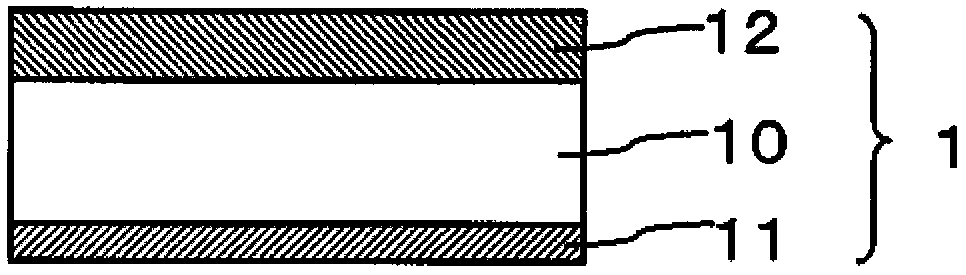
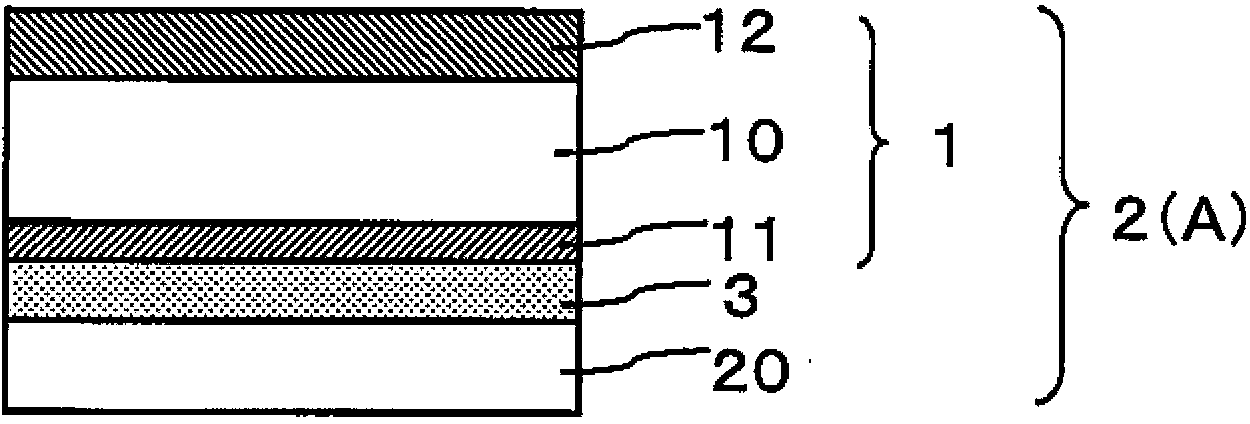
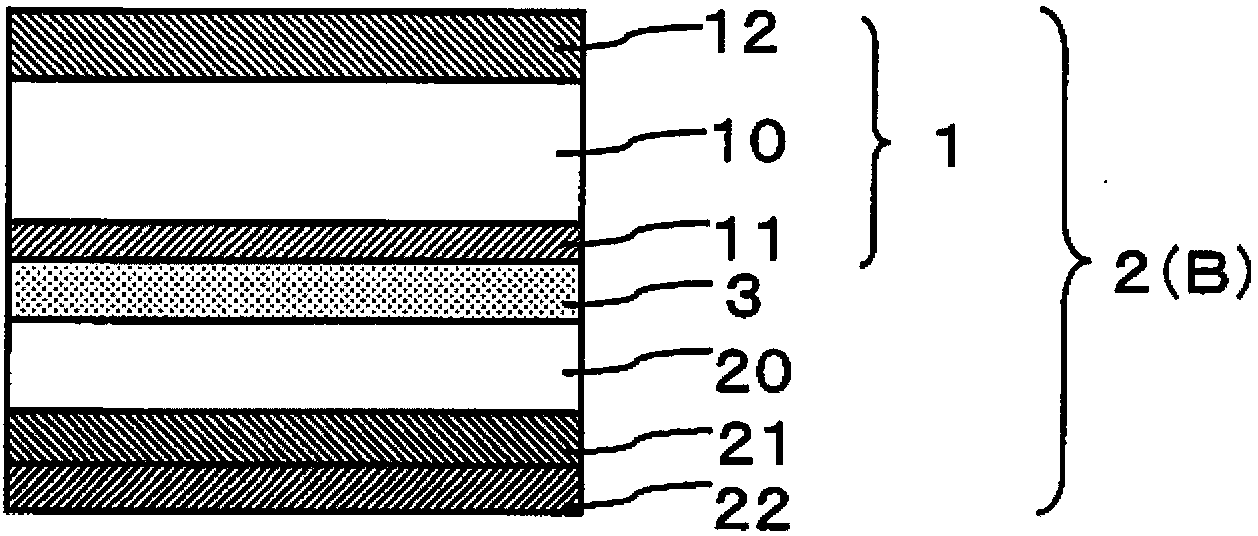
Method for producing laminated film
一种制造方法、薄膜的技术,应用在层叠薄膜领域,能够解决透明导电性薄膜白化等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0105] (Formation of hard coat layer)
[0106] As a hard coat forming material, it was prepared as follows: Add 5 parts by weight of 1-hydroxy-cyclohexyl-phenyl to 100 parts by weight of acrylic and polyurethane resin (UNIDIC17-806 manufactured by DAINIPPON INK AND CHMICALS INCORPORATED (DIC)) Ketone (IRGACURE184, manufactured by Ciba Specialty Chemicals Co., Ltd.) was diluted with toluene to a concentration of 30% by weight as a photopolymerization initiator.
[0107] The material for forming the hard coat layer was applied as a first transparent resin film on one side of a polyethylene terephthalate film having a thickness of 125 μm, and dried at 90° C. for 3 minutes. Thereafter, use a high-pressure mercury lamp at a cumulative light intensity of 300mJ / cm 2 Under UV irradiation, a hard coat layer with a thickness of 7 µm was formed.
[0108] (Preparation of the first lamination film: Formation of the cured layer)
[0109] Prepare a cured layer forming material containing ...
Embodiment 2
[0117] In the preparation of the first laminated film (formation of the cured layer) in Example 1, except for the use of 2-hydroxy-1-{4-[4-(2-hydroxy-methyl-propionyl)benzyl]phenyl}- 2-Methyl-propan-1-one (IRGACURE127, manufactured by Ciba Specialty Chemicals, 10% thermal weight loss temperature in the thermal weight loss test: 263°C) was used as a photopolymerization initiator, and a second laminated film was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1. . In addition, crystallization treatment was performed in the same manner as in Example 1.
reference example 1
[0121] 1-Hydroxy-cyclohexyl-phenyl ketone (IRGACURE184, manufactured by Ciba Specialty Chemicals, Inc., 10% thermal weight loss temperature in the thermal weight loss test: 154°C) was used in the production of the first laminated film of Example 1 (formation of the cured layer) A second laminated film was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the drying temperature of the coating layer was changed to 80° C. as the photopolymerization initiator, and heat treatment was performed at 150° C. for 1 minute after ultraviolet irradiation. In addition, crystallization treatment was performed in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0122] The following evaluations were performed on the first laminated film obtained in Examples and Comparative Examples and the second laminated film (transparent conductive laminated film) subjected to the crystallization treatment. The results are shown in Table 1. In addition, Table 1 describes the thermal weight loss of the photoinitia...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| heat shrinkage ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com