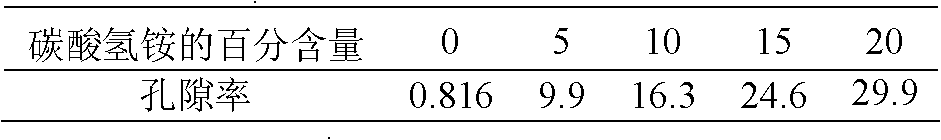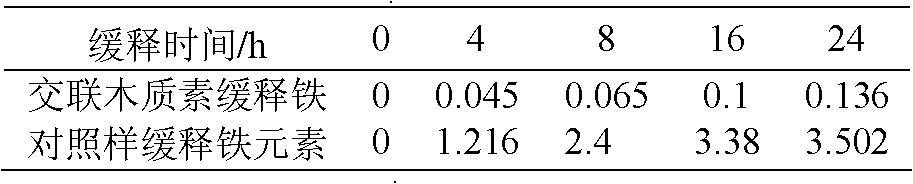Porous lignin particle composite fertilizer preparation method
A technology of lignin and compound fertilizer, which is applied in the direction of fertilization device, fertilizer mixture, application, etc., and can solve problems such as poor effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Weigh 3.0g of industrial lignin and add 0.6mL of 20% NaOH solution, then adjust the pH to 10 with distilled water, then add 4.8mL of formaldehyde, mix well and transfer to a 100mL three-necked bottle, stir in a constant temperature water bath at 90°C to generate crosslinking React for 2 hours, cool to prepare lignin cross-linked body A, and then mix A, an appropriate amount of ammonium bicarbonate and a lignin particle setting agent evenly. The pH was adjusted to 5 with 10% HCl solution, and 2.03 g of urea and 0.4 g of ferric nitrate were added. React in a water bath at 90°C for 2 hours to fully react the lignin cross-linking compound to obtain a porous lignin compound fertilizer D with a nitrogen content of 23.96% and an iron content of 0.375% (see the relationship between the amount of ammonium bicarbonate and the porosity) Table 1), mix the porous lignin compound fertilizer D with peat, starch, and water in a blender at a ratio of 50:5:42:3, and use a granulator to e...
Embodiment 2
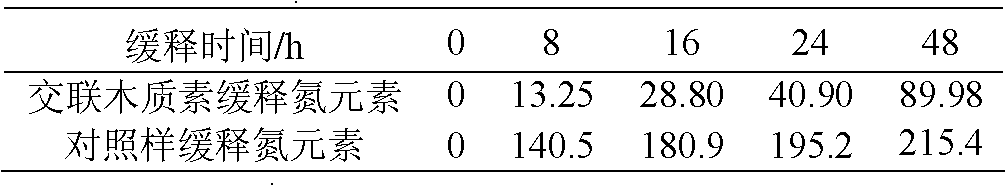
[0025] Accurately weigh 1.0 g of the porous granular lignin compound fertilizer in the above-mentioned Example 1 and place it in a 250 mL dry conical flask, add 100 mL of distilled water for soaking, take 3 groups of samples for filtration at regular intervals, and accurately take 0.05 g of the test sample after the filter residue is dried. The sample was digested with sulfuric acid, and the nitrogen content of the remaining residue in the corresponding sample was measured by the Kjeldahl method, and the average value of the three sets of data was taken. After calculation, the slow release of iron element in the porous lignin particle compound fertilizer (iron content: 3.75 mg / g) within 48 hours is shown in Table 3.
[0026] Table 3 Example 1 The slow release situation (unit: mg / g) of porous lignin particle composite fertilizer iron element
[0027]
Embodiment 3
[0029] The lignin cross-linked body A was prepared according to the steps described in Example 1, and A, an appropriate amount of potassium nitrate and 1% sodium alginate were uniformly mixed. Adjust the pH value of the composite system to 5, make the A-coated potassium nitrate settle, and centrifuge to obtain the solid mixture B. B was removed by washing with water to obtain porous lignin C. Mix C and 0.4g ferric nitrate evenly, and dry to prepare porous lignin compound fertilizer D. The porous granular lignin compound fertilizer was prepared according to the granulation process described in Example 1, and the data of its porosity are shown in Table 4.
[0030] Accurately weigh 1.0 g of the porous granular lignin compound fertilizer in the above-mentioned embodiment 3 and place it in a 250 mL dry conical flask, add 100 mL of distilled water to soak, take 3 groups of samples for filtration at regular intervals, and accurately take 0.05 g of the test sample after the filter re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com