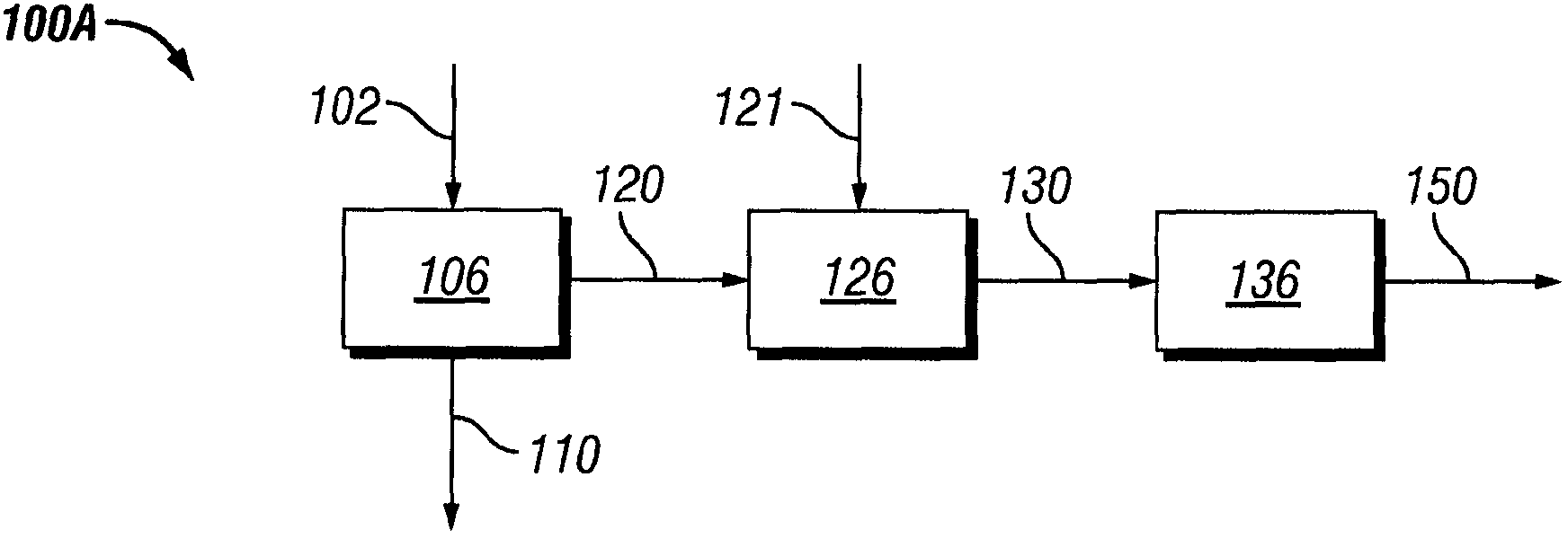
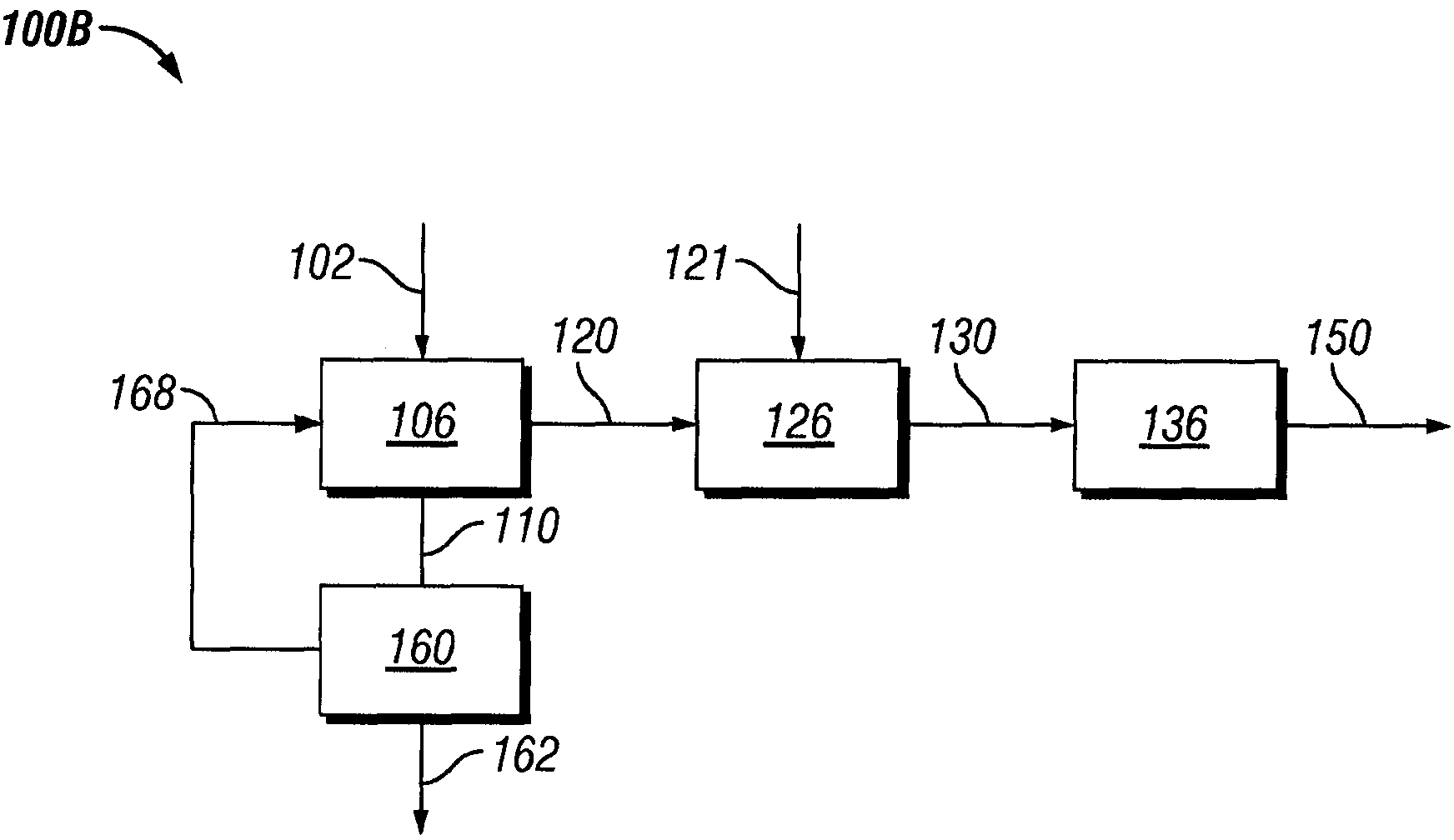
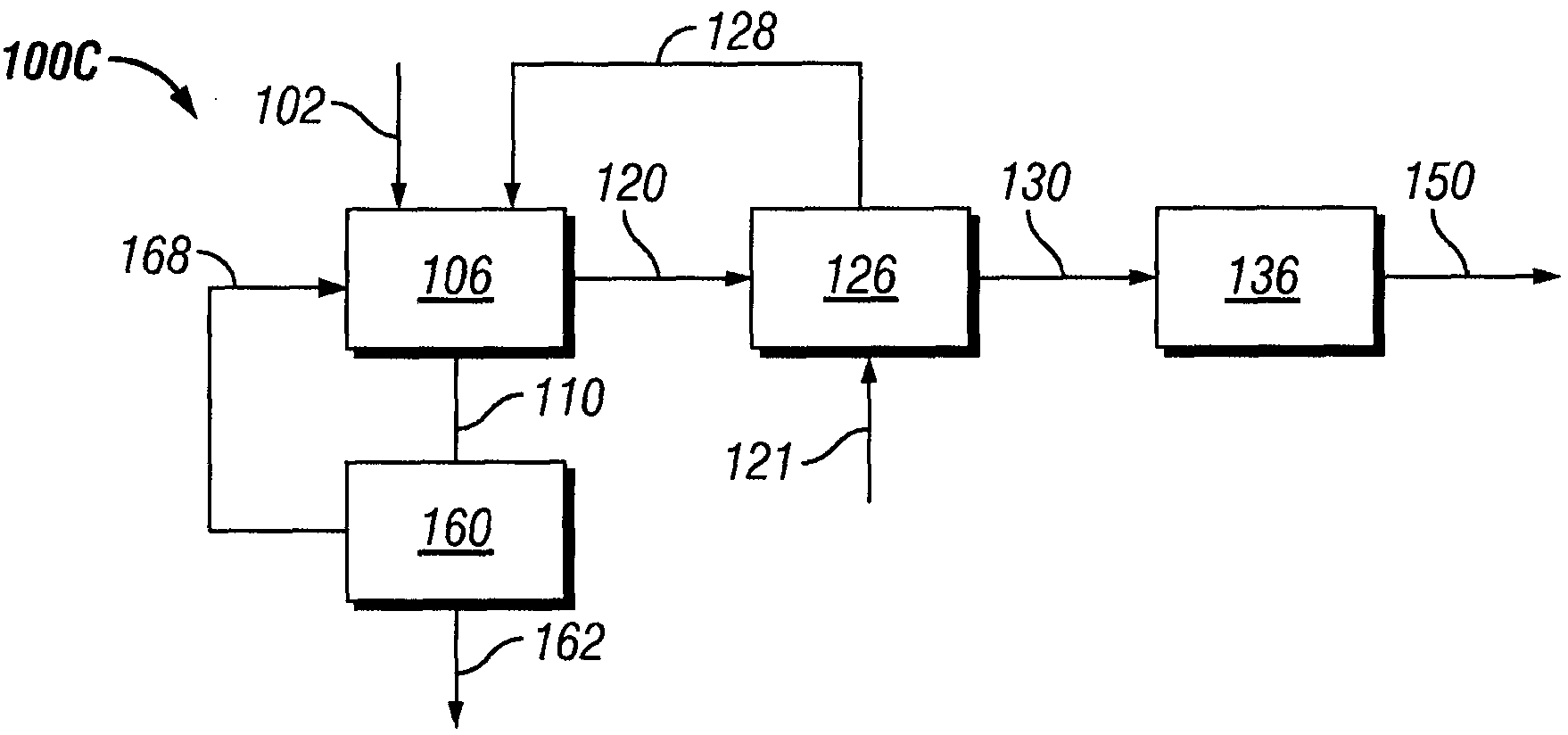
Process to produce biofuel from biomass
A liquid fuel, carbohydrate technology, applied in the field of advanced hydrocarbons, can solve the problem of costly production and net carbon saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0131] Example 1: Hydrogenolysis catalyst poisoning caused by N, S amino acids
[0132] Two Parr 5000 reactors were charged with 20 g of a 50% mixture of glycerol in deionized water and 0.35 g of a 1.9% Pt-Re / zirconia catalyst reduced with hydrogen at 400°C. Glycerol is one of the intermediates derived from monosaccharides or sugar alcohols in hydrogenolysis or hydrodeoxygenation reaction sequences and can react to form monooxygenate intermediates such as acetone, 2-propanol and ethanol. It thus represents a model component for the study of hydrogenolysis and hydrodeoxygenation.
[0133] 0.03 g of N,S aminocysteine was added to Reactor B instead of A. Reactor with 3500kPa of H 2 Pressure was added, then heated to 255°C, maintained for 6.5 hours under conditions corresponding to hydrogenolysis (HG) and hydrodeoxygenation, and then cooled for GC analysis of the product. The results showed that for Reactor A, 84.7% of the glycerol was converted to monooxygenates and other de...
Embodiment 2
[0136] Example 2: Poisoning of Pt / alumina catalysts by N,S amino acids and N-only amino acids
[0137] The experiment of Example 1 was repeated using the 5% Pt / alumina catalyst Escat 2941 (Strem Chemicals). In addition to reactors A (no amino acid) and B (1500 ppm cysteine), a third reactor C was charged with 1500 ppm alanine (N only amino acid). For Reactors A to C, the measured conversions were 56.7%, 42.3% and 45.4%, corresponding to apparent first order rate constants of 10.2, 3.0 and 3.2 / h / weight catalyst. Addition of 1500 ppm of N,S amino acids or N-only amino acids was observed to reduce the rate of hydrogenolysis or hydrodeoxygenation of glycerol by a factor of greater than 3 for the unpromoted Pt / alumina catalyst.
Embodiment 3
[0138] Example 3: Poisoning of Ru catalysts under hydrogenolysis or hydrodeoxygenation conditions
[0139] Example 1A and B were repeated with 5% Ru / C Escat 4401 catalyst (Strem Chemicals, 50% wet) with an initial loading of 6000 kPa H 2 . Reactor A (no amino acid) had a conversion of 56.5%, while Reactor B (1500ppm cysteine) had a conversion of only 9%. The apparent first order rate constant for B (1500 ppm cysteine) is only 1.7 / h / wt catalyst, while the rate constant for Reactor A is 14.7 / h / wt catalyst. This result indicates the poisoning of the Ru-based catalyst by amino acid in the tests carried out under hydrogenolysis or hydrogenolysis conditions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com