Crosspoint-type variable-esistance non-volatile storage device
A non-volatile storage, resistance change technology, applied in information storage, static storage, digital storage information, etc., to achieve the effect of easy manufacturing and high practical value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
reference example 1
[0163] [Description of circuit structure]
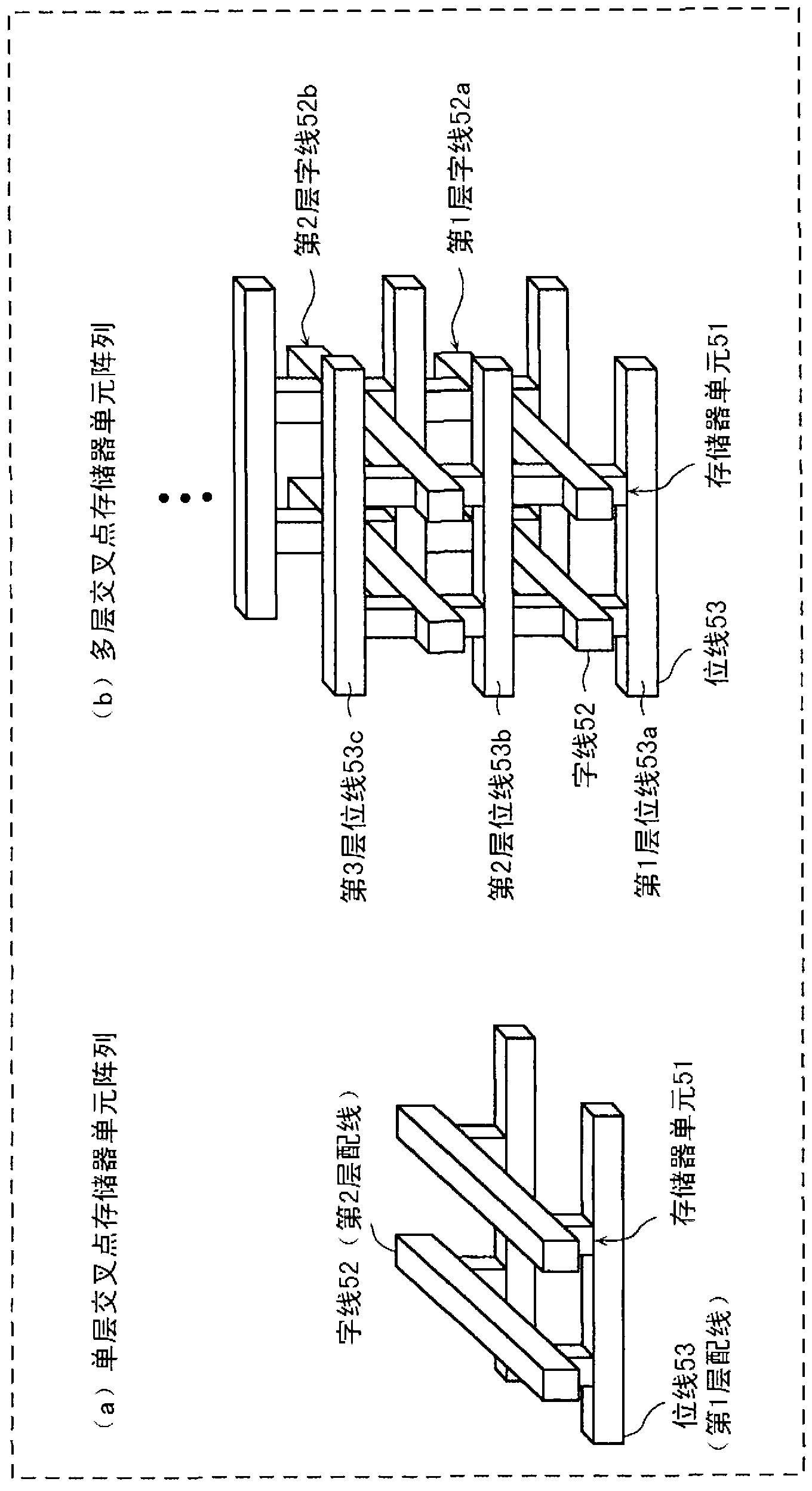
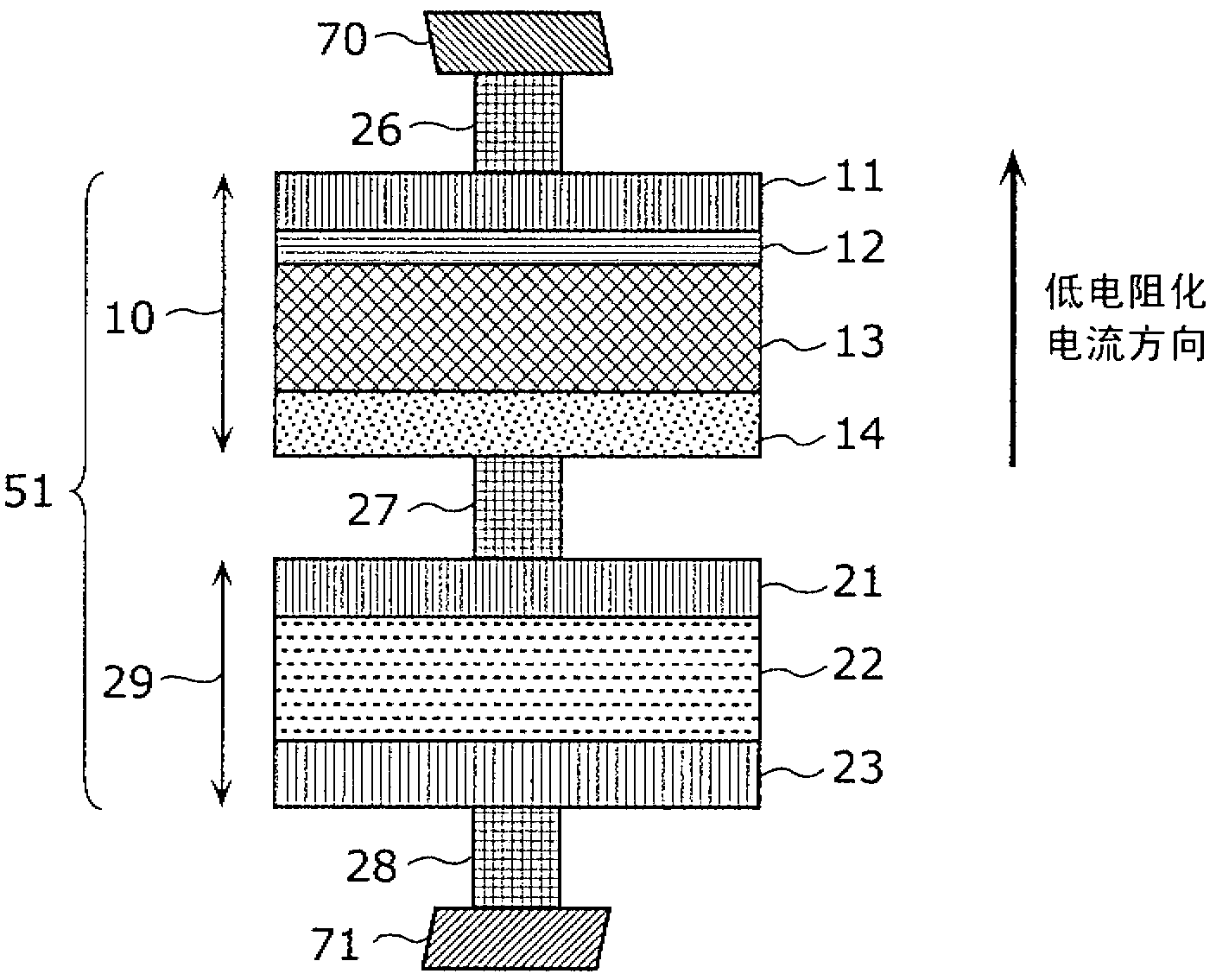
[0164] Picture 10 This is a diagram showing a cross-sectional structure of a memory cell 51 that constitutes a cross-point variable resistance nonvolatile memory device of a memory cell array with a multilayer structure of Reference Example 1.
[0165] The memory cell 51 has a structure in which the following elements are sequentially stacked: a first electrode 23 made of tantalum nitride (TaN); a current control layer 22 made of nitrogen-deficient silicon nitride; a second electrode 21 made of TaN; Use oxygen-deficient tantalum oxide (TaO x ) The first variable resistance layer 13 constituted; it is formed by oxidizing the first variable resistance layer 13 in an oxygen plasma atmosphere, and the oxygen deficiency is less than TaO x TaO y (X <y) A second variable resistance layer 12 composed of; and a third electrode 11 composed of platinum (Pt). A lower wiring 71 made of aluminum (Al) is arranged in the lower layer of the memory cell 5...
reference example 2
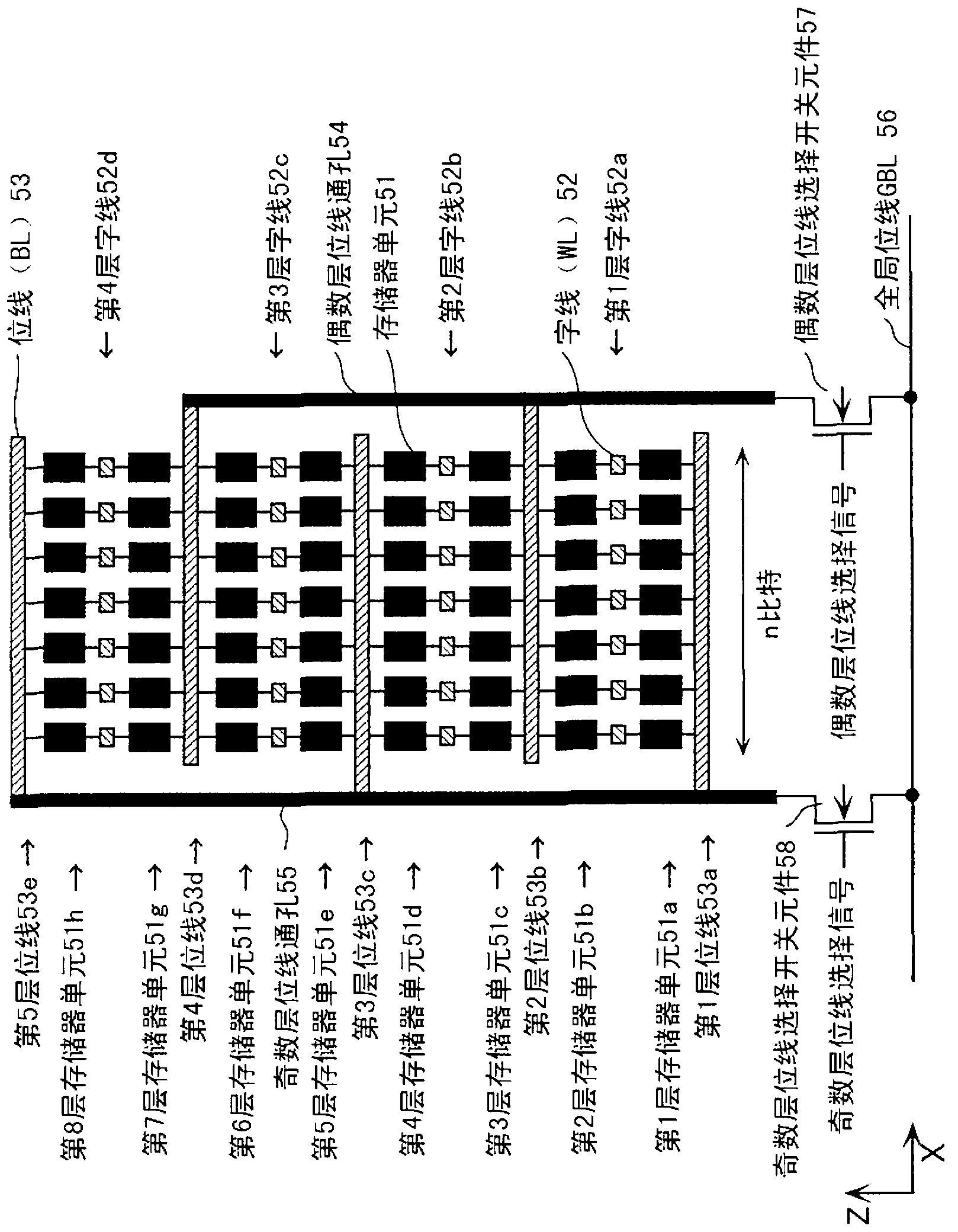
[0412] In Reference Example 1, in the writing operation to the nonvolatile memory device of the multi-layer cross-point structure, the following cases are described. Depending on the memory array layer to be written, the flow to the memory cells belonging to the memory array layer The direction of the current in the direction of lower resistance is to activate only the transistor of the current limiting element of the N-type current limiting element 90 or the P-type current limiting element 91, which produces a greater substrate bias effect, to perform a low-resistance operation, and reduce The current limit of resistive writing is the action mode of the source follower (ie, the source follower mode).
[0413] In Reference Example 2, it is assumed that the N-type current limiting element 90 and the P-type current limiting element 91 have the same structure, but the control method is different. Depending on the memory array layer to be written, a desired voltage is applied to the ...
Embodiment approach )
[0694] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In addition, the embodiments described below are all used to show a preferred specific example of the present invention. The numerical values, shapes, materials, components, arrangement positions and connection methods of components, steps, order of steps, etc. shown in the following embodiments are merely examples, and the gist of the invention is not limited. The present invention is limited only by the claims. Therefore, with regard to the constituent elements of the following embodiments, the constituent elements not described in the independent claims representing the highest concept of the present invention are not necessarily the constituent elements required to realize the subject of the present invention, but merely constitute more The components of the preferred mode are described.
[0695] In addition, in the following embodiments, the description will...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com