Process for extracting lignin from lignocellulose biomass
A technology for lignocellulose and biomass, which is applied in the technical field of extracting lignin, can solve the problems of low extraction rate, affecting processing efficiency, and inability to completely separate out lignin, and achieves the effects of high extraction efficiency and concise process route.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
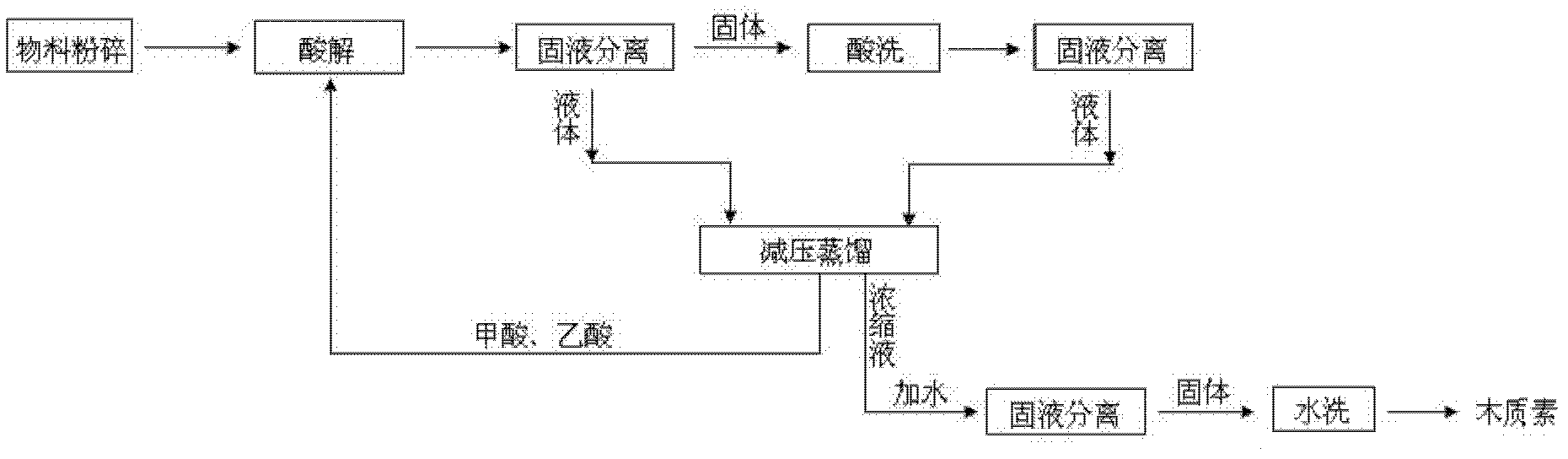
[0043] In the present embodiment, first corn cob (mass component composition: moisture 18.73%, cellulose 39.33%, hemicellulose 30.73%, lignin 29.94%) is crushed and crushed to a particle size of 0.5-20cm, preferably 2- 5cm.
[0044] The comprehensive utilization technique of lignocellulosic biomass described in this embodiment comprises the steps:
[0045] (1) After the biomass raw material is crushed and pretreated, use an organic acid solution containing 90% formic acid, 5% acetic acid and 5% water to carry out acid hydrolysis of the treated lignocellulosic biomass, and control the reaction temperature 70°C, reacting for 150 minutes, the liquid-solid mass ratio of the organic acid liquid and the biomass raw material is 1:6, and the obtained reaction liquid is subjected to solid-liquid separation for the first time;
[0046] Add the solid obtained from the above separation to an organic acid liquid containing 90% formic acid, 5% acetic acid and 5% water for acid washing at a...
Embodiment 2
[0053] In the present embodiment, first corn cob (mass component composition: moisture 18.73%, cellulose 37.22%, hemicellulose 33.73%, lignin 29.05%) is crushed and crushed to a particle size of 0.5-20cm, preferably 2- 5cm.
[0054] The comprehensive utilization technique of lignocellulosic biomass described in this embodiment comprises the steps:
[0055] (1) After the biomass raw material is crushed and pretreated, use an organic acid solution containing 80% formic acid and 10% acetic acid and 10% water to carry out acid hydrolysis on the treated lignocellulosic biomass, and control The reaction temperature is 140°C, the reaction is 60min, the liquid-solid mass ratio of the mixed acid solution of formic acid and acetic acid to the biomass raw material is 1:10, and the obtained reaction solution is subjected to solid-liquid separation for the first time;
[0056] Add the solid obtained from the above separation to an organic acid liquid containing 80% formic acid, 10% acetic...
Embodiment 3
[0063] In the present embodiment, first corn cob (mass component composition: moisture 16.25%, cellulose 31.45%, hemicellulose 34.77%, lignin 33.78%) is crushed and crushed to a particle size of 0.5-20cm, preferably 2- 5cm.
[0064] The comprehensive utilization technique of lignocellulosic biomass described in this embodiment comprises the steps:
[0065] (1) After the biomass raw material is pulverized and pretreated, the lignocellulosic biomass after treatment is acid-hydrolyzed by using an organic acid solution containing 60% formic acid and 30% acetic acid and 10% water to control The reaction temperature is 120°C, the reaction is 120min, the liquid-solid mass ratio of the organic acid liquid and the biomass raw material is 1:8, and the obtained reaction liquid is subjected to solid-liquid separation for the first time;
[0066] Add the solid obtained from the above separation to an organic acid solution containing 50% formic acid, 40% acetic acid and 10% water for acid ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com