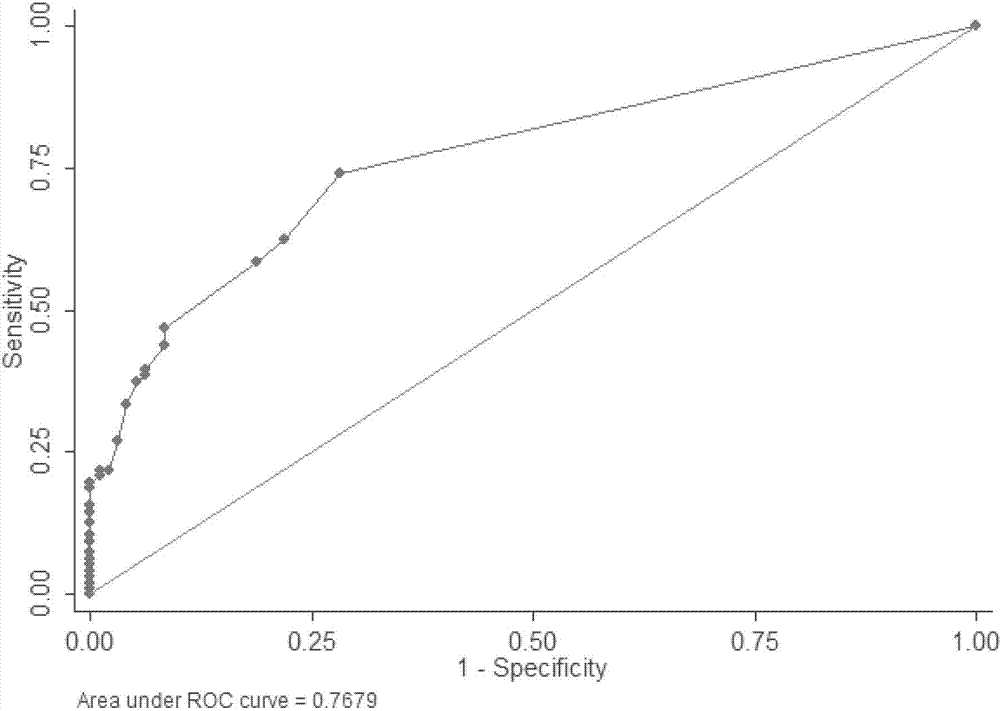
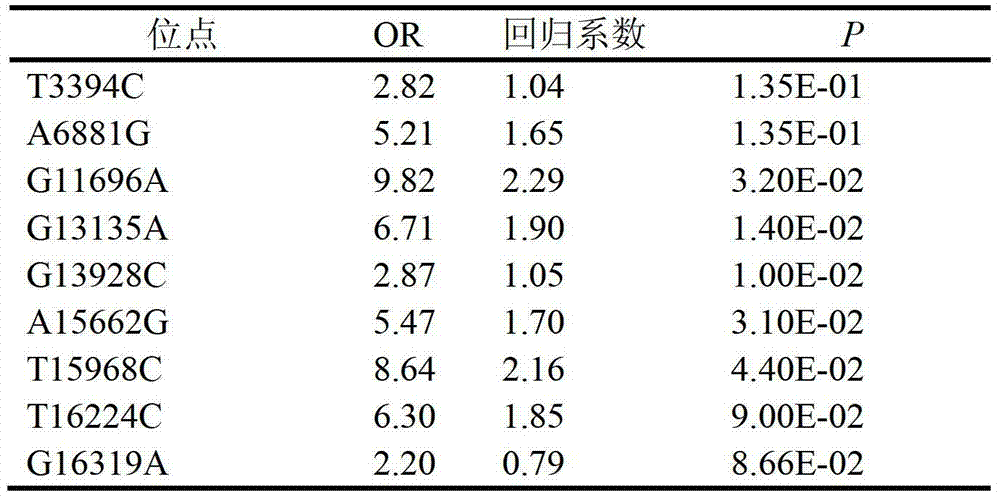
A mitochondrial DNA SNP marker associated with noa of unknown clinical cause and its application
A marker, unknown technology used in genetic engineering and reproductive medicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Example 1: collection of samples and arrangement of sample data
[0082] The inventor collected a large number of blood samples of NOA patients from the Reproductive Medicine Center of Nanjing Medical University from June, April, 2007 to January, 2011. After sorting out the sample data, the inventor selected 1409 samples that met the following criteria Experimental samples for genome-wide microarray scanning and single SNP TaqMan genotyping:
[0083] 1. Repeated semen quality test / testicular biopsy, diagnosed as azoospermia;
[0084] 2. The semen of one ejaculation was centrifuged without spermatozoa, and obstructive etiology was ruled out;
[0085]3. Sexual function is normal. Exclude patients with known causes such as cryptorchidism, history of vascular trauma, orchitis, vas deferens obstruction, vasectomy, polychromosomal abnormalities, and Y chromosome azoospermia factor microdeletion;
[0086] 4. Healthy male controls matched with the age of the cases.
[0087]...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Whole Genome Scanning of SNP in Example 2 Peripheral Blood DNA
[0089] Among the above-mentioned eligible 192 patients with NOA of unknown clinical cause and 192 healthy male controls, the two groups were age-matched. The two groups of people were sequenced by Illumina to obtain relevant results. The specific steps are:
[0090] 1. Add hemolysis reagent (i.e. lysate, 40 parts) to the peripheral blood stored in a 2ml cryopreservation tube. Dilute the TrisHcl solution to 2000ml, the same below), mix it upside down and transfer it completely;
[0091] 2. Removal of red blood cells: Fill the 5ml centrifuge tube to 4ml with hemolysis reagent, mix by inverting, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 10min, and discard the supernatant. Add 4ml of hemolysis reagent to the precipitate, invert and wash again, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 10min, and discard the supernatant;
[0092] 3. Extract DNA: Add 1ml of extract solution to the precipitate (each 300ml contains 122.5ml0.2M sodium chlorid...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Example 3 TaqMan Genotyping of Single Genetic Variations
[0102] The SNPs found to be associated with the onset of NOA of clinically unknown cause by the above genome-wide scan were detected in another 536 cases of NOA of clinically unknown cause and 489 healthy male controls. The specific steps were as follows:
[0103] 1. Add the hemolysis reagent to the peripheral blood stored in the 2ml cryopreservation tube, mix it upside down and transfer it completely;
[0104] 2. Removal of red blood cells: Fill the 5ml centrifuge tube to 4ml with hemolysis reagent, mix by inverting, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 10min, and discard the supernatant. Add 4ml of hemolysis reagent to the precipitate, invert and wash again, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 10min, and discard the supernatant;
[0105] 3. Extract DNA: Add 1ml of extract solution and 8μl of proteinase K to the precipitate, fully oscillate and mix on the shaker, and bathe overnight at 37°C;
[0106] 4. Remove protein: add 1ml of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com