyme: the volume ratio of water is 1:0.05:5, and the enzyme is ligninase: the mass ratio of cellulase is 1:0.5. A hydrochloric acid solution was used to adjust the pH of the system to 8, and the temperature of the water bath was 65°C. Enzymolysis activated honeysuckle leaf base material for 2 hours.
[0034] In step (3), the mass of the pretreated honeysuckle leaf solid waste: the volume ratio of the ethanol solution is 1:8. The ultrasonic power is 40W, the ultrasonic temperature is 55°C, and the ultrasonic time is 10min; the filtrate is centrifuged at 4000r / min, and the centrifugation time is 5min.
[0035] In the (4) step, ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] A method for extracting chlorogenic acid by enzymatically activating honeysuckle leaves, same as in Example 1, wherein:
[0038] In the (1) step, the mesh number of honeysuckle leaves is 20 mesh, the oven temperature is 85° C., and the drying time is 90 minutes.
[0039] In the (2) step, the quality of the honeysuckle leaf solid waste after pretreatment: the quality of enzyme: the volume ratio of water is 1: 0.3: 30, and described enzyme is ligninase: cellulase mass ratio is 1: 3. A hydrochloric acid solution was used to adjust the pH of the system to 3, and the temperature of the water bath was 20°C. Enzymolysis activated honeysuckle leaf base material for 14 hours.
[0040] In step (3), the mass of honeysuckle leaf enzymolysis activation base material: the volume ratio of ethanol solution is 1:15. The ultrasonic power is 200W, the ultrasonic temperature is 25°C, and the ultrasonic time is 45min; the filtrate is centrifuged at 2500r / min, and the centrifugation time ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com