Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with strong anti-freezing capacity and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to processing of frozen blank
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and yeast strains, applied in the application, microorganism, fungi and other directions, can solve the problems of low antifreeze resistance of antifreeze yeast, difficult cell catalysis ability, low fermentation ability of frozen dough, etc., and achieve strong adaptability , Good frozen storage stability, improve the effect of freshness control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] This example illustrates the method for obtaining the target strain of the present invention, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) AFY-1 strain.
[0048] A. The starting strain and its source
[0049] Saccharomyces cerevisiae (CGMCC2.1423) was used as the starting strain, which was purchased from China Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center.
[0050] B. Activation and preservation of starting strains
[0051] (1) Preparation of solid medium:
[0052] According to mass percentage: glucose: 1%, peptone: 1%, yeast extract: 0.5%, agar: 2%.
[0053] (2) Activation of bacteria
[0054] Use an inoculation loop to take the starting strain out of the ampoule and inoculate it into the slant medium. The slant medium was placed in a biochemical incubator at 30°C for 48 hours.
[0055] (3) Strain preservation
[0056] After two successive generations of slant culture, the starting strains were preserved under the temperature conditions of 4°C and...
Embodiment 2
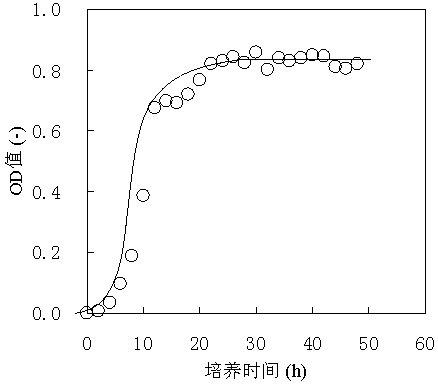
[0072] This example illustrates the method for determining the number of yeast cells of the strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) AFY-1 of the present invention.
[0073] Before measuring the number of cells, dilute the yeast liquid sample to an appropriate multiple, take 0.1 mL and 0.9 mL of methylene blue solution in a test tube, and stain for 10 min. Take 3 parallel samples for each sample.
[0074] First wipe the counting chamber and the cover glass gently with lens cleaning paper, cover the cover glass on the counting chamber, then use the inoculation loop to take the treated sample solution, touch the edge of the cover glass, and make the bacterial solution along the slide The gap with the coverslip penetrates into the counting chamber and fills the chamber.
[0075]Place the counting plate on the stage of the microscope, first find the large grid on the counting plate under the low power lens, then move the counting chamber to the center of the fie...
Embodiment 3
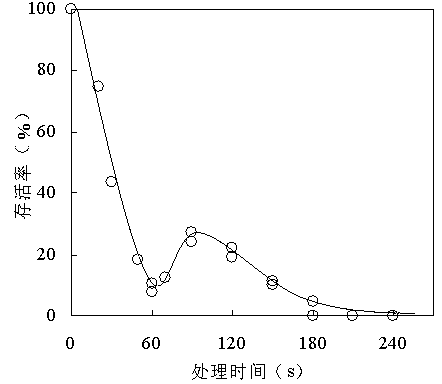
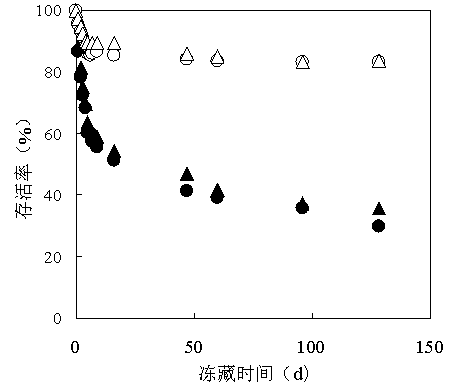
[0077] This example illustrates the method for determining the content of intracellular components of the strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) AFY-1 strain of the present invention.
[0078] The content of trehalose, glycerol and amino acid in the starting yeast and freeze-resistant yeast cells before freezing and after freezing was determined. The freezing conditions are -20°C, 24h.
[0079] 1) Determination of trehalose and glycerin content
[0080] (1) Extraction of trehalose and glycerol in yeast cells
[0081] Accurately weigh 1.0g of yeast slime and place it in a beaker, add 20mL of deionized water to make a bacterial suspension, and then put the beaker into a microwave oven (PJ23C-SC1, Midea Microwave Manufacturing Co., Ltd.), at 2450MHz (medium-high heat) Under treatment 3 times, 25s each time, heated until the bacterial suspension slightly boiled to break the yeast cells, each time the temperature of the bacterial suspension was cooled to room ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com