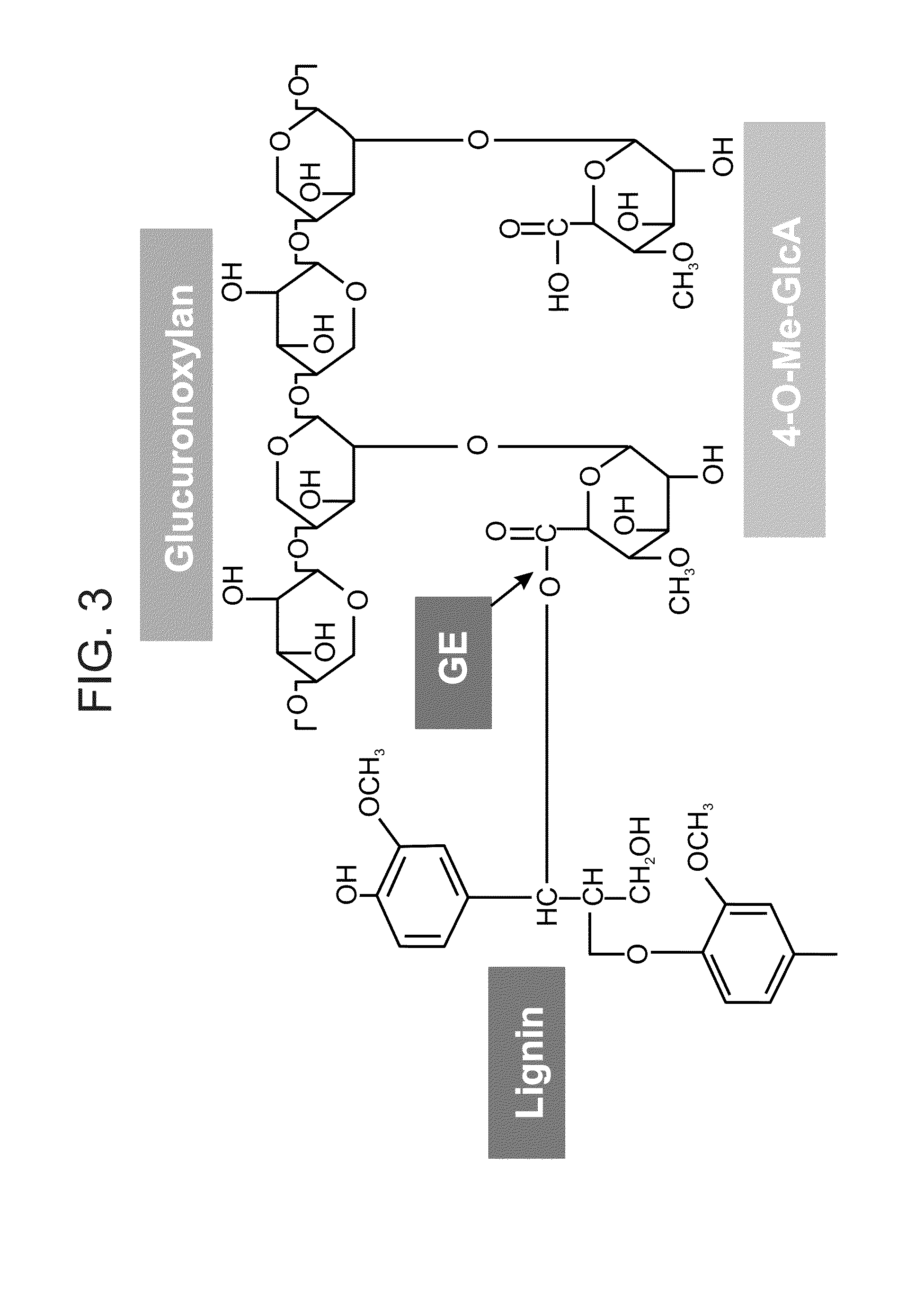
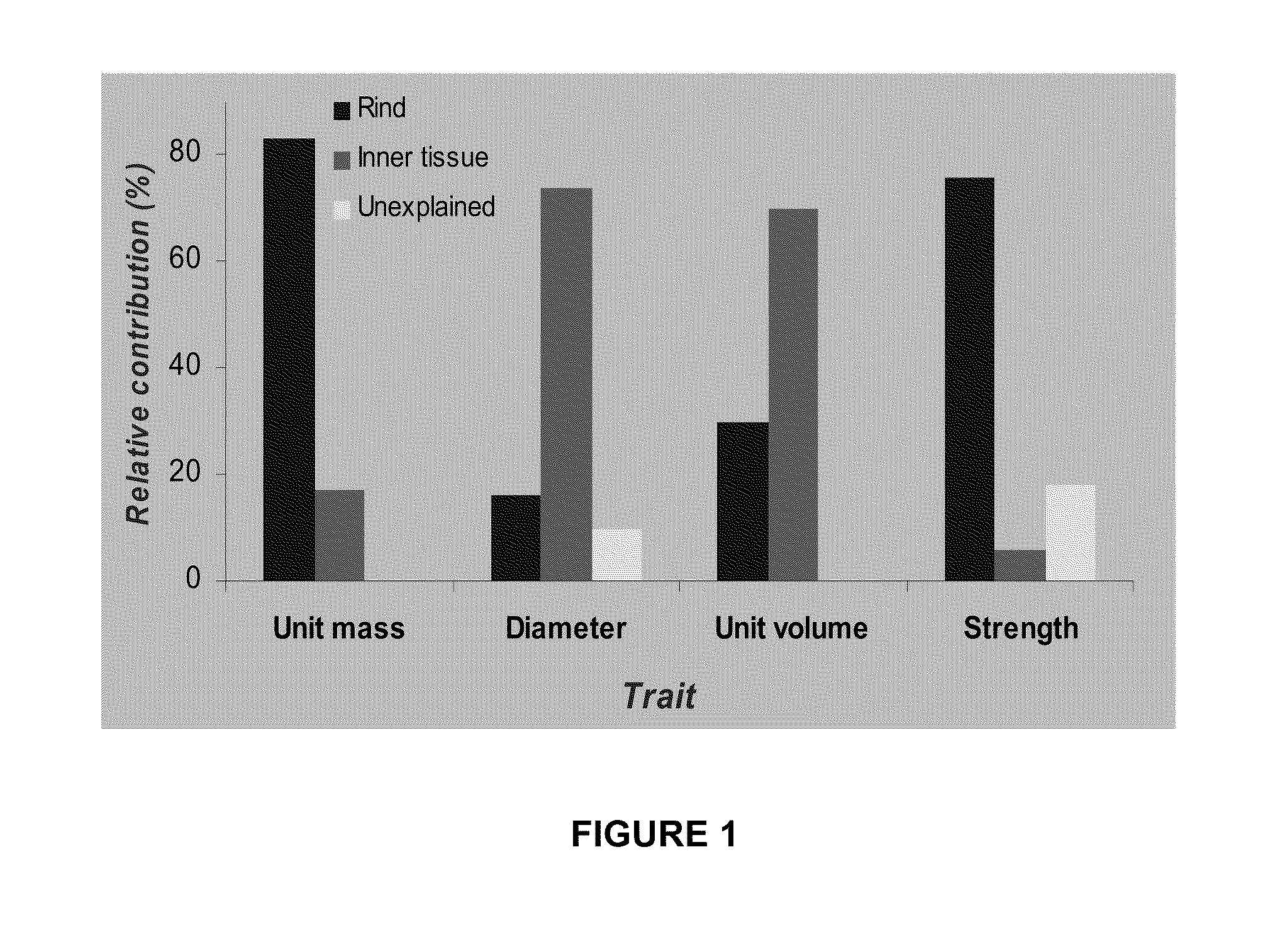
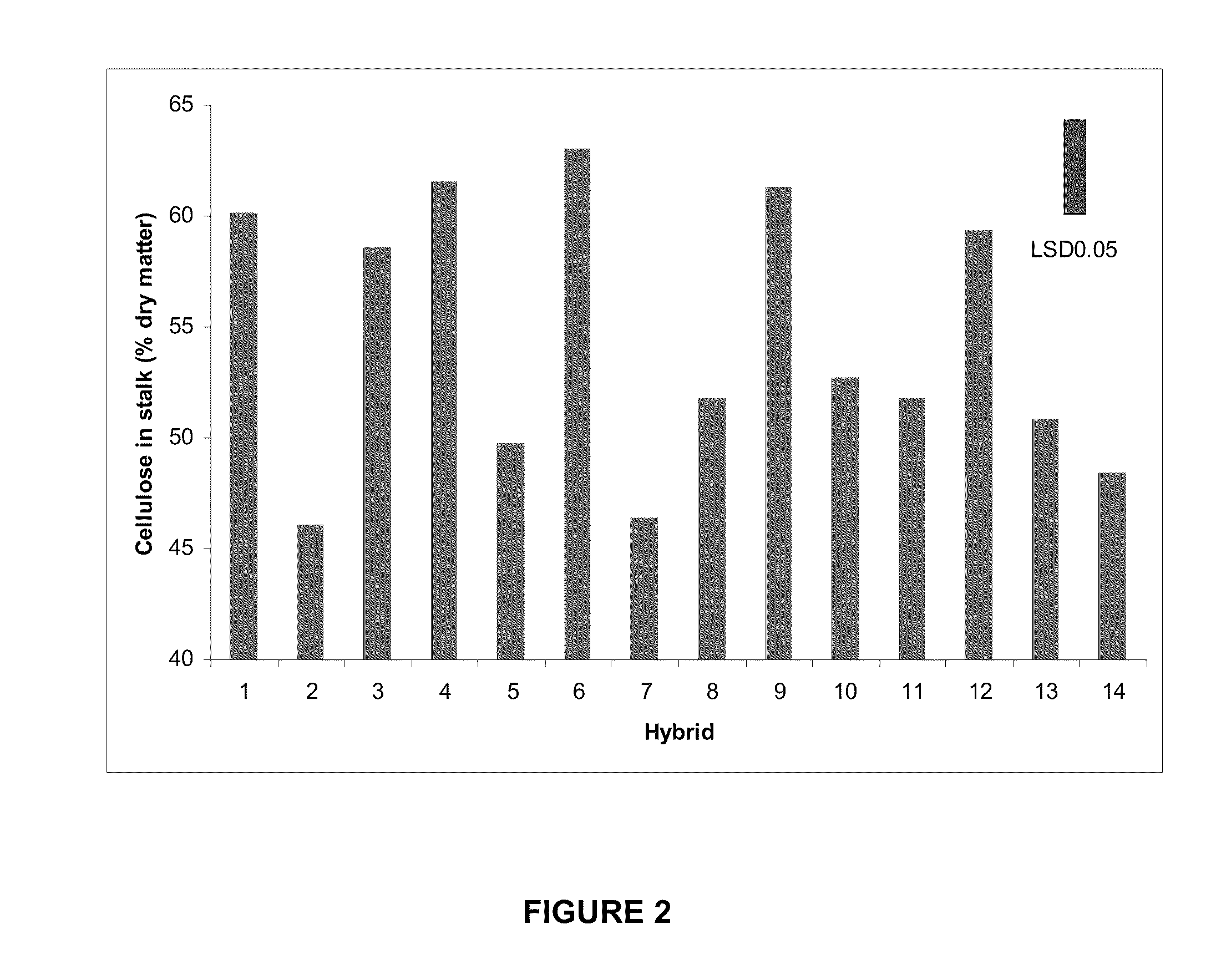
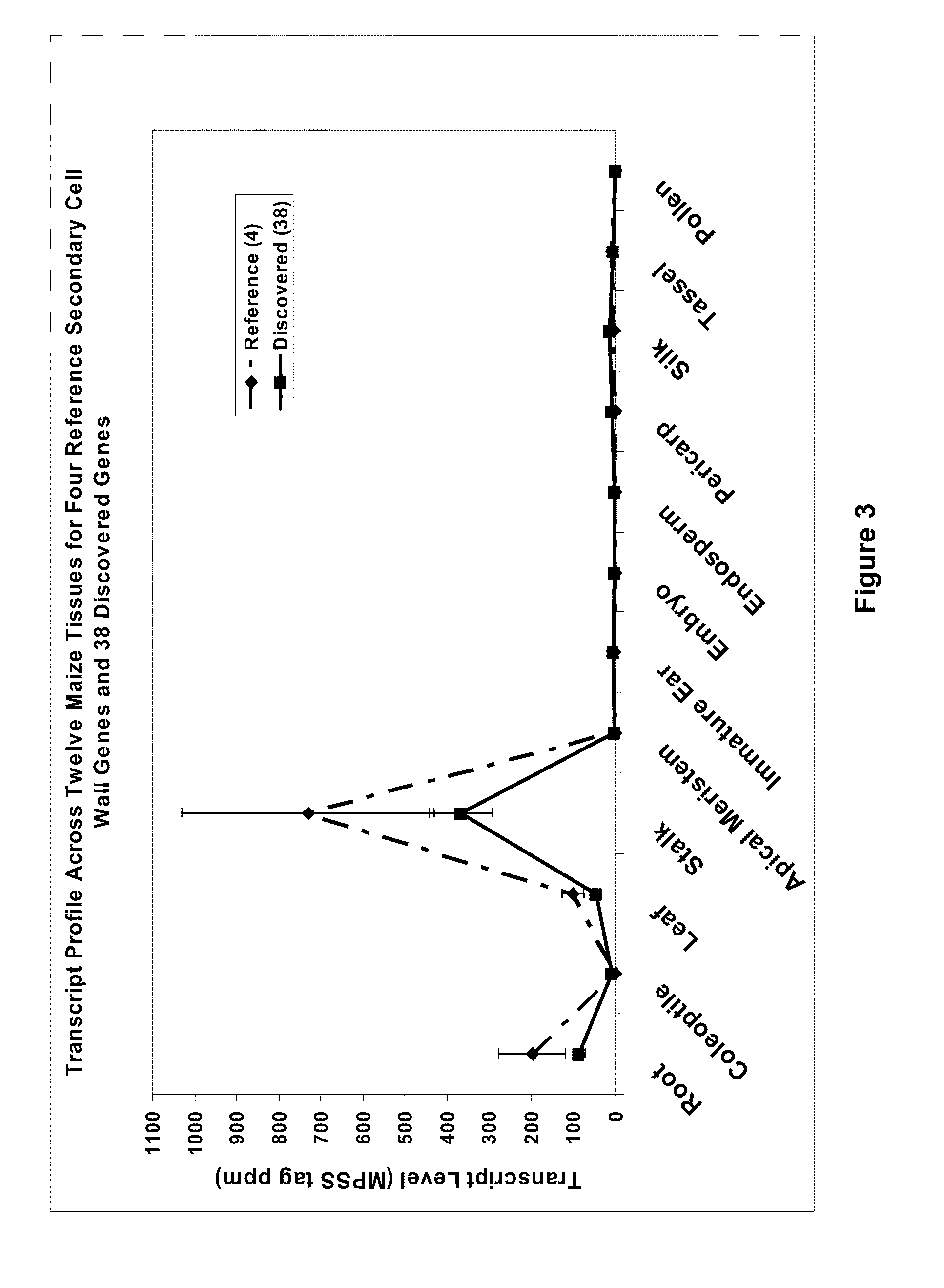
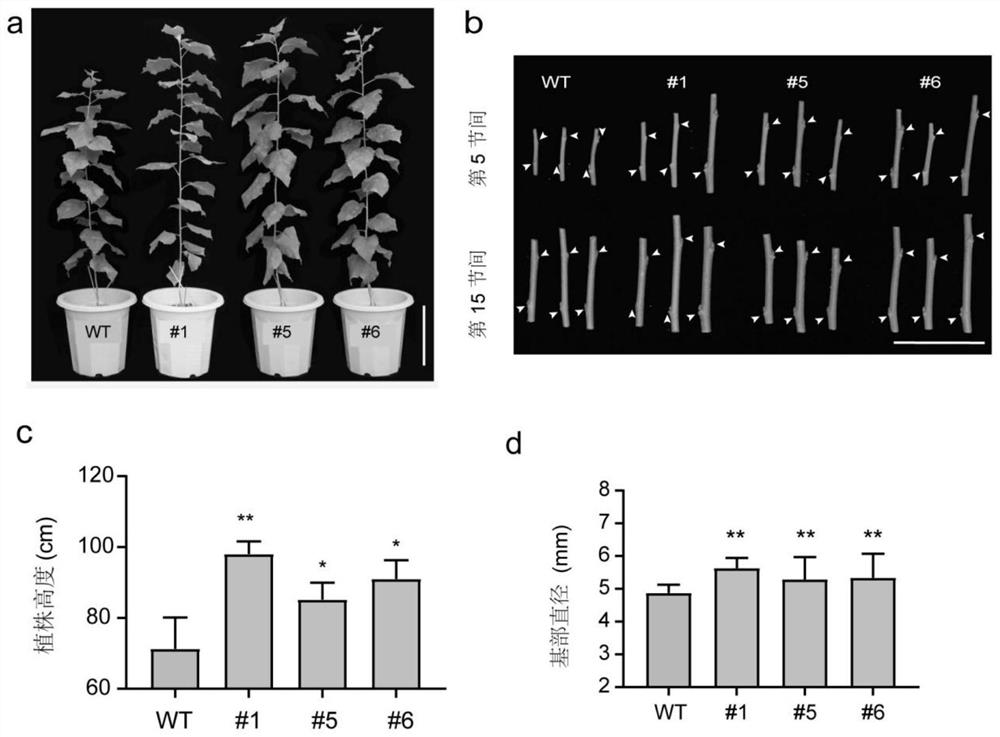
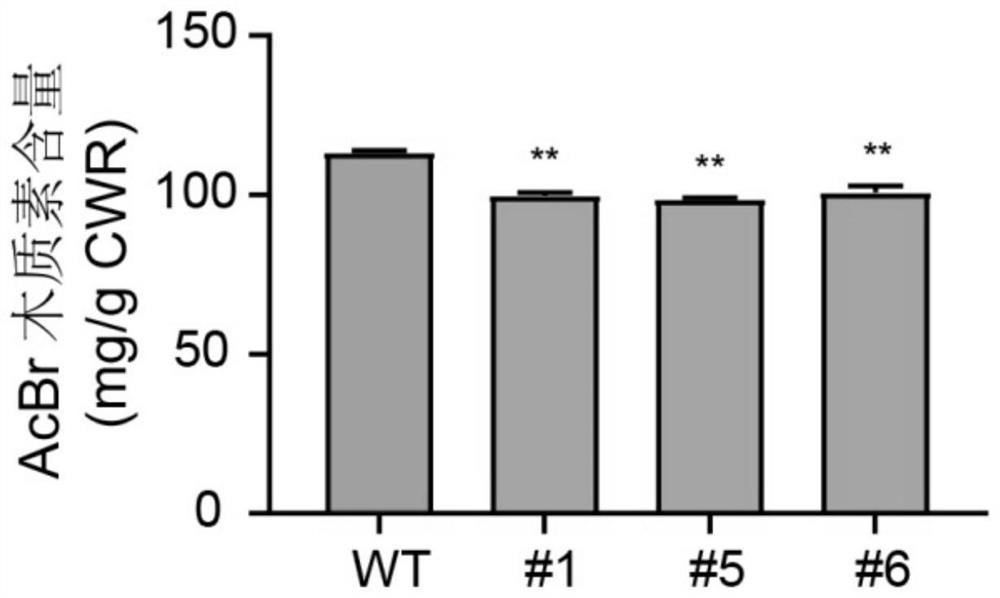
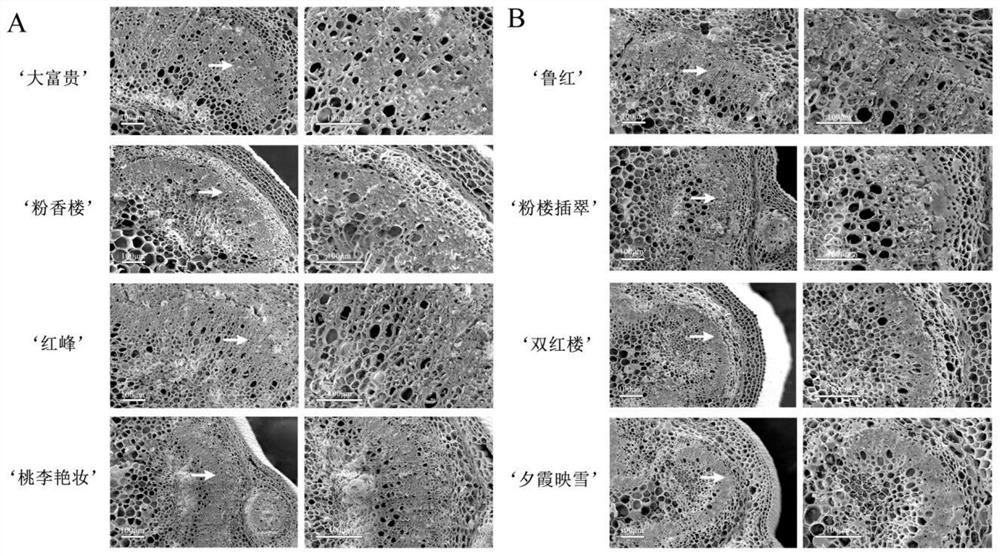
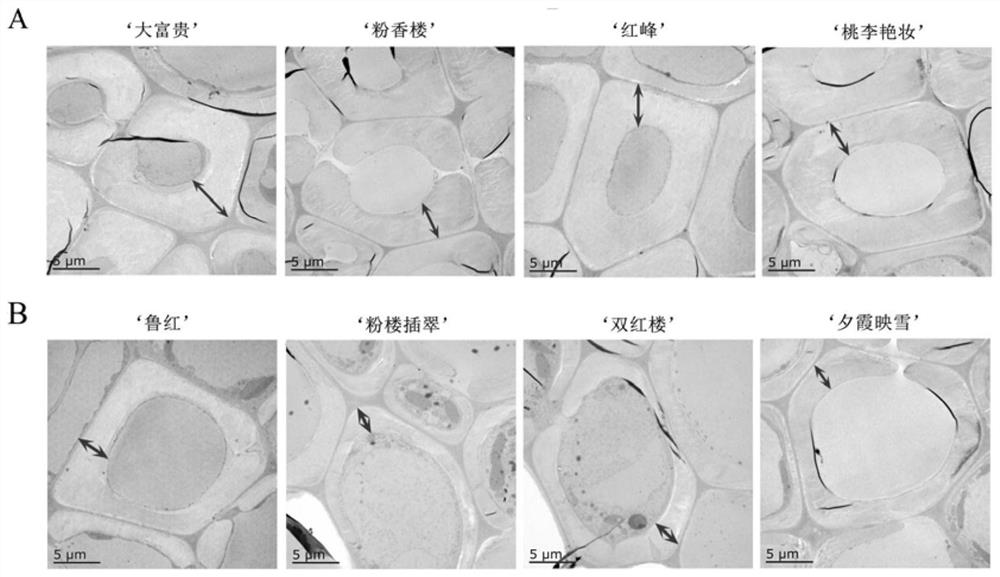
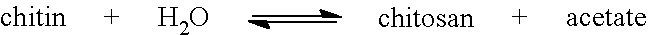Patents
Literature
40 results about "Secondary cell wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The secondary cell wall is a structure found in many plant cells, located between the primary cell wall and the plasma membrane. The cell starts producing the secondary cell wall after the primary cell wall is complete and the cell has stopped expanding.
Method for testing lignification degrees of plant cell walls
InactiveCN102435594AEasy to makeOvercome limitations of preparationPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringPlant cellRaman microscope
The invention discloses a method for testing lignification degrees of plant cell walls based on a confocal Raman microscopic technology. The method comprises the following steps of: testing Raman spectrums of the plant cell walls under the in-situ state by using a confocal Raman microscope to obtain Raman spectrum imaging graphs of lignin in the cell walls; and determining the content of the lignin in the cell walls according to Raman signal intensities, and determining the lignification degrees of different secondary cell walls and different form areas of fiber cell walls. The testing method is based on a pure spectrum method, samples are quickly prepared, chemical pollutants are not generated, and the information of the lignification degrees of the plant cell walls can be acquired under the in-situ state.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
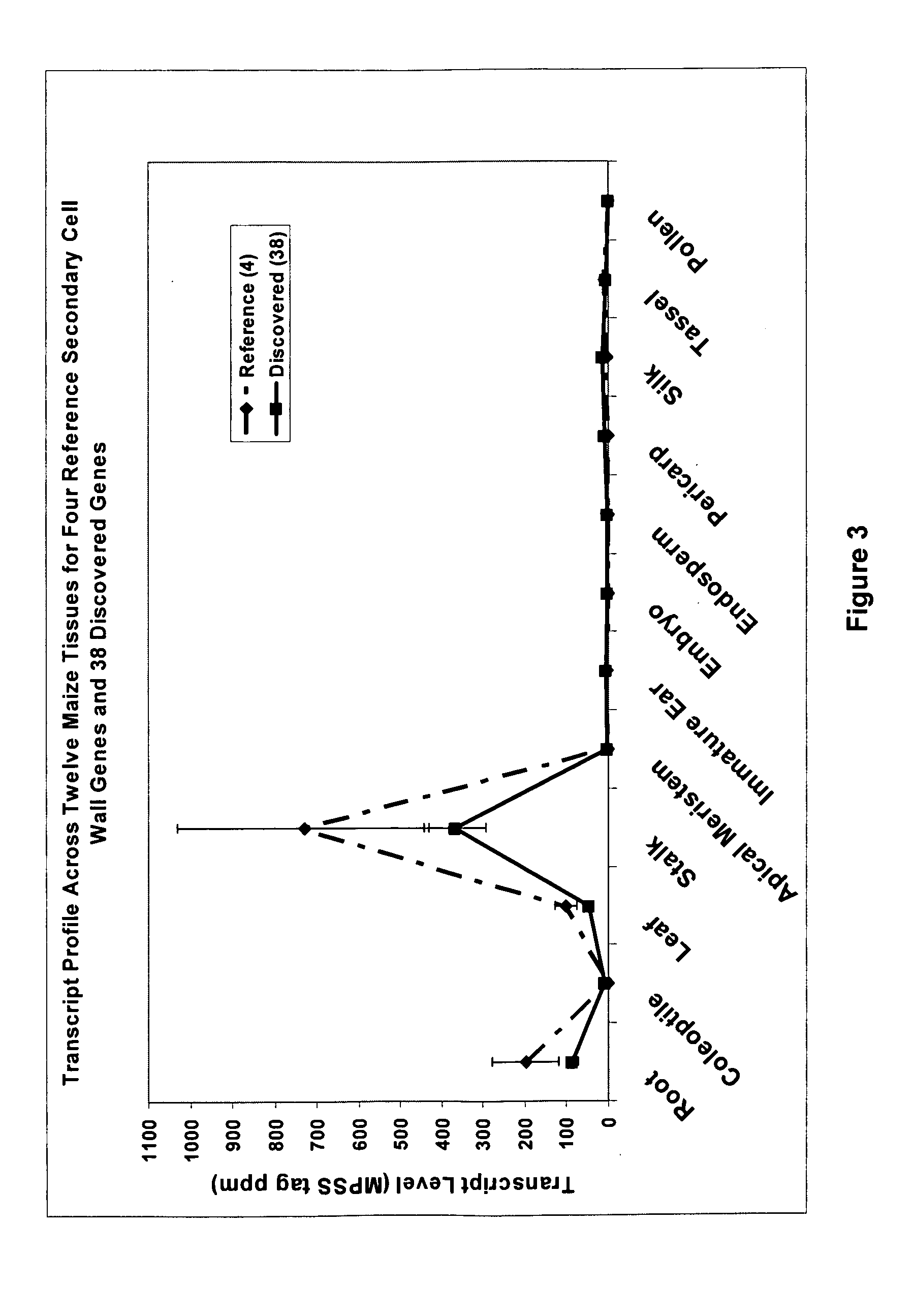
Secondary Wall Forming Genes From Maize and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20080313777A1Increase and decrease levelIncrease productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGrowth plantPolynucleotide
The present invention provides polynucleotides and related polypeptides of the class of genes involved in maize secondary wall (ZmSCW) formation. The invention provides genomic sequence for the ZmSCW genes. ZmSCW are responsible for controlling plant growth, secondary cell wall development and yield in crop plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Methods for modifying plant cell walls and modified plants produced thereby
InactiveUS7317136B1Improve digestibilitySpeed up the processClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellPlant traits
The present invention provides methods for modulating cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin composition and deposition in secondary cell wall layers of plants to improve plant traits that are commercially desirable (e.g., enhanced digestibility of forage crops by animals, increased post-harvest processing of wood and crops for energy production and pulping, increase mechanical strength of plants, and others). The invention also provides methods for identifying genes encoding transcription factors that regulate the formation of secondary cell walls, polynucleotide sequences that encode key components of secondary cell walls, and transgenic plants comprising these sequences.
Owner:ARBORGEN
Spatially modified gene expression in plants
The invention provides methods of engineering plants having lignin deposition or xylan deposition that is substantially localized to the vessels of xylem tissue in the plant. The invention also provides methods of engineering plants to increase production of a desired biosynthetic product, e.g., to have increased secondary cell wall deposition or increased wax / cutin accumulation. The engineered plants of the present invention can be used for bioenergy production, e.g., by improving the density and the digestibility of biomass derived from the plant and to improve water usage requirements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
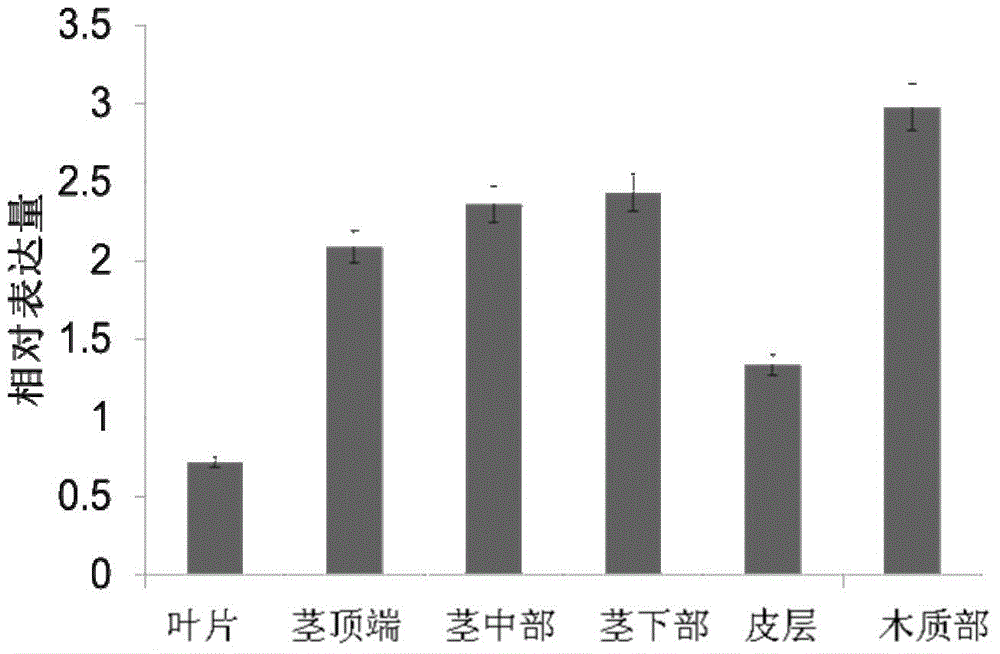
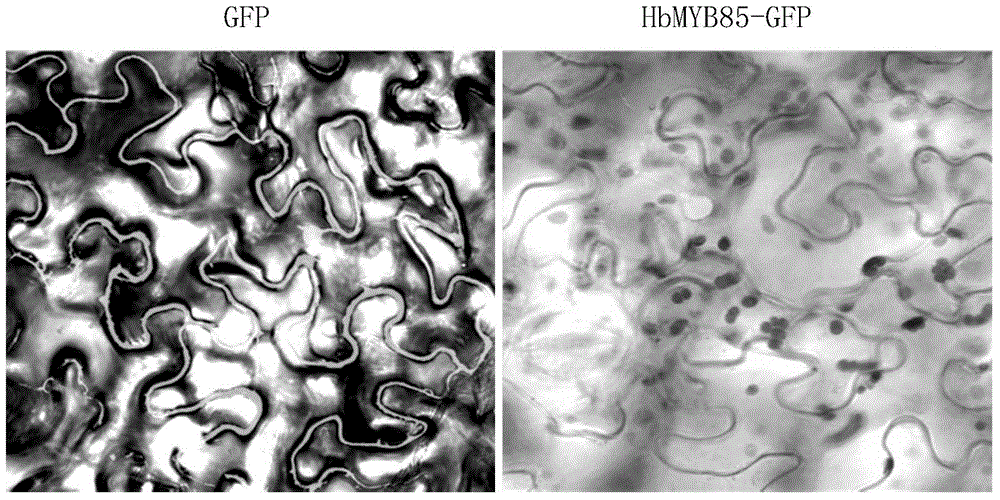
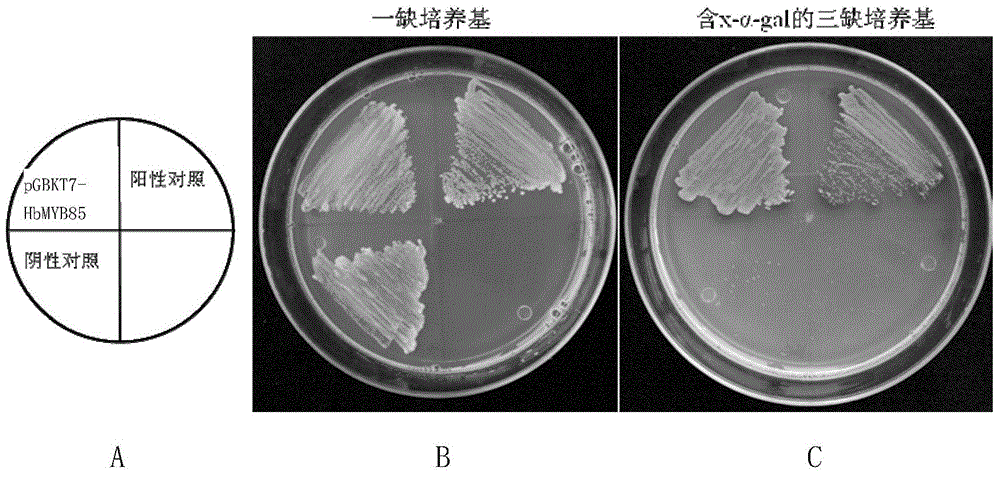
Regulatory protein HbMYB85 synthesized by virtue of rubber tree lignin as well as encoding gene and application of regulatory protein HbMYB85
InactiveCN104829702ASignificant application valueGood thickeningPlant peptidesFermentationBiologyGMO Plants
The invention discloses a regulatory protein HbMYB85 synthesized by virtue of rubber tree lignin as well as an encoding gene and application of the regulatory protein HbMYB85. The protein is named HbMYB85 protein and is shown as follows (a) or (b): (a) a protein formed by amino acid sequences shown by a sequence 1; and (b) a regulatory protein which is derivated by the sequence 1 and formed by replacement and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequences shown by a sequence 1 and synthesis of thickness of a plant secondary cell wall and / or lignin. An HbMYB85 gen also belongs to the protection range of the invention. The invention also protects a method of cultivating a transgenic plant. The method comprises the following steps: introducing the HbMYB85 gene into a target plant to obtain the transgenic plant with the thickness of the plant secondary cell wall and / or the content of the lignin higher than that or those of the target plant. The regulatory protein HbMYB85 has important significance of promoting thickness increase of the plant secondary cell wall and accumulation of the lignin and particularly quality genetic improvement of rubber woods and cultivation of a new wind-resistant variety.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Transgenic plants with improved saccharification yields and methods of generating same
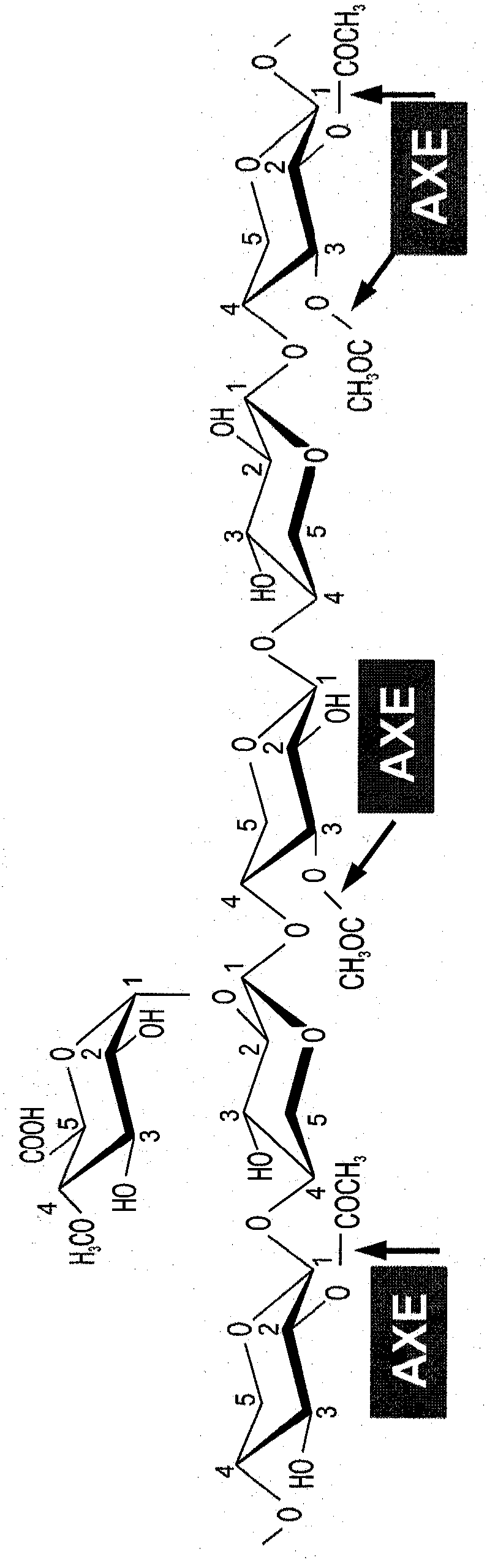
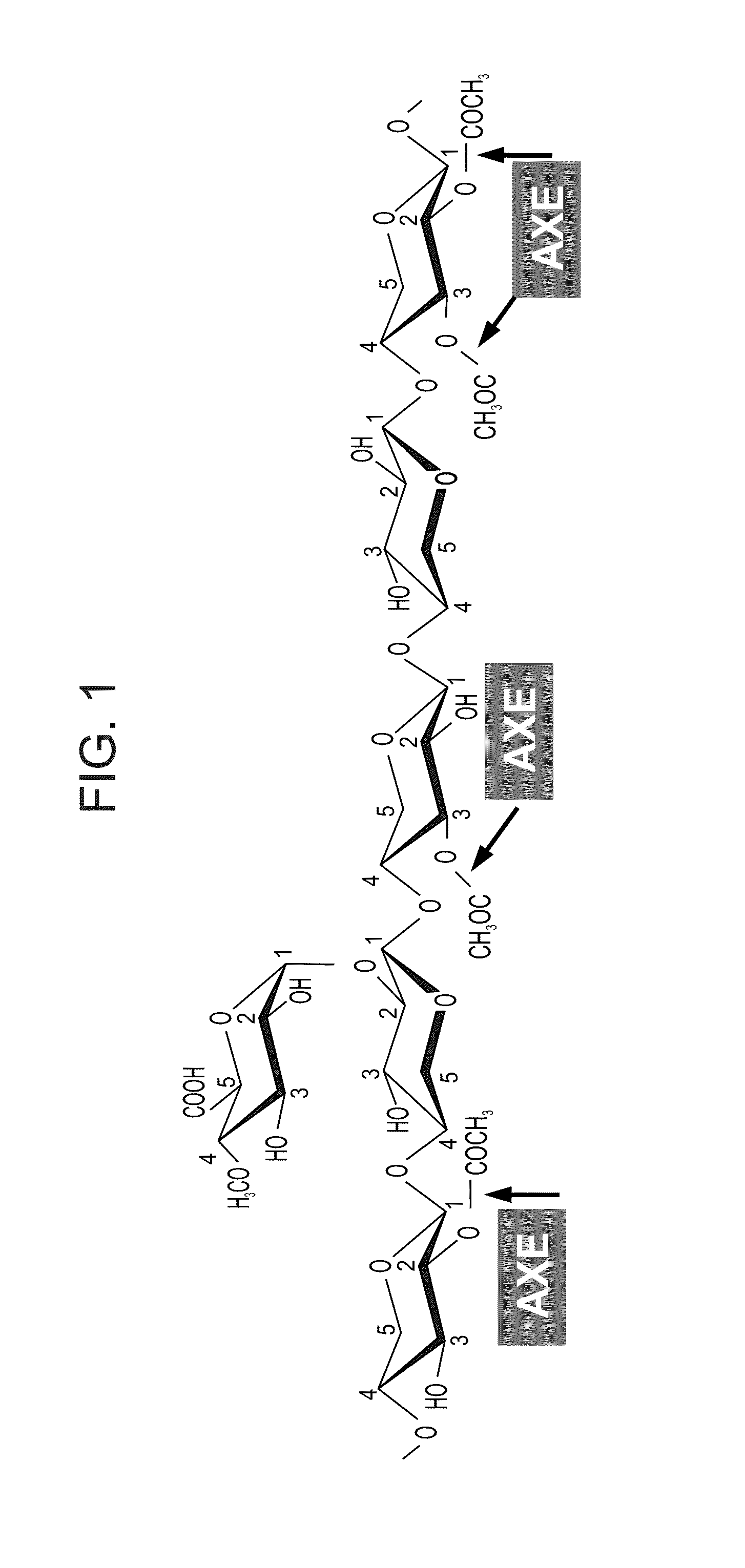
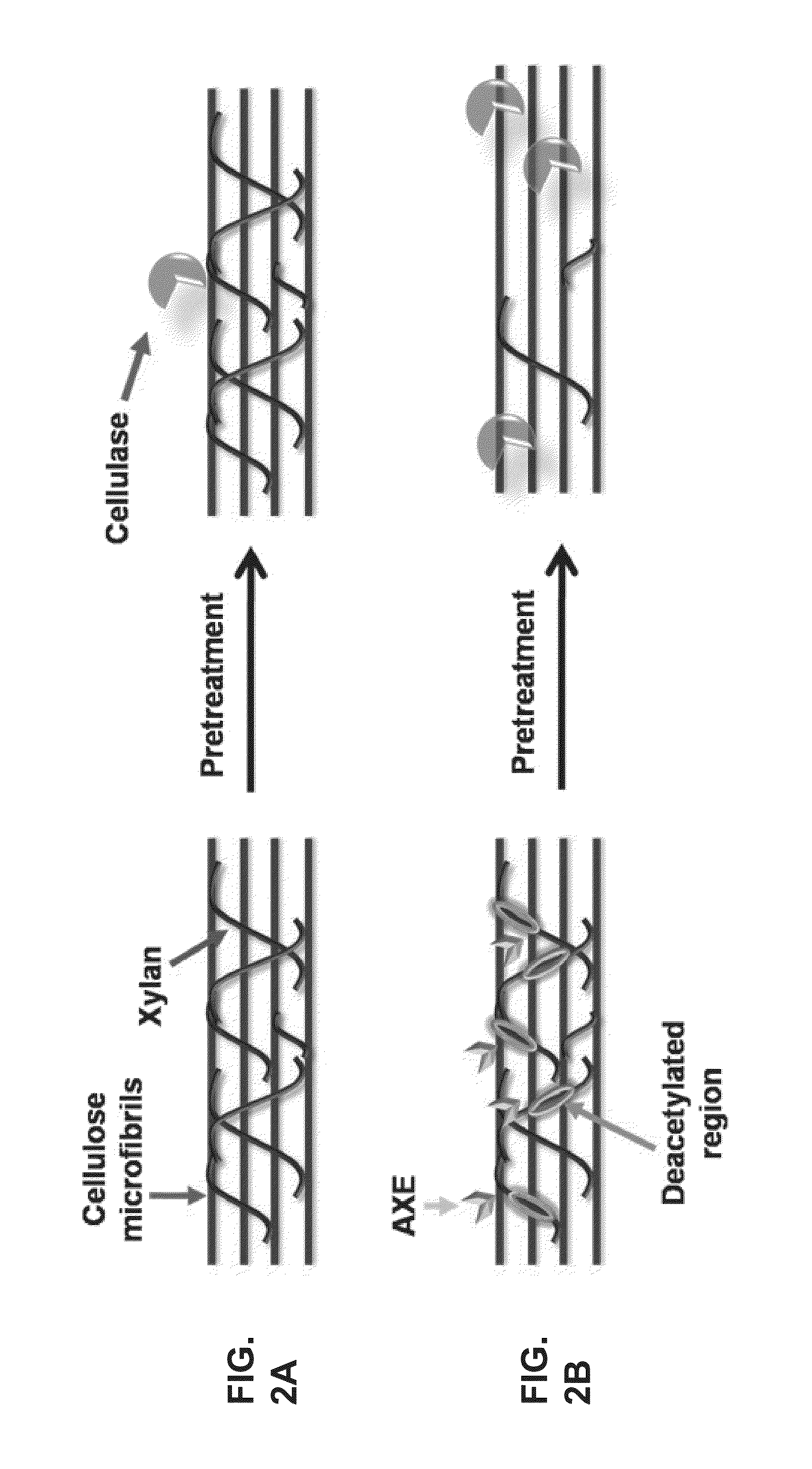
InactiveCN103237895AHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousAcetylxylan esterase
A method of engineering a plant having reduced acetylation in a cell wall is disclosed. The method comprising expressing in the plant cell wall at least one isolated heterologous polynucleotide encoding an acetylxylan esterase (AXE) enzyme under the transcriptional control of a developmentally regulated promoter specifically active in the plant cell wall upon secondary cell wall deposit, thereby engineering the plant having reduced acetylation in the cell wall.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
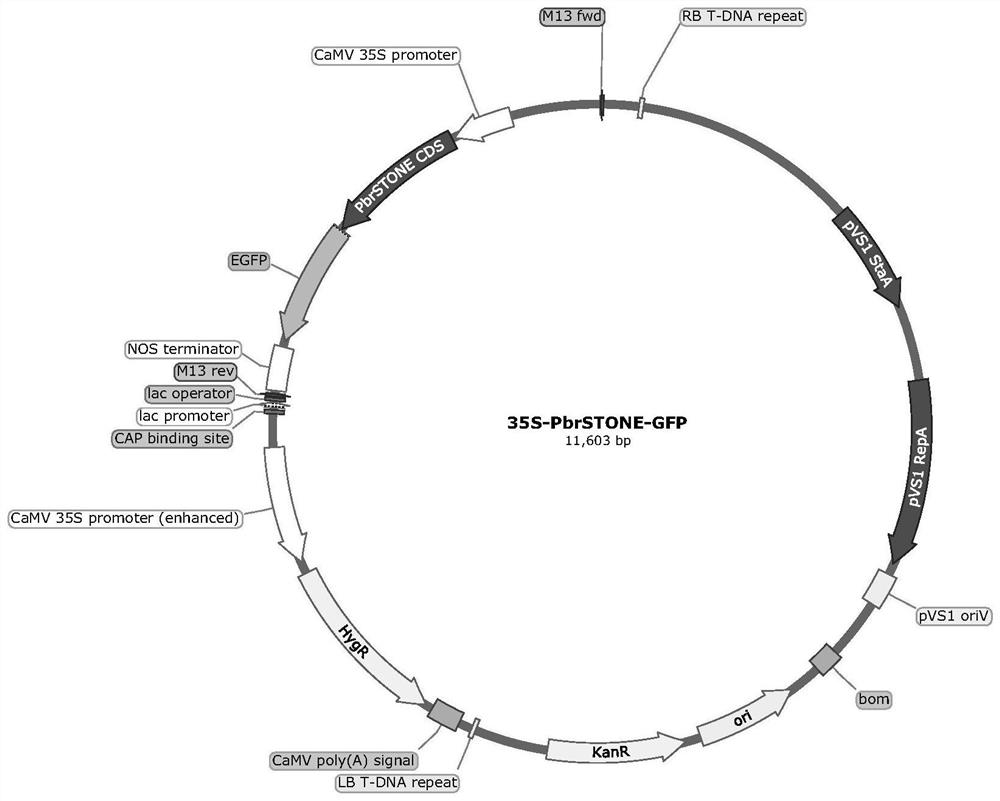
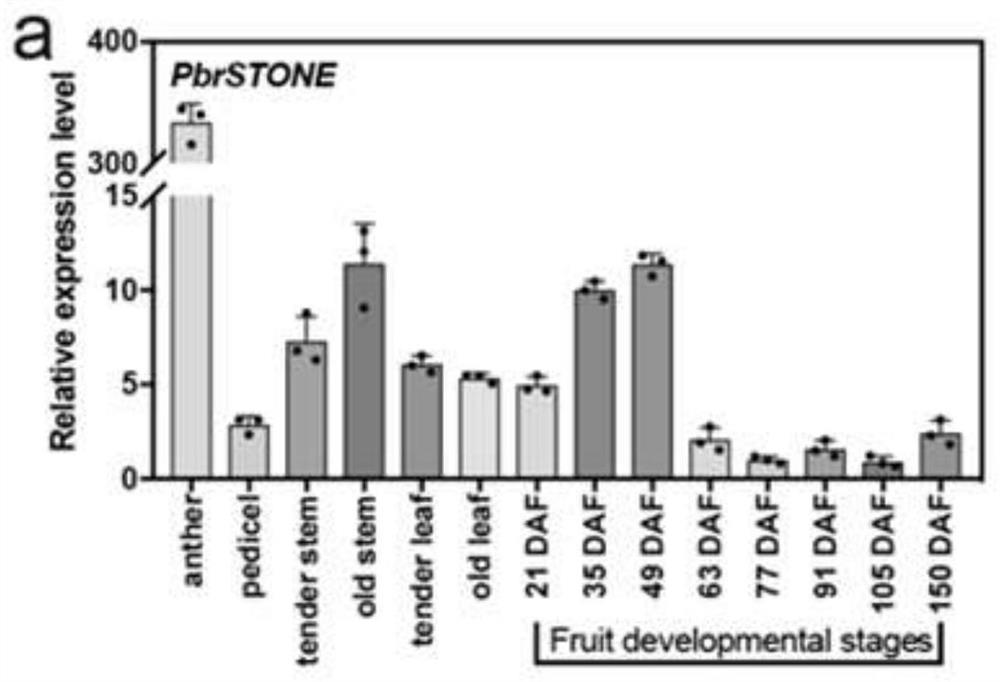
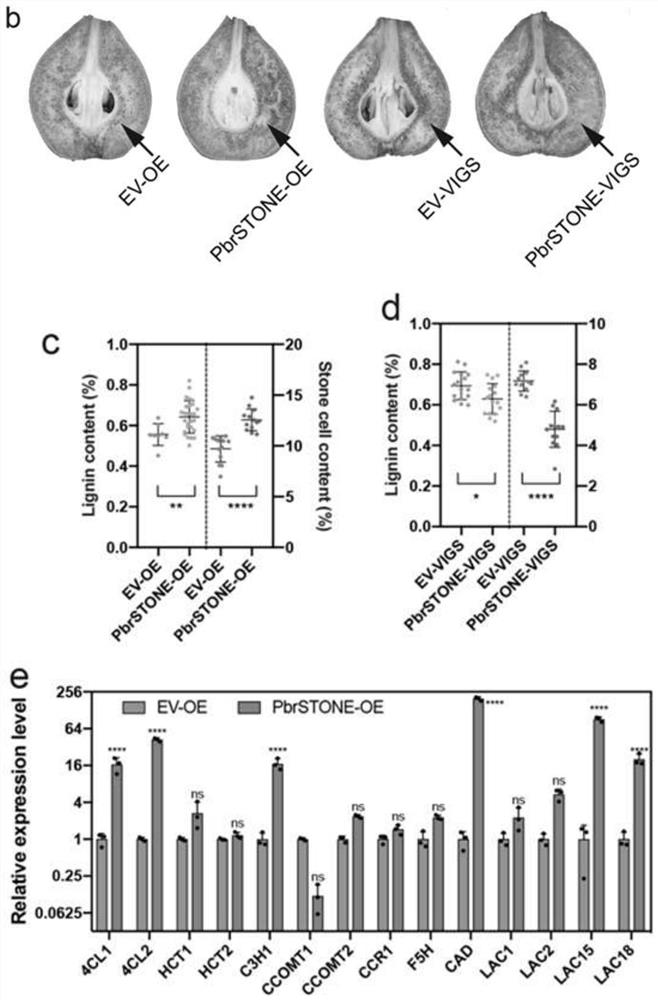
Pear PbrSTONE gene and application thereof
ActiveCN112876550AIncrease the number of layersHigh lignin contentPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a pear PbrSTONE gene and an application of the pear PbrSTONE gene. The PbrSTONE gene which is separated from Dangshan pears and has the function of adjusting the development of the stone cells of the pear fruits has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and an amino acid sequence coded by the PbrSTONE gene is as shown in SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table. Through instantaneous overexpression in pear fruits and a gene silencing technology, it is proved that PbrSTONE can change the accumulation process of fruit stone cells and lignin; in the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana inflorescence stem of overexpression PbrSTONE, the lignin content and G-type monomer thereof are significantly increased. Meanwhile, the number of lignified inter-bundle fiber cell layers is increased, and the secondary cell wall of conduit cells is significantly thickened. Therefore, the PbrSTONE gene participates in adjusting and controlling the formation of the lignin of the stone cells of the pear fruits.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Transgenic plants with improved saccharification yields and methods of generating same
A method of engineering a plant having reduced acetylation in a cell wall is disclosed. The method comprising expressing in the plant cell wall at least one isolated heterologous polynucleotide encoding an acetylxylan esterase (AXE) enzyme under the transcriptional control of a developmentally regulated promoter specifically active in the plant cell wall upon secondary cell wall deposit, thereby engineering the plant having reduced acetylation in the cell wall.
Owner:FUTURAGENE ISRAEL +1
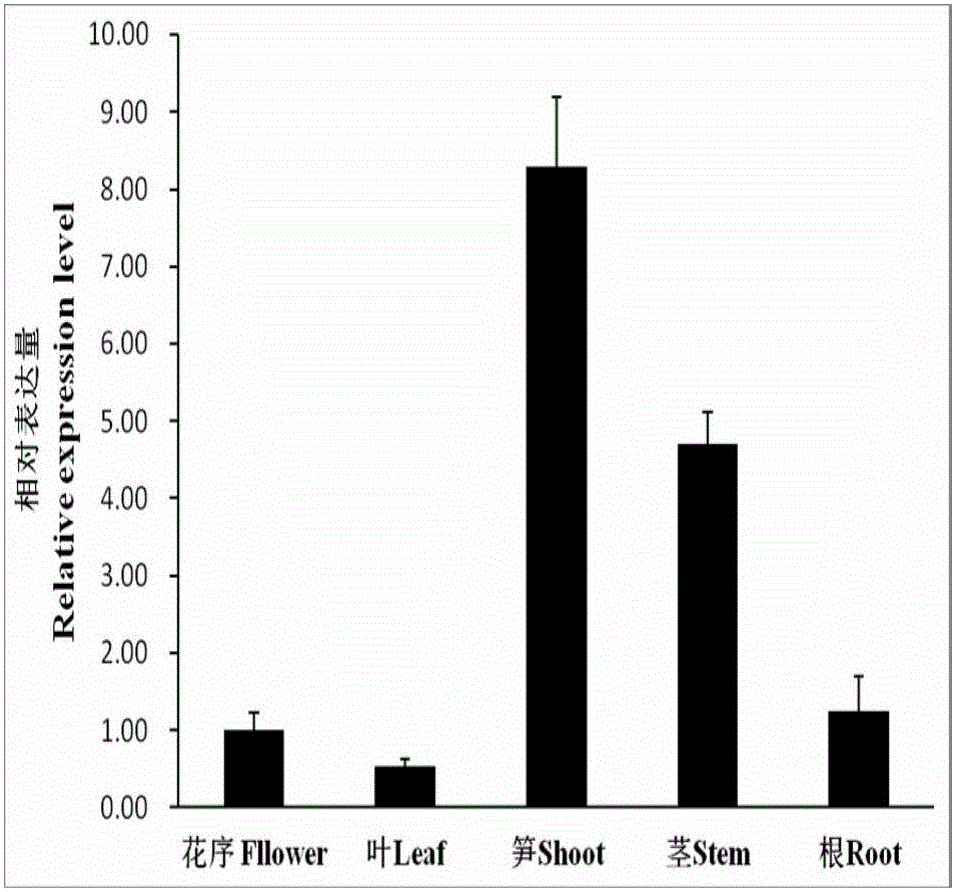
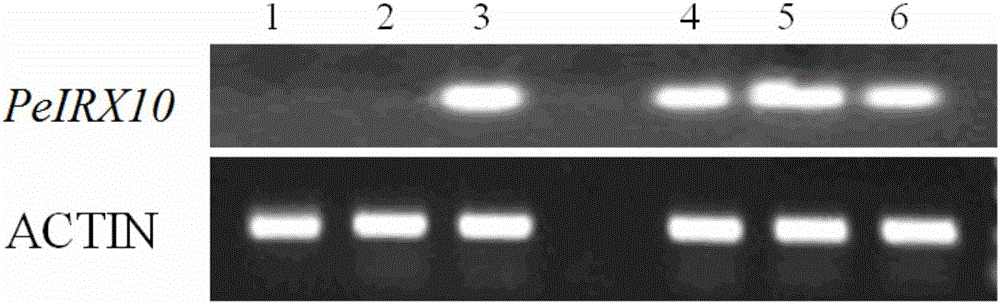
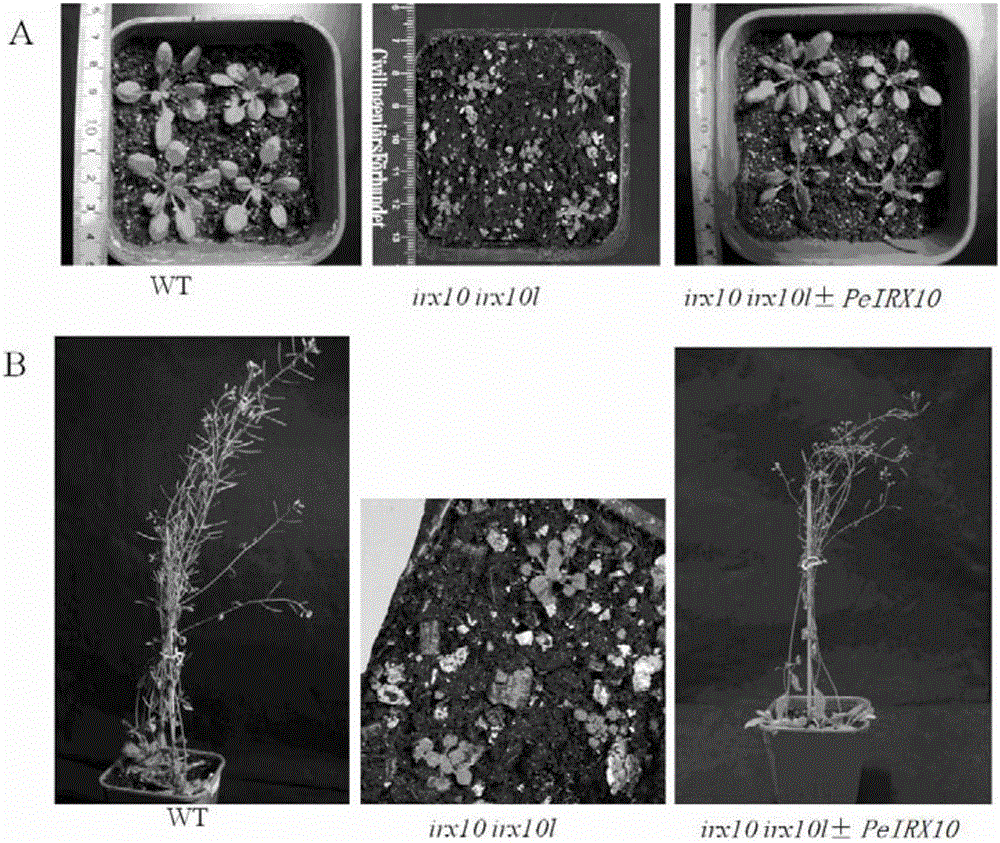
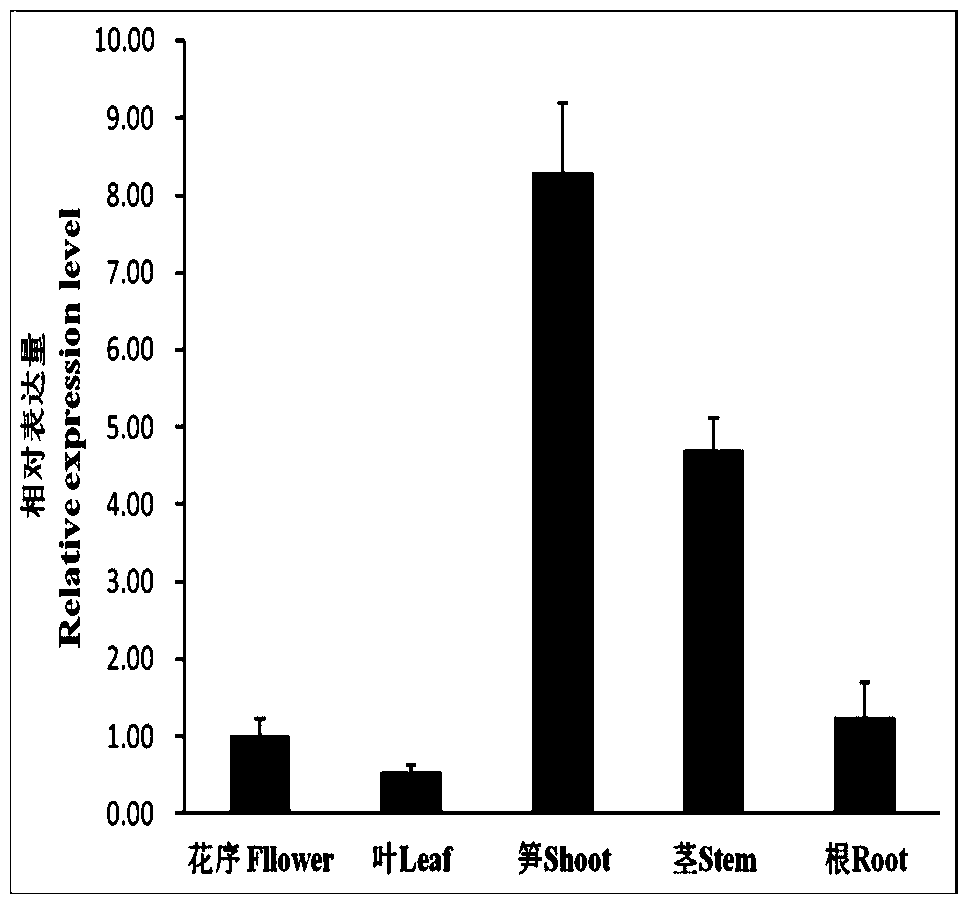
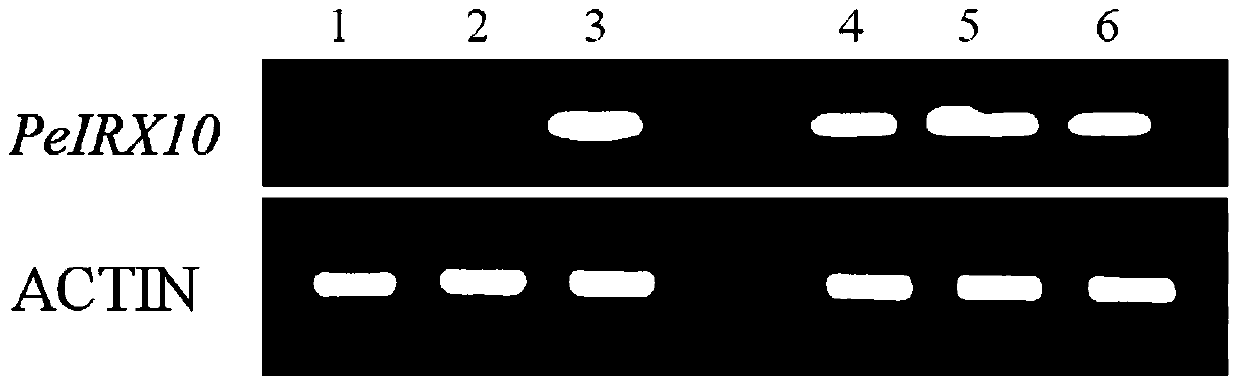
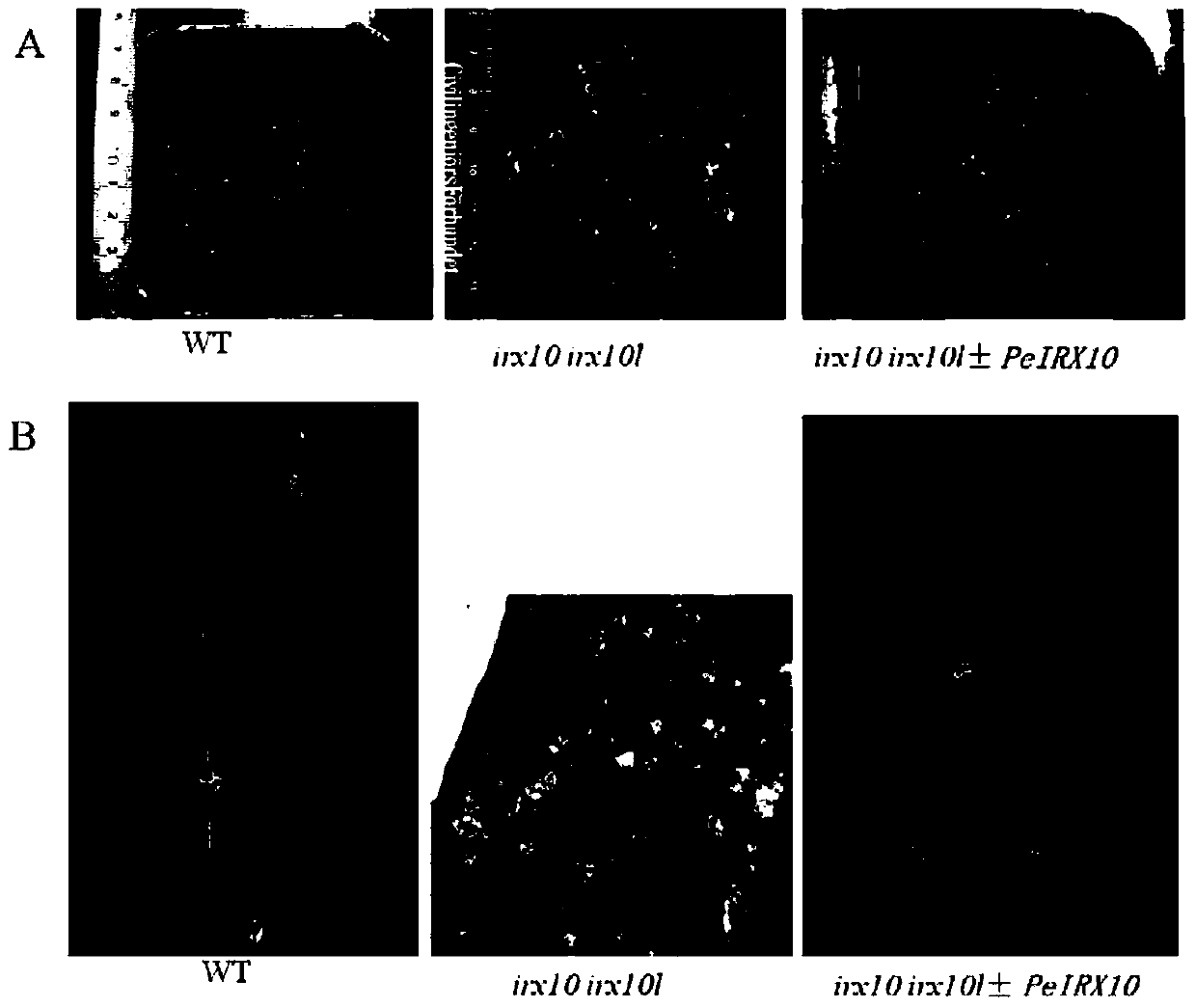
Clone and application of key gene PeIRX10 for phyllostachys edulis xylan synthesis
ActiveCN105925591ARepair Synthetic DefectsRepair secondary cell wall defectsEnzymesFermentationNucleotidePhyllostachys edulis
The invention belongs to the fields of molecular biology and genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a Gts (glycosyltransferases) key gene PeIRX10 taking part in xylan synthesis. The gene has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No:1. The invention provides a powerful tool for knowing the formation of the secondary cell wall and illuminating the molecular basis of the fast growth of phyllostachys edulis tissues. The effects that the xylan synthesis defects in arabidopsis mutants can be overcome by using the PeIRX10, and the defects of the secondary cell wall in the arabidopsis mutants can be overcome in a complementary way are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
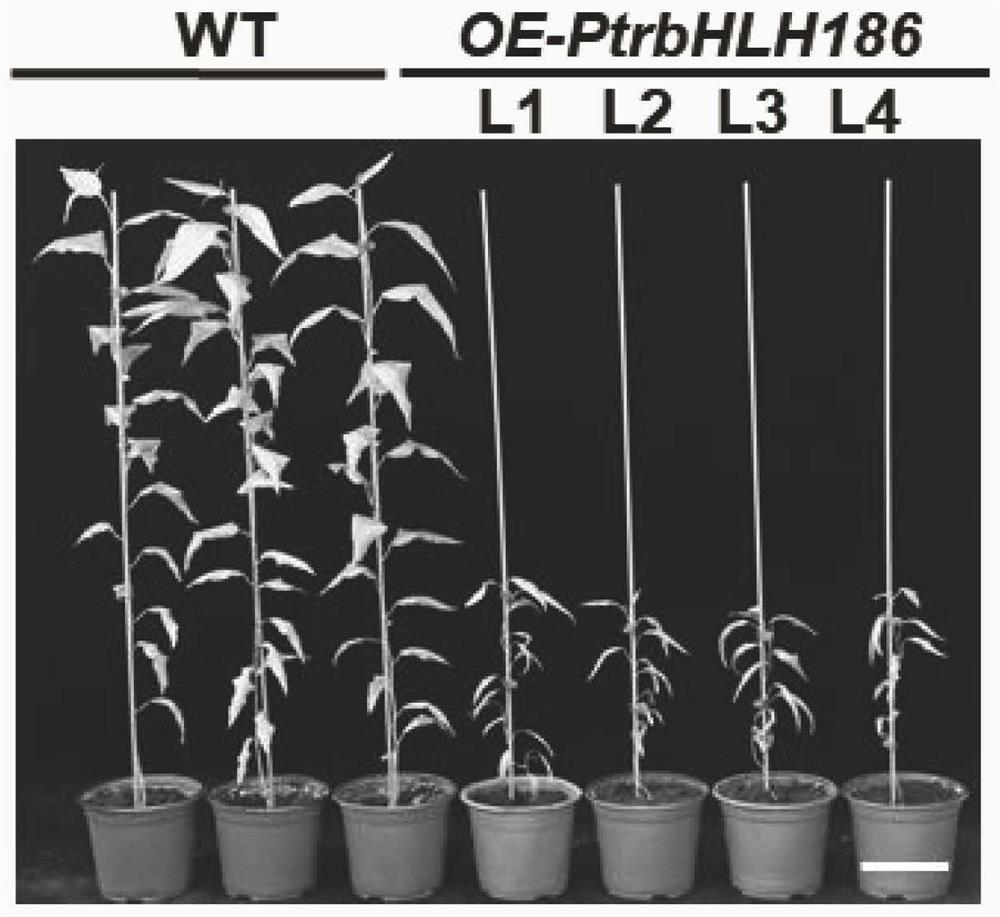
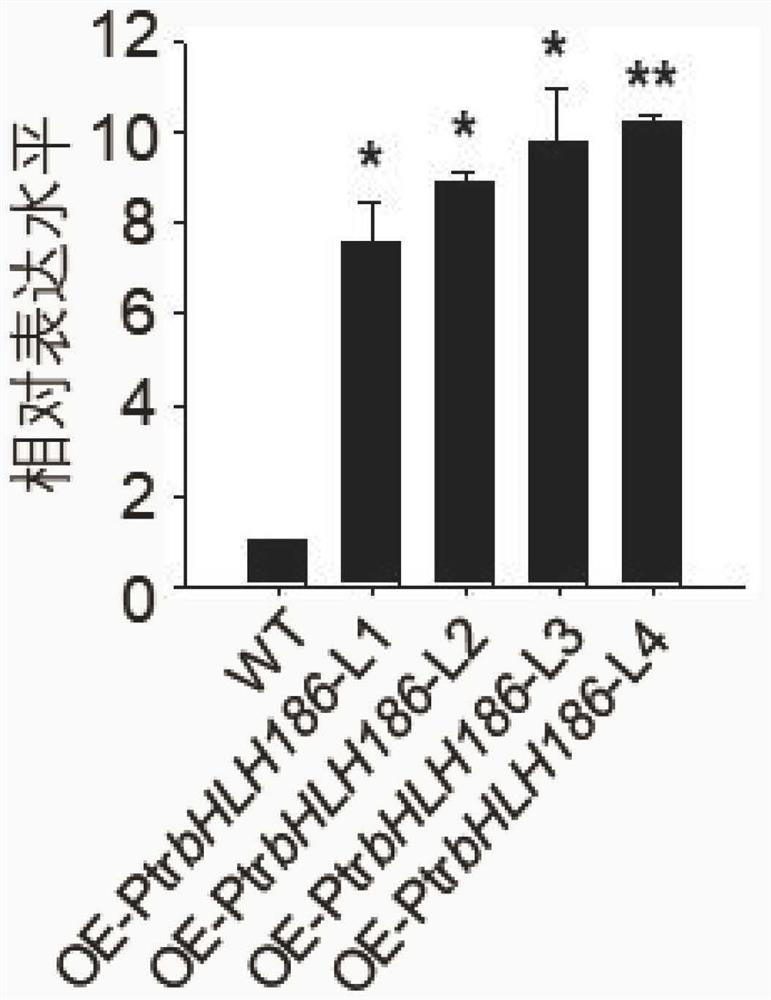
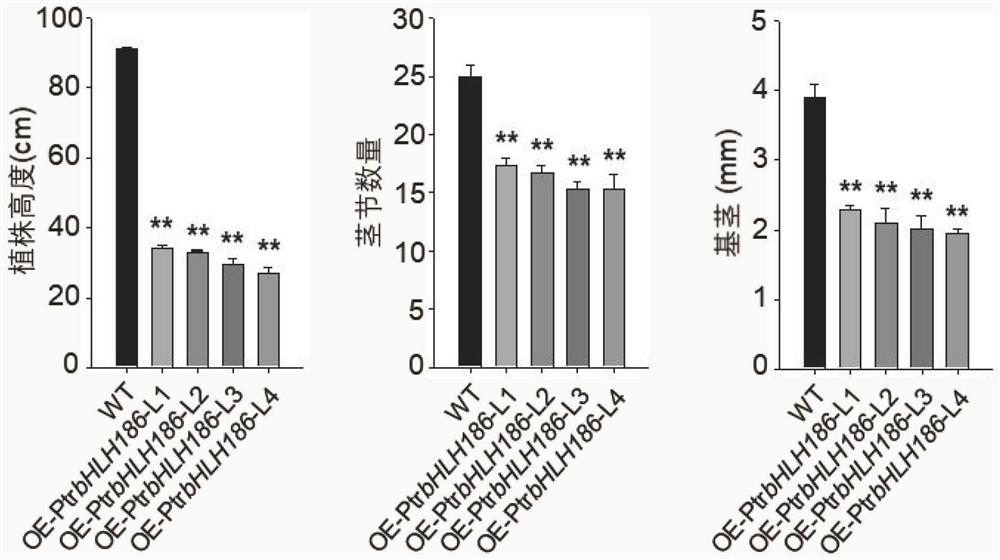
Application of populus trichocarpa PtrbHLH186 gene in regulation and control of secondary xylem development of trees
ActiveCN114195873AGrowth retardationIncrease the occupied areaPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyPopulus trichocarpa
The invention relates to application of a populus trichocarpa PtrbHLH186 gene in regulation and control of secondary xylem development of trees, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. In order to solve the problems that the need for wood quantity and quality is increased day by day and the biological function of the PtrbHLH186 transcription factor is unknown, a PtrbHLH186 overexpressed populus trichocarpa transgenic plant is obtained through an agrobacterium-mediated populus trichocarpa genetic transformation system, and then a series of technical means are utilized for analysis and discovery that the PtrbHLH186 overexpressed populus trichocarpa transgenic plant is found to have the advantages that the PtrbHLH186 overexpressed populus trichocarpa transgenic plant; the overexpression of the PtrbHLH186 transcription factor affects the growth and development of plants and the formation of wood, which is mainly embodied in that the lignin synthase gene is regulated by the gene to affect the deposition of lignin in the secondary cell wall of a tree, so that the morphological structure and distribution of xylem cells are changed; the results show that the PtrbHLH186 transcription factor has a certain regulation effect on the development of the secondary xylem of the tree. The research content provided by the invention has important theoretical guiding significance for cultivating new varieties of high-quality woods and forests.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Wood fiber microfilament dissociation method based on soft nanometer paper base material
ActiveCN103952939AEnhance water absorption and swellingEasy to peelPulp beating methodsFiberMicrometer
The invention provides a wood fiber microfilament dissociation method based on a soft nanometer paper base material. The wood fiber microfilament dissociation method comprises the following steps: cutting off and cutting short paper pulp fibers by a pulping machine, and controlling the length of the cut fibers between 500 micrometers and 1000 micrometers; squashing the cut paper pulp fibers by hammering force which is perpendicular to the axial direction of the fibers until the primary cell wall and secondary cell wall outer layers of the fibers are broken or peeled; then utilizing rubbing and shearing force perpendicular to the axial direction of the fibers to separate microfilament layers so as to obtain primarily nano-crystallized fiber microfilaments; finally carrying out high-shear flattening treatment on the primarily nano-crystallized fiber microfilaments to obtain the soft nanometer fibers with uniform size. The method has the advantages of high product yield, uniform size and capability of batch preparing.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
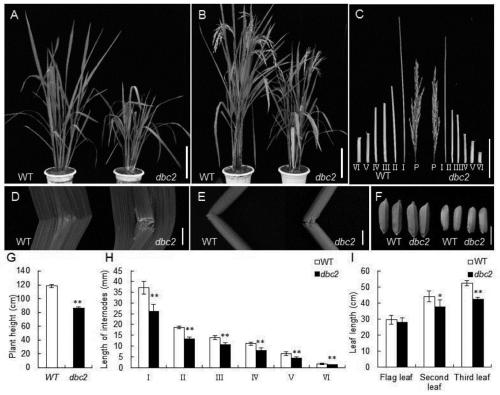
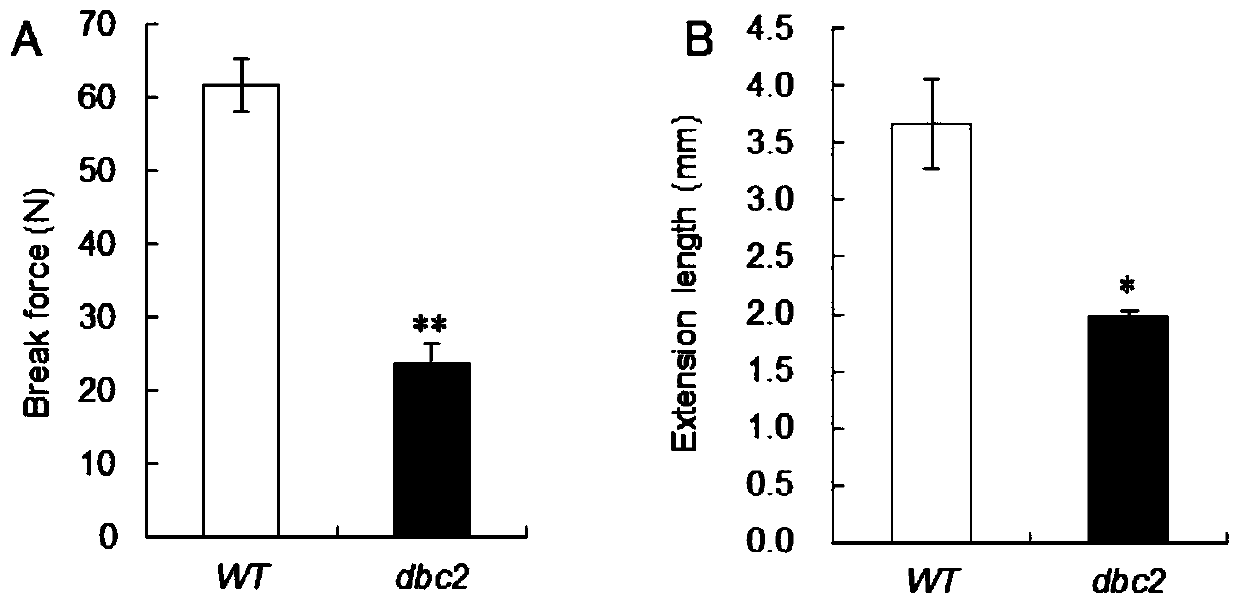
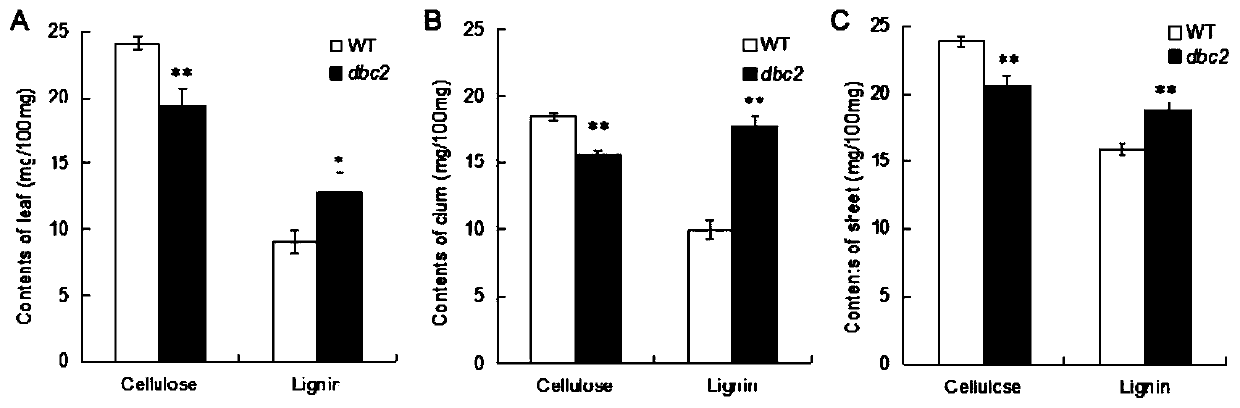
Rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2 and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of rice breeding, and particularly relates to a rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2 and application thereof. The invention discloses the rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2, the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and a protein encoded by the gene is glucoside hydrolase OsGH9A3 with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2.The rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2 disclosed by the invention regulates rice brittle stem traits and dwarfing traits by directly or indirectly influencing the expression quantity of celluloseand lignin synthesis genes and secondary cell wall growth related transcription factor genes, and the regulation of the expression of the brittle stem traits is also regulated by temperature. The rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2 is applied to rice improvement, rice with brittle and tender stems is expected to be modified, the brittle and tender stems can be used for feed production, and theproblem that existing rice stems are inconvenient to treat is solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
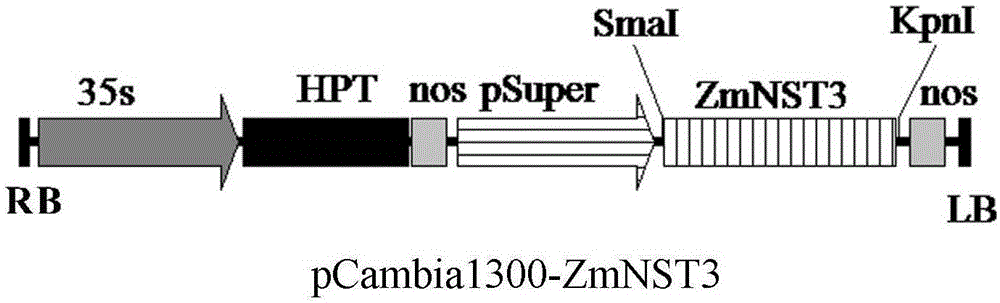
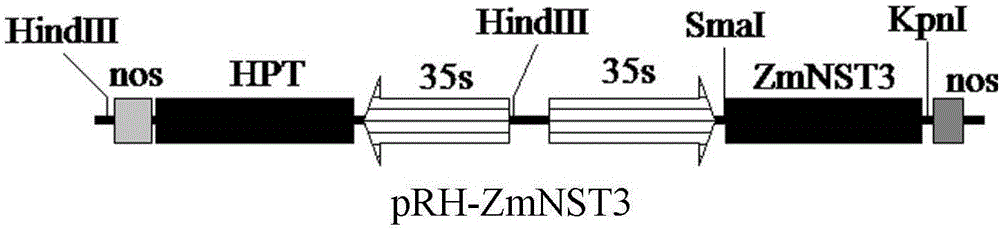
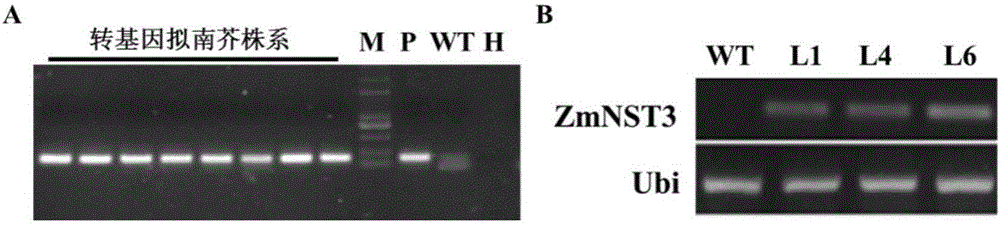
Corn ZmNST3 gene and application
InactiveCN106801061APromote accumulationImprove cellulosePlant peptidesFermentationBiomassSecondary cell wall
A CDS sequence (SEQ ID No.1) of a ZmNST3 gene related to development of a secondary cell wall of corn is firstly obtained through cloning, and the gene is transformed into the plant, so that accumulation of the secondary cell wall in plant stems can be improved, and the content of cellulose and lignin in the cell wall is improved. The invention provides a novel method for improving accumulation of the secondary cell wall of a plant by using the ZmNST3 gene. The corn ZmNST3 gene can be used for cultivation of a novel high-biomass plant variety, and is beneficial to development and utilization of biomass energy.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Secondary wall forming genes from maize and uses thereof
InactiveUS7994398B2Increase food productionIncrease and decrease levelBryophytesSugar derivativesNucleotidePolynucleotide
The present invention provides polynucleotides and related polypeptides of the class of genes involved in maize secondary wall (ZmSCW) formation. The invention provides genomic sequence for the ZmSCW genes. ZmSCW are responsible for controlling plant growth, secondary cell wall development and yield in crop plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Related gene for regulating and controlling wood development and application thereof
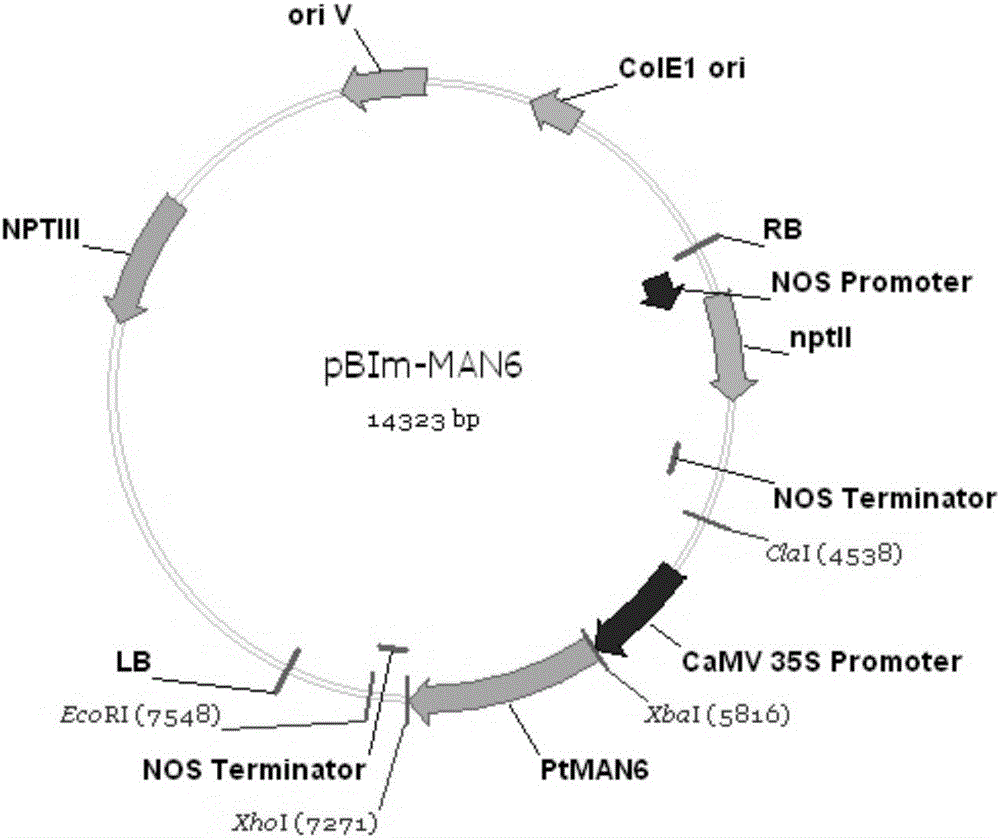
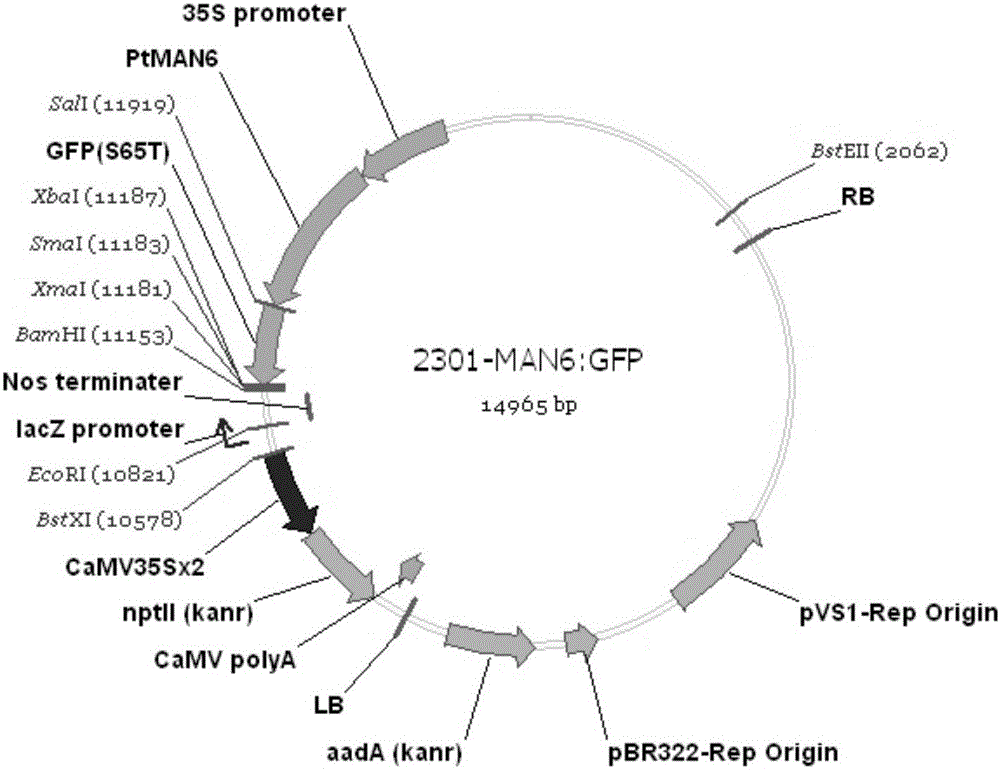
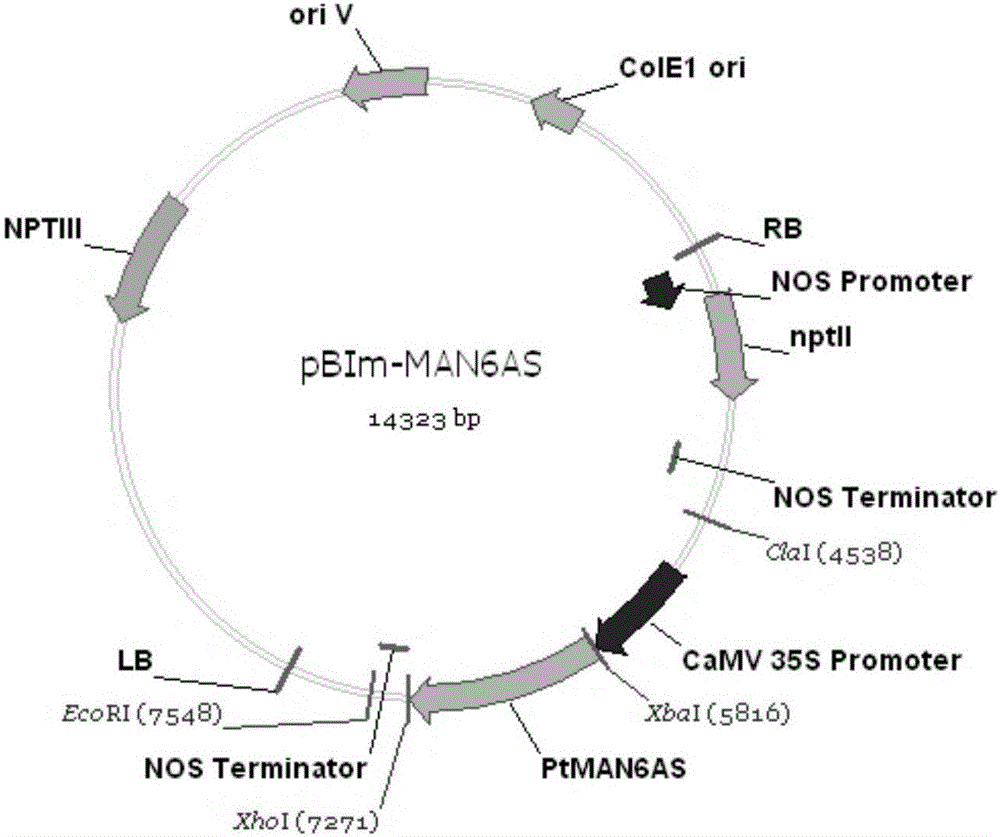
The invention relates to a related gene for regulating and controlling wood development and application thereof, and particularly provides a novel PtMAN6 polypeptide or a coding sequence thereof. An amino acid sequence of the PtMAN6 polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID NO.:2, and the coding sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.:1.The invention further provides a PtMAN6 gene and application of protein coded by the PtMAN6 gene. The PtMAN6 gene can reduce synthesis of xylem secondary cell walls and / or reduce accumulation of crystalline fiber biomass; mannan hydrolase of mannan hemicellulose can be enriched and degraded in plants by excessively expressing the PtMAN6; meanwhile, due to the regulating and controlling effect of the PtMAN6, the lignin content in transgenic plants is decreased, crystalline cellulose is decreased, and therefore the cost in lignocelluloses ethanol producing and paper making industry is greatly reduced; a promoter of the PtMAN6 gene has the specific duct cell positioning function and can precisely regulate and control expression of the gene in xylem duct cells.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Microscopic authentication method for stem strength of paeonia lactiflora pall cut flower
ActiveCN109060856ANo interference from human factorsReduce mistakesMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionCut flowersCell layer
The invention discloses a microscopic authentication method for the stem strength of a paeonia lactiflora pall cut flower. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) fixing the stem of the paeonia lactiflora pall cut flower: cutting off the stem of the paeonia lactiflora pall cut flower, and fixing in pentanediol and paraformaldehyde solution; (2) observing the number of cell layers of which the xylem secondary wall is thickened; (3) observing the thickness of the secondary cell wall of which the xylem is thickened; and (4) carrying out statistical analysis on the number of cell layersof which the xylem secondary wall is thickened of the paeonia lactiflora pall cut flower and the thickness of the secondary cell wall, and through the two indexes, authenticating the stem strength ofthe paeonia lactiflora pall cut flower. The method can directly carry out observation and authentication according to a microscopic structure so as to be simple, convenient, free from human factor interference and low in error; and in addition, the method is free from the restriction of time, samples can be preserved for a long time and observed, in addition, repeated measurement can be carried out, and the method is high in feasibility.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for obtaining anti-wilting hydrangea macrophylla flowers
The invention provides a method for obtaining anti-wilting hydrangea macrophylla flowers, and relates to the technical field of gardening. The method comprises the steps that an Xre cellulose overexpression gene is introduced into a hydrangea macrophylla plant, so that the hydrangea macrophylla plant expresses Xre cellulose overexpression protein; the hydrangea macrophylla flowers with anti-wilting capability are obtained. The plant is changed through genetic engineering; the plant has lignin depositions or xylan depositions basically concentrated on xylem tissue ducts of the plant, so that the increased secondary cell wall depositions or the increased wax / cutin depositions are obtained. The plant subjected to engineering modification can be used for bioenergy production; the anti-lodgingand anti-wilting goals are achieved by improving the density and cellulose content of biomass from the plant.
Owner:范瑶飞
Methods for Enhancing Expression of Secondary Cell Wall Cellulose Synthases in Plants
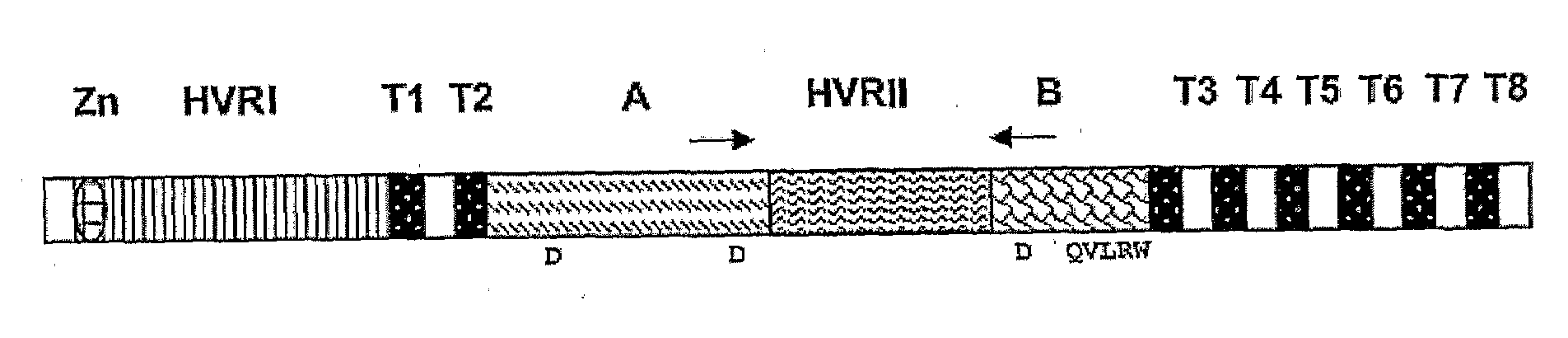
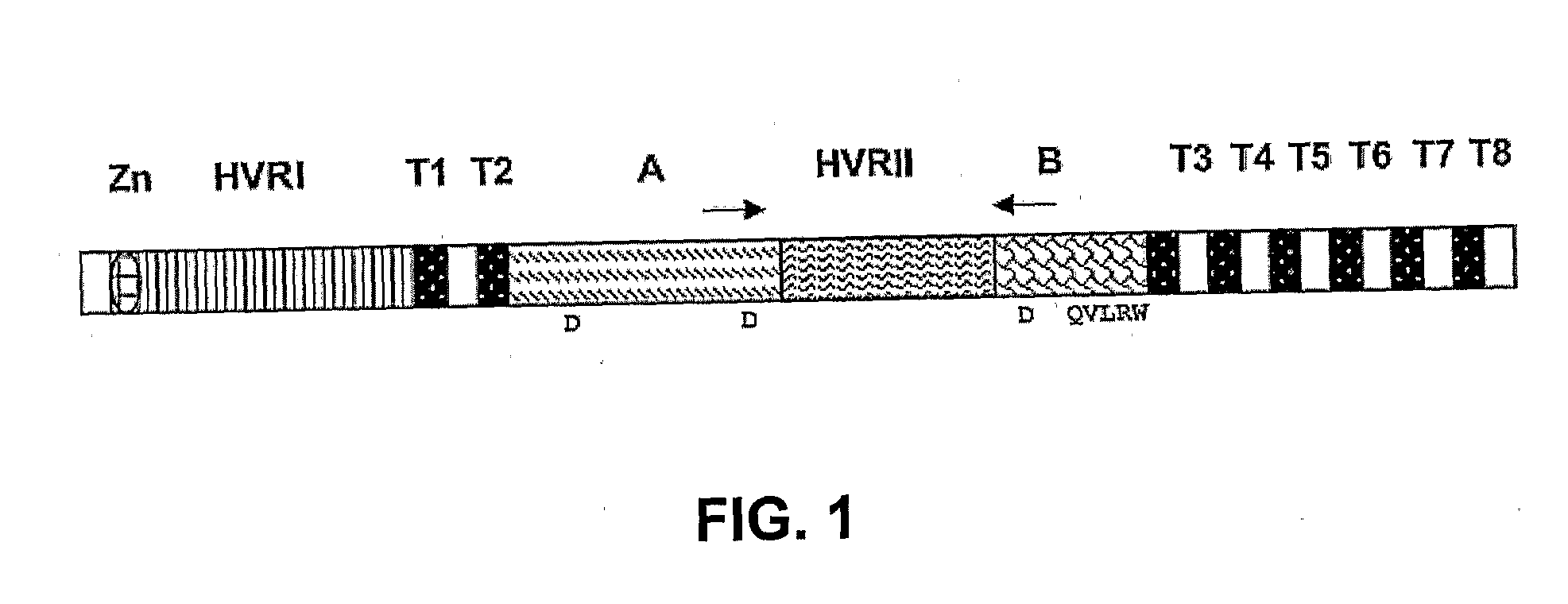
Described are methods for making transgenic plants capable of expressing secondary cell wall cellulose synthases and methods of enhancing expression of secondary cell wall cellulose synthases in plants. Also described are plants produced by the methods. Plants comprising at least three exogenous polynucleotides encoding secondary cell wall cellulose synthases are also provided.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Cloning and identification of GhDUF231L1 gene related with cotton fiber development
InactiveCN104711267APromote growthIncrease plant heightMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesFiberMonosaccharide composition
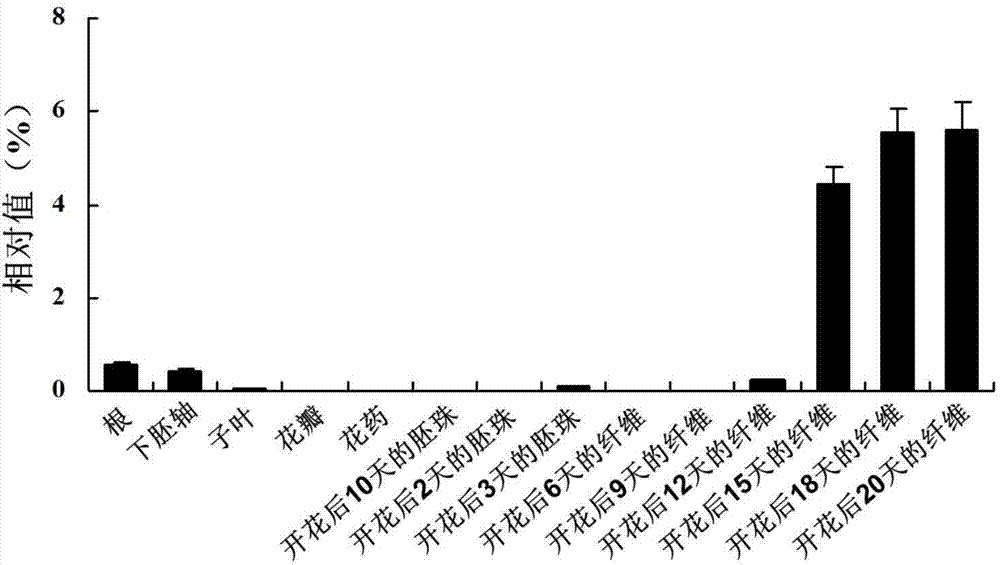
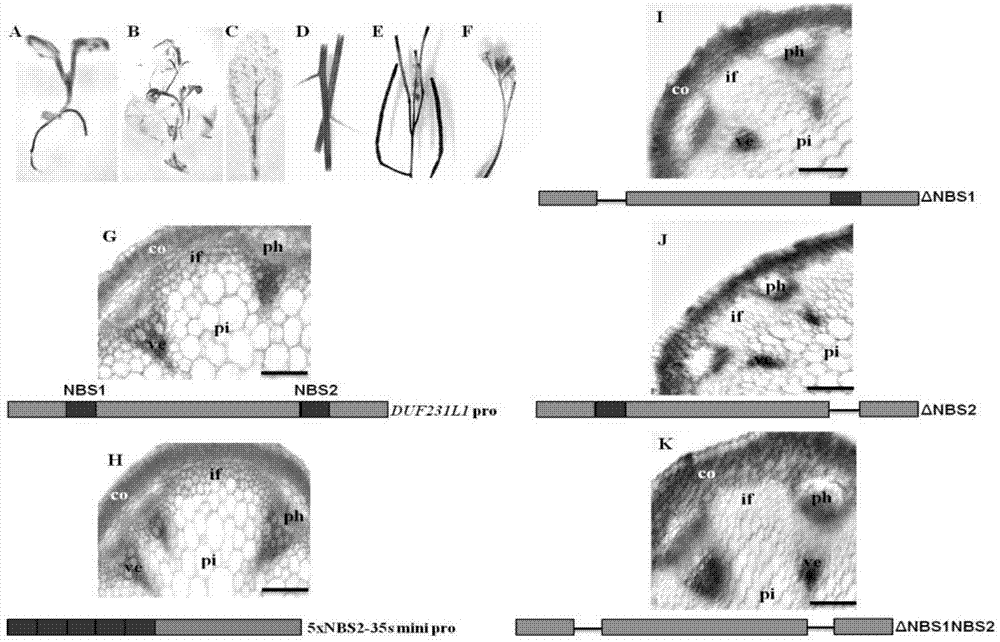
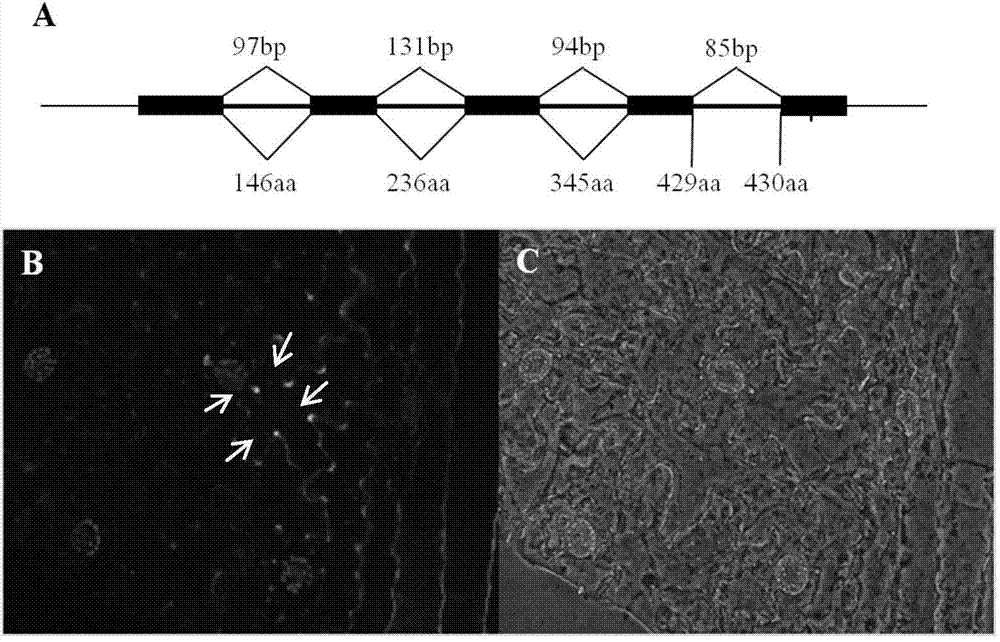
The invention discloses a full-length sequence of a new cotton fiber specific expression gene GhDUF231L1, of which a function relates to formation and modification of cotton fiber secondary wall materials. The GhDUF231L1 gene comprises five exons and four introns as well as a 1.6kb promoter fragment and an encoded 430 amino acid. The gene is a cotton fiber secondary wall development specific gene, of which the expression quantity is rapidly increased in fibers after flowering for 15 days and the expression quantity reaches a peak value after the flowering for 20 days. The GhDUF231L1 promoter mainly expresses in a vascular system of leaf veins and stems of transgenic arabidopsis thaliana leaves and also expresses in roots, flowers and legumes; a promoter area contains a cis-acting element which can be bonded with upstream transcription factors. Transgenic plants are enlarged, the cellulose content is increased and the contents of cell wall monosaccharide compositions are changed because GhDUF231L1 is over-expressed in arabidopsis thaliana. The results prove that GhDUF231L1 participates in plant growth, in particular to the biological synthesis of secondary cell walls, so that GhDUF231L1 possibly plays a key role in cotton fiber development.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Modulation of plant cell wall deposition via hdzipi
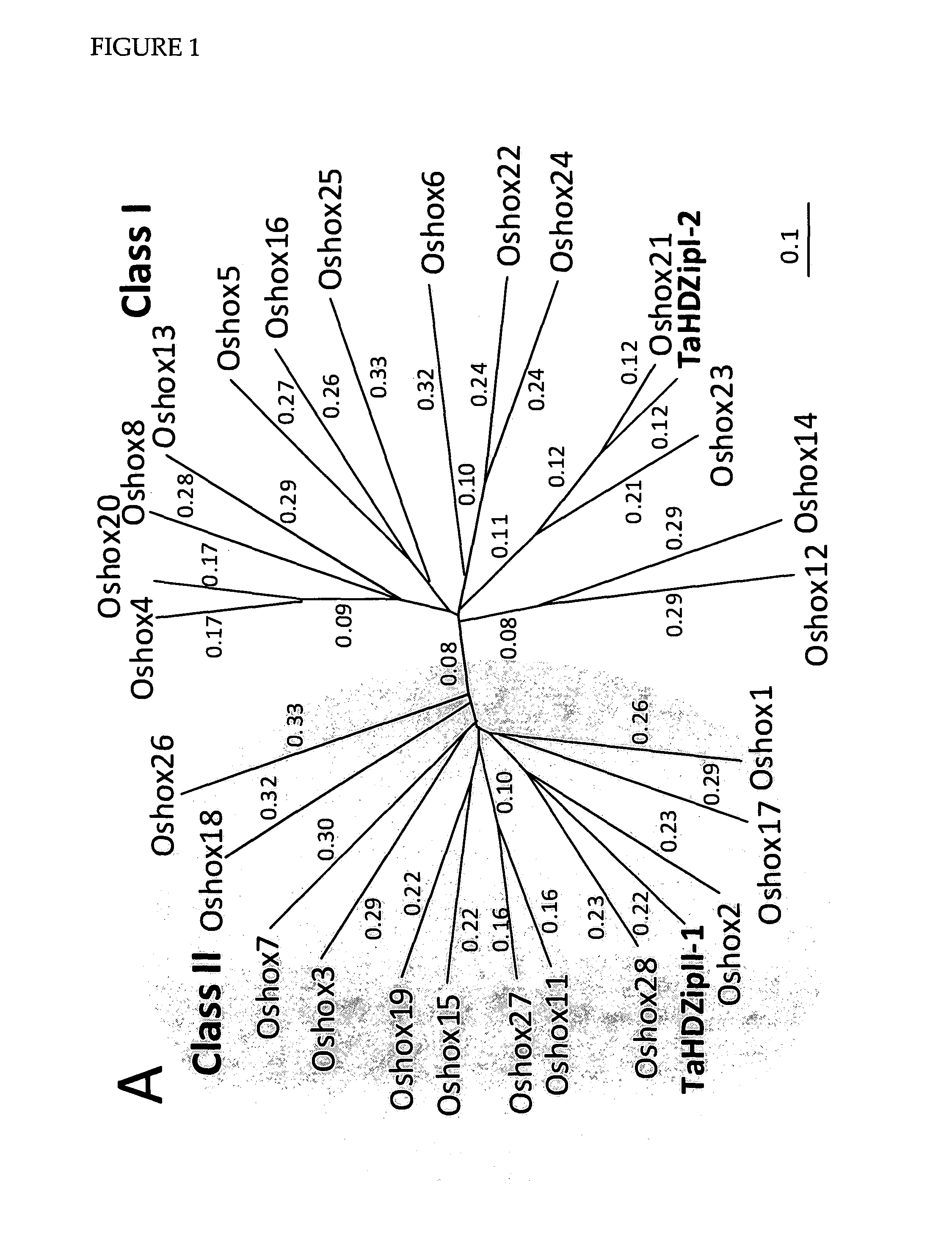
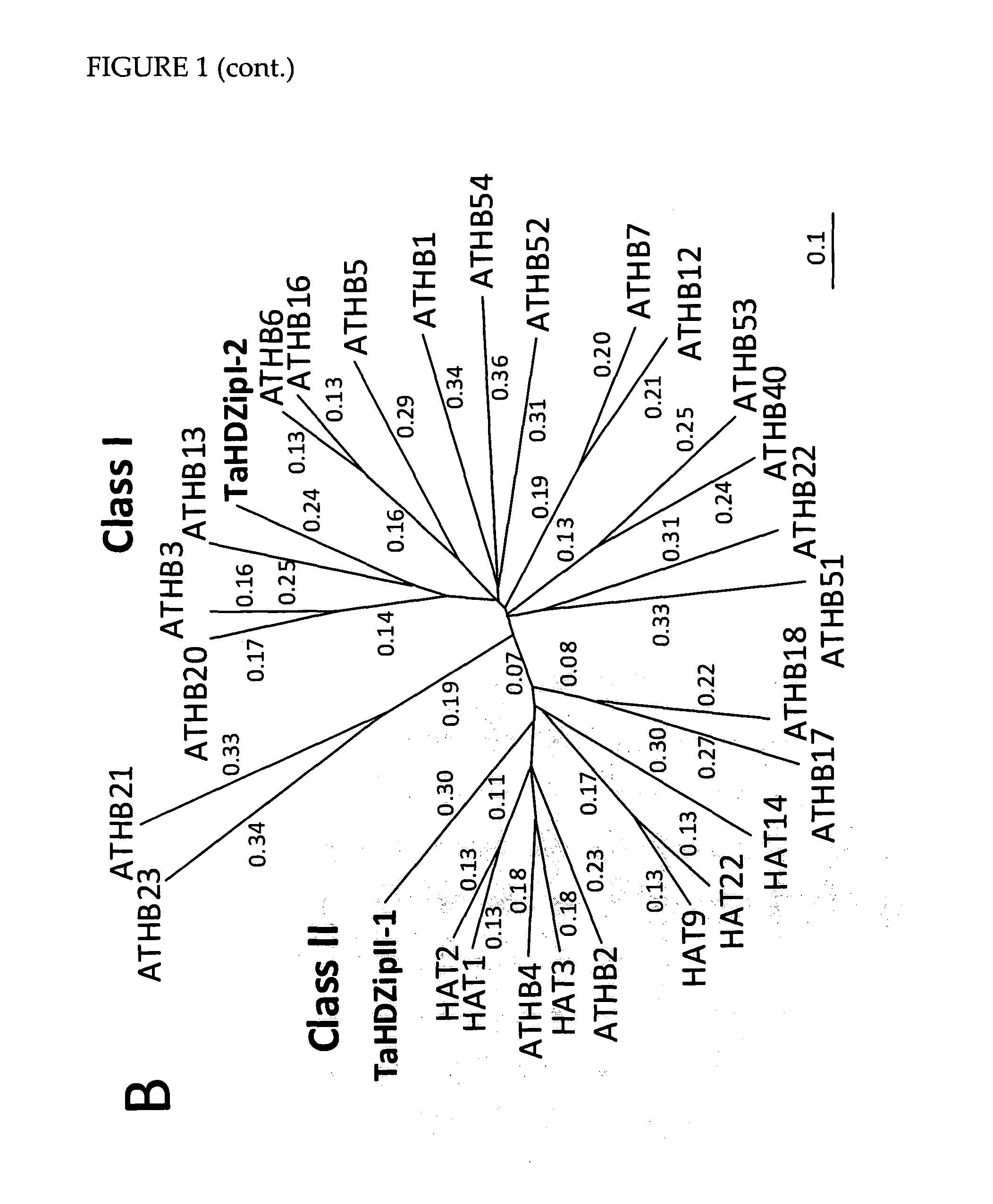
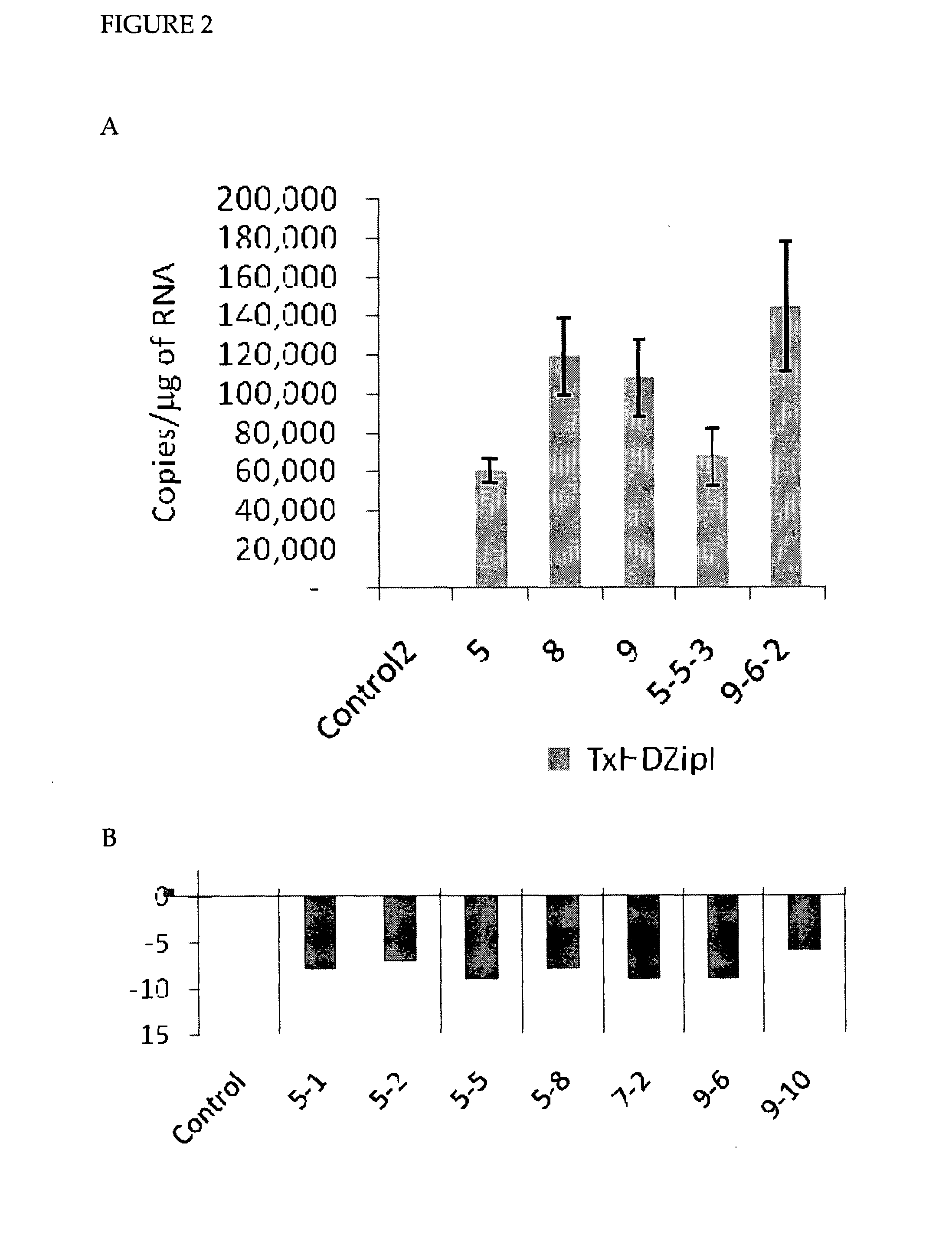
InactiveUS20110321186A1High expressionReduce expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellSecondary cell wall
The instant invention is predicated, in part, on the functional characterization of homeodomain / leucine zipper (HDZip) polypeptides which modulate various aspects of cell wall deposition in plants, including secondary cell wall deposition. The present invention provides, among other things, methods for modulating cell wall deposition in plant cells; plant cells and plants having modulated cell wall deposition; and methods for determining and / or predicting the rate and / or extent of cell wall deposition in plant cells and plants.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN CENT FOR PLANT FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS
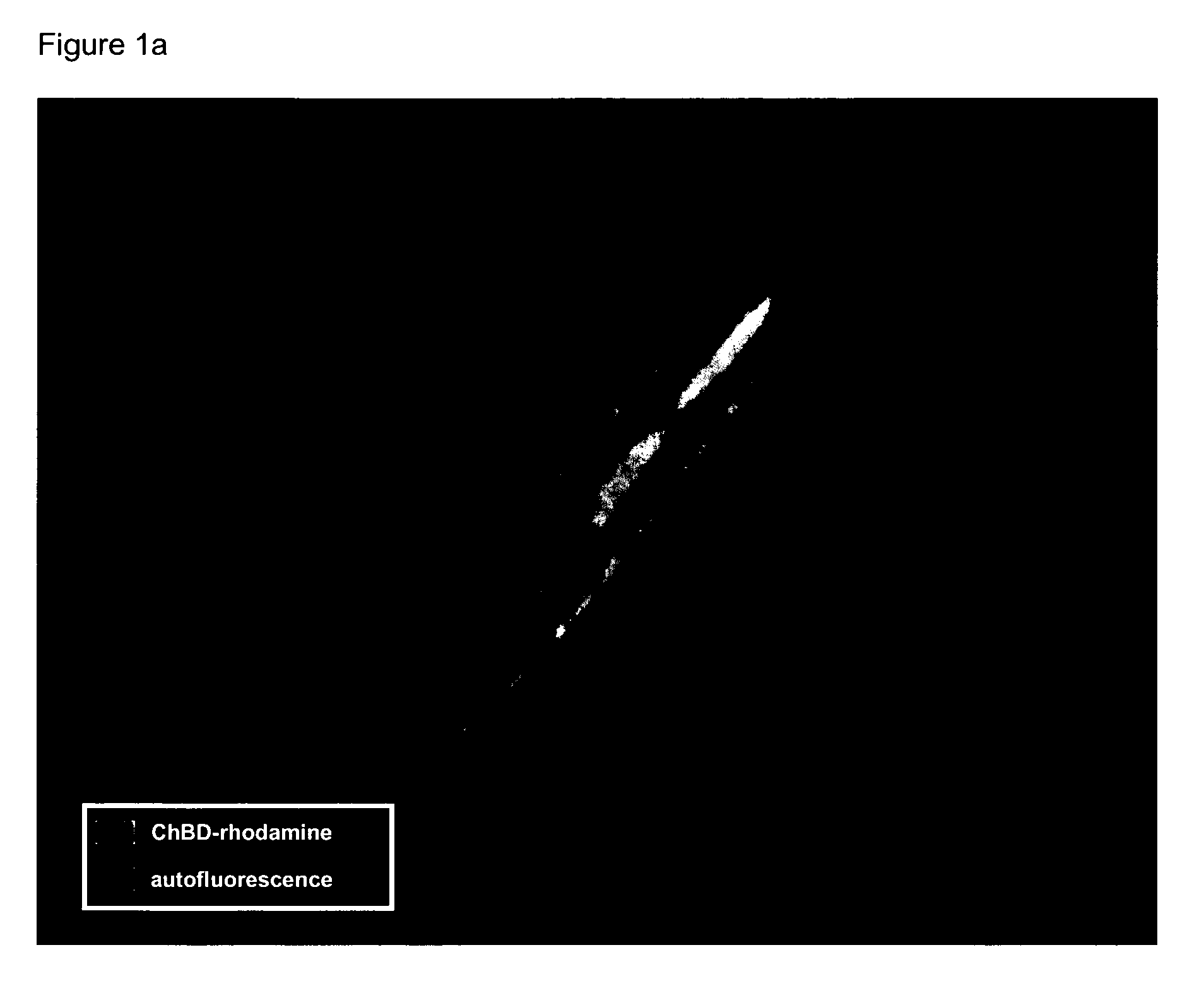
Methods for manufacturing plant cell walls comprising chitin
Methods and means are provided for the modification of the reactivity of plant secondary cell walls, particularly in cotton cell walls found in cotton fibers. This can be conveniently achieved by expressing a chimeric gene encoding a Saprolegnia monoica chitin synthase in cotton plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
miR408 and application of biological material related to miR408
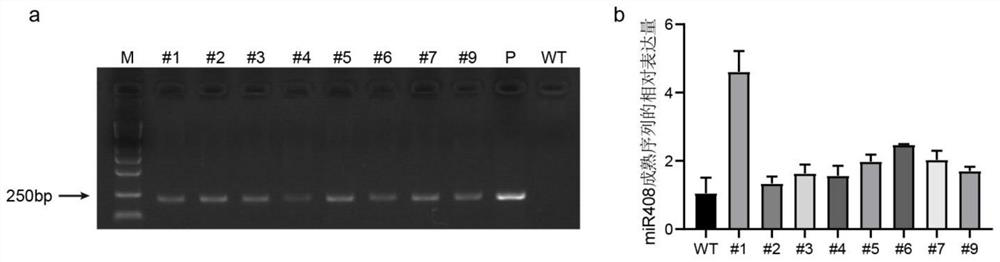
PendingCN113462687APromote heightening and thickening growthDelayed lignificationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGrowth plantPlant stem
The invention discloses miR408 and the application of a biological material related to the miR408. The invention firstly discloses the application of miR408 in improving saccharification efficiency of plant stems or delaying lignification of the plant stems or reducing lignin content of the plant stems or reducing lignin content of secondary cell walls of the plant stems or promoting plant growth. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the transgenic plant. Tests prove that overexpression miR408 can promote height and thickness increasing growth of poplars, postpone lignification of stems and reduce the lignin content of the stems; under the condition of no acid pretreatment, the saccharification efficiency of the poplar stems by 84.76%-92.44% is remarkably improved, so that the utilization efficiency of biomass energy is improved, and the method has important application value and environmental protection benefits for cultivating efficient biomass energy tree species in forestry production.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A lignofiber microfibril dissociation method based on flexible nano-paper-based materials
ActiveCN103952939BEnhance water absorption and swellingEasy to peelPulp beating methodsFiberMicrometer
The invention provides a wood fiber microfilament dissociation method based on a soft nanometer paper base material. The wood fiber microfilament dissociation method comprises the following steps: cutting off and cutting short paper pulp fibers by a pulping machine, and controlling the length of the cut fibers between 500 micrometers and 1000 micrometers; squashing the cut paper pulp fibers by hammering force which is perpendicular to the axial direction of the fibers until the primary cell wall and secondary cell wall outer layers of the fibers are broken or peeled; then utilizing rubbing and shearing force perpendicular to the axial direction of the fibers to separate microfilament layers so as to obtain primarily nano-crystallized fiber microfilaments; finally carrying out high-shear flattening treatment on the primarily nano-crystallized fiber microfilaments to obtain the soft nanometer fibers with uniform size. The method has the advantages of high product yield, uniform size and capability of batch preparing.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A Microscopic Appraisal Method for Peony Cut Flower Stem Strength
ActiveCN109060856BNo interference from human factorsReduce mistakesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionMicro structurePolyoxymethylene
A microcosmic identification method for the stem strength of cut peony flowers, comprising the following steps: (1) fixing the stems of cut flowers of peony: cutting the stems of cut flowers of peony and fixing them in pentylene glycol + paraformaldehyde solution; (2) adding (3) Observation of the thickness of the secondary cell wall thickened by the xylem; (4) Statistical analysis of the thickened cell layer and the thickness of the secondary cell wall of the xylem secondary wall of the peony cut flower stalk, through which Two indicators were used to identify the stem strength of peony cut flowers. The method adopted in the present invention can be directly observed and identified according to the microstructure, is convenient and simple, has no interference from human factors, and has low error; and is not limited by time, the sample can be preserved and observed for a long time, and repeated measurements can be made, and the method has high feasibility.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for site-directed mutagenesis of plant cellulose synthase CESA and application of cesa mutant in preparation of nanocrystals
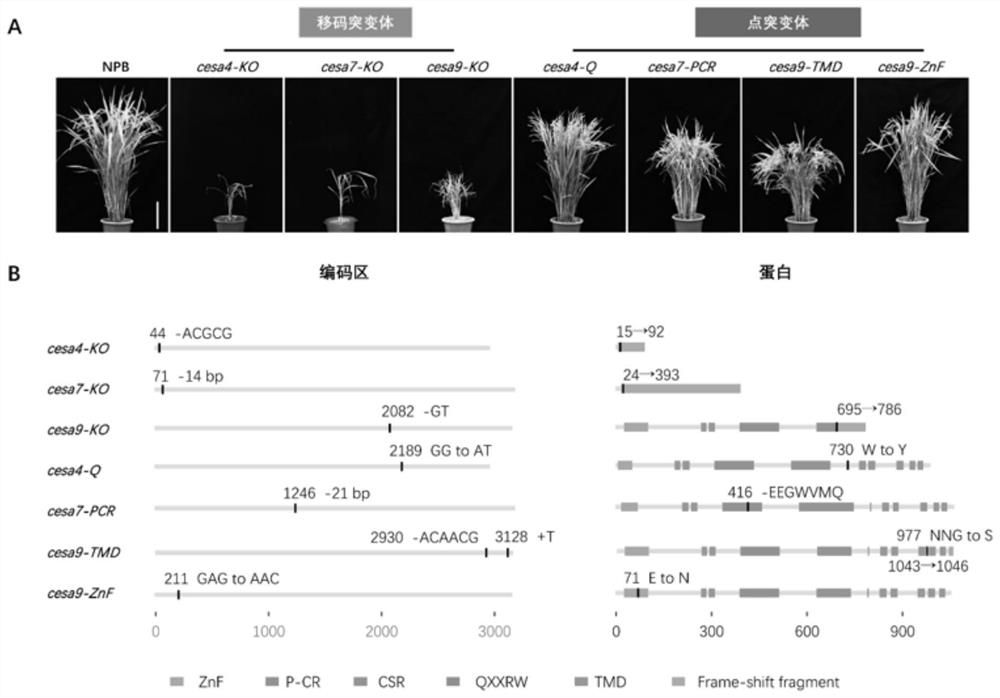
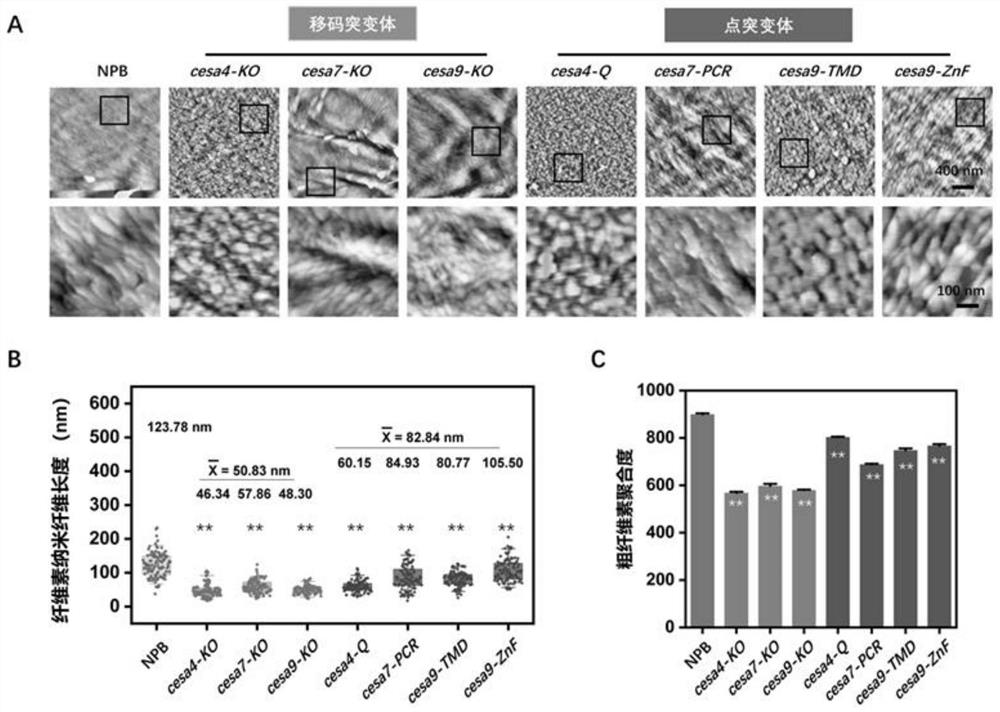
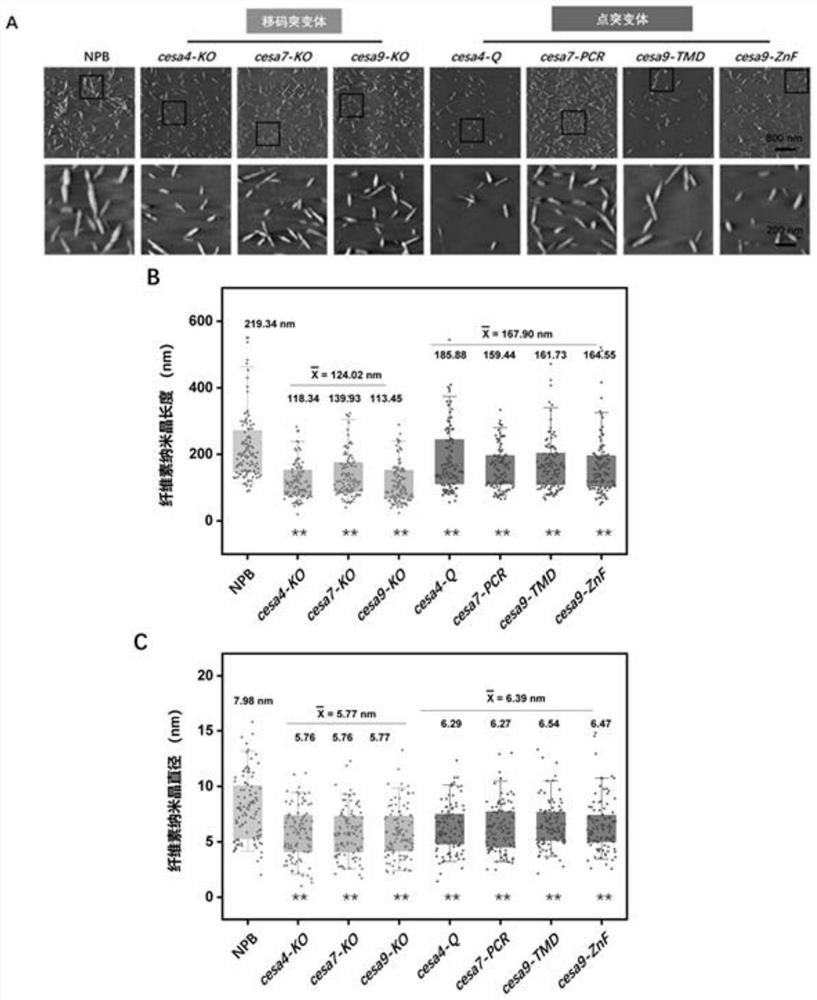
PendingCN114317592AReduce the degree of polymerizationShorten the lengthMaterial nanotechnologyTransferasesBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a method for site-directed mutagenesis of plant cellulose synthase CESA and application of a cesa mutant in preparation of nanocrystals, and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering and nanomaterials. The method comprises the following steps: (1) editing a target site according to CRISPR / Cas9 of a cellulose synthase CESA gene, designing a primer, and amplifying to construct a target sequence; (2) constructing the target sequence on a vector to obtain a recombinant vector; and (3) transforming the recombinant vector into a plant to obtain point mutants and frame-shift mutants of the three CESA genes of the secondary cell wall. The structure and the property of the transgenic plant cellulose containing the point mutant or the frameshift mutant are changed, and the cellulose nanocrystal with a smaller size can be prepared by hydrolyzing the transgenic plant straw through an acid hydrolysis method. The rice cellulose nanostructure is improved by utilizing a gene editing technology, and a low-cost and high-quality cellulose raw material is provided for efficiently preparing small-size cellulose nanocrystal particles.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Preparation method of alkali-resistant penetrating agent for mercerizing
InactiveCN108342900AGood emulsification and dispersionAlkali resistantBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsGrip property fibresActive agentSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of an alkali-resistant penetrating agent for mercerizing. The method is characterized by firstly using n-tetradecanol and ethylene oxide as raw materials,then adding n-caprylic alcohol and glucosum anhydricum, using crude glycosides, which is not completely dealcoholized after synthesis of alkyl glycoside, as a raw material, using remained fatty alcohol as a solvent, adding phosphorus pentoxide to obtain a wetting and penetrating main accessory ingredient with the characteristics of high wetting power, better alkali resistance, better temperature resistance, and the like; using an inorganic acid byproduct produced through an active agent for preparing block type silicone oil, and adding the block type silicone oil to the alkali-resistant penetrating agent, so that the yellowing of a mercerized fabric is reduced, and the softness and the fineness are improved; forming an anti-microbial protection film through chitosan surface film-forming; finally, adding a composite biological enzyme preparation so as to damage and remove a primary cell wall on an outer layer of cellulose, so that pectic substances between the primary cell wall and a secondary cell wall are exposed, hydrophobic impurities such as the pectic substances and waxes on fabric are removed, the penetrating agent adsorbed on the surface of the fabric is reduced, so as to becleanly removed during water washing, and the fabric is level and uniform.
Owner:江苏新亿源环保科技有限公司
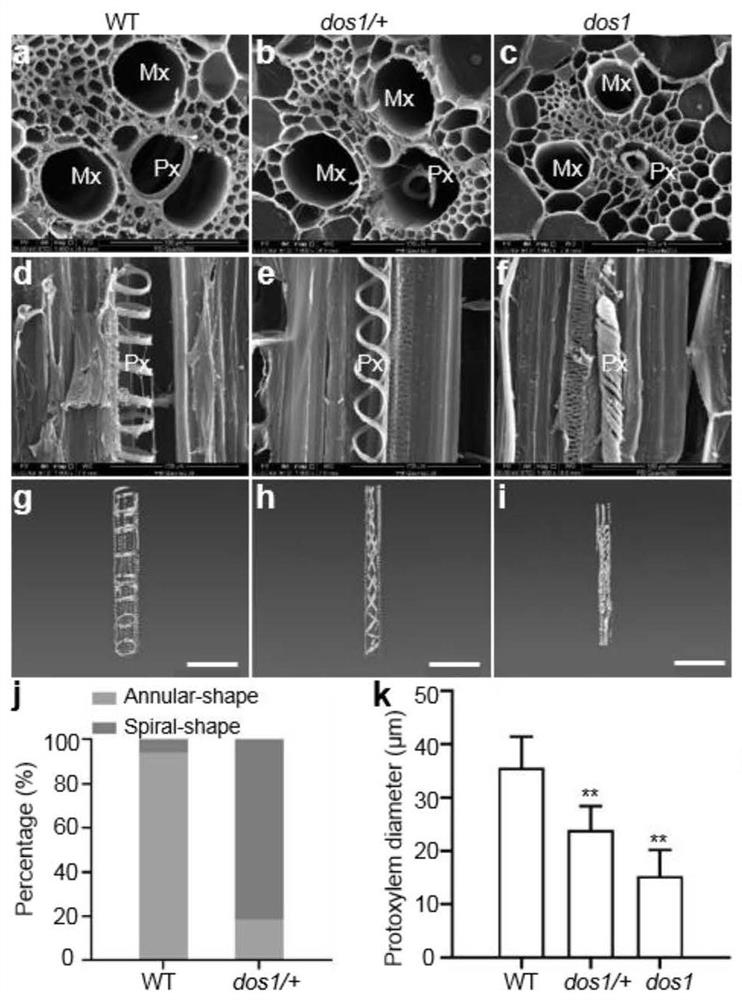
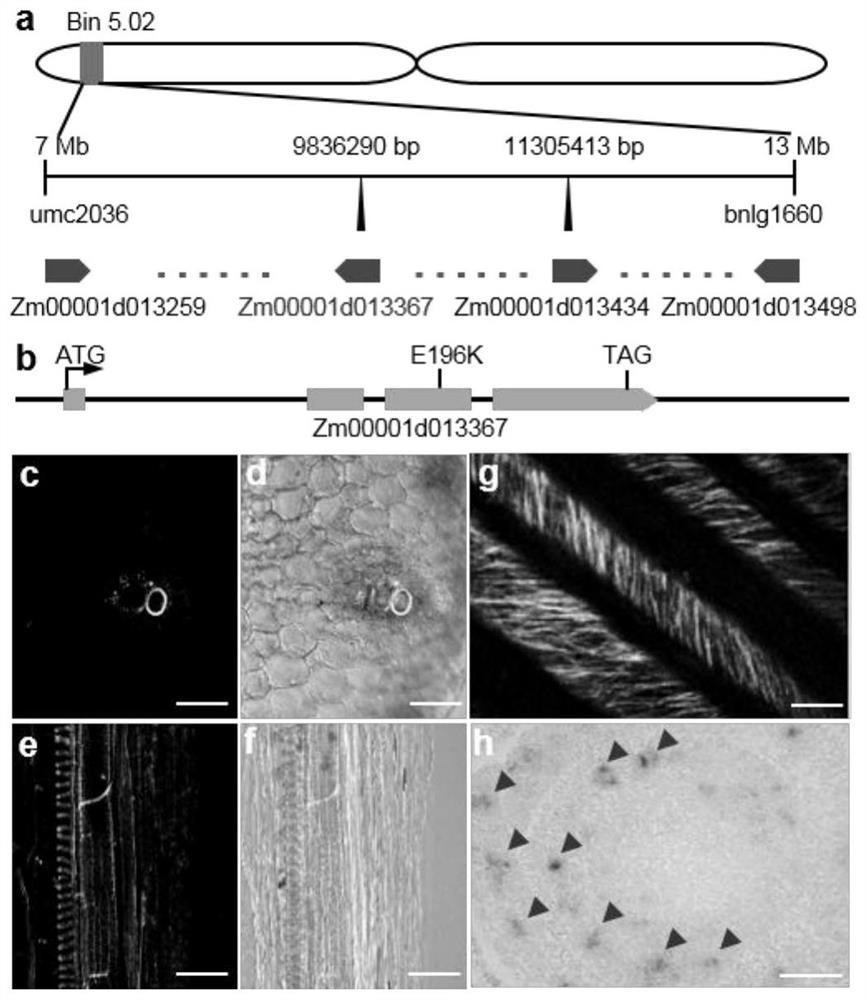
Application of corn Zm00001d013367 gene to regulation and control of development and water transport of native xylem of
ActiveCN113913452AEasy to breedGood for water transportClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly discloses an application of a corn Zm00001d013367 gene to regulation and control of development and water transport of native xylem. The nucleotide sequence of the Zm00001d013367 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, the amino acid sequence of a protein coded by the Zm00001d013367 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and the Zm00001d013367 gene is used for regulating and controlling a secondary cell wall deposition process in the development process of the native xylem of the corn. The Zm00001d013367 gene disclosed by the invention is used for regulating and controlling the development and the water transport of the native xylem.
Owner:SANYA INST OF HENAN UNIV +1
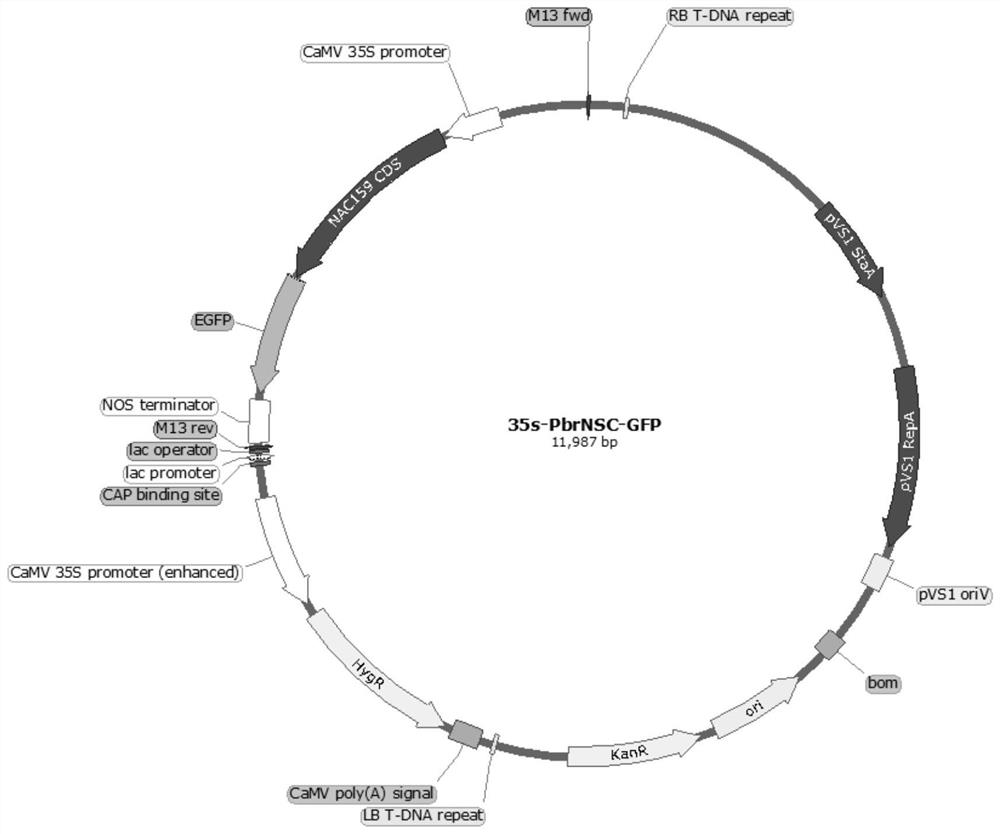
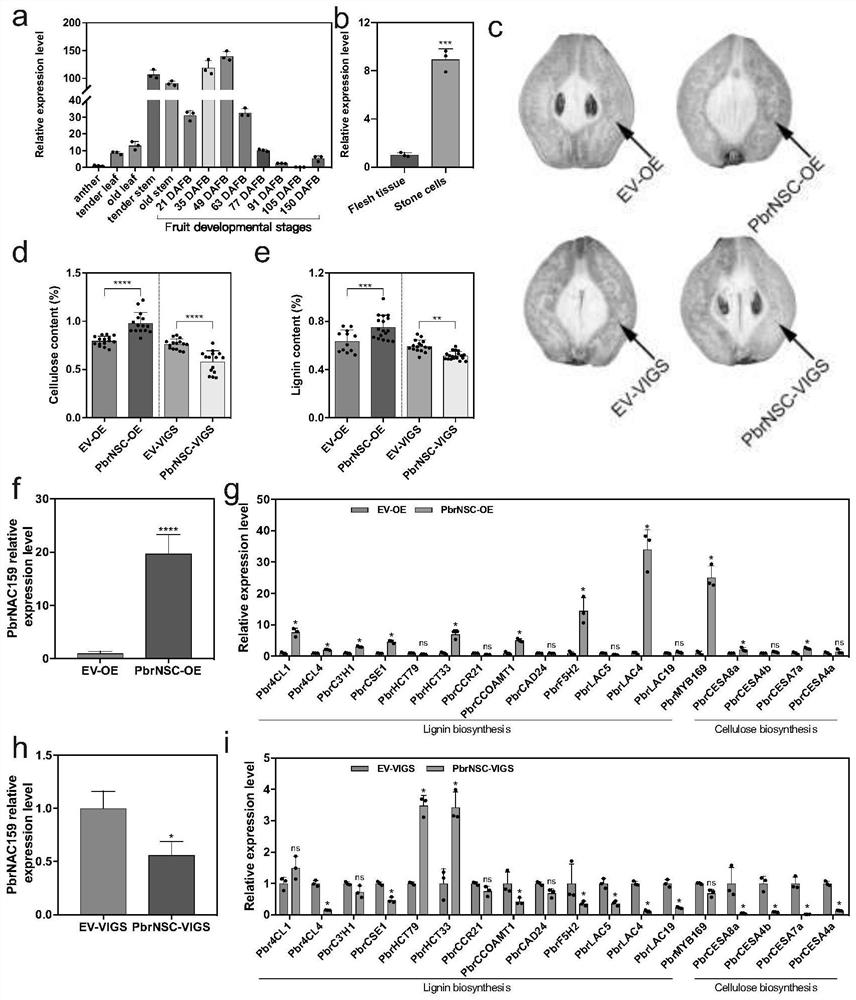
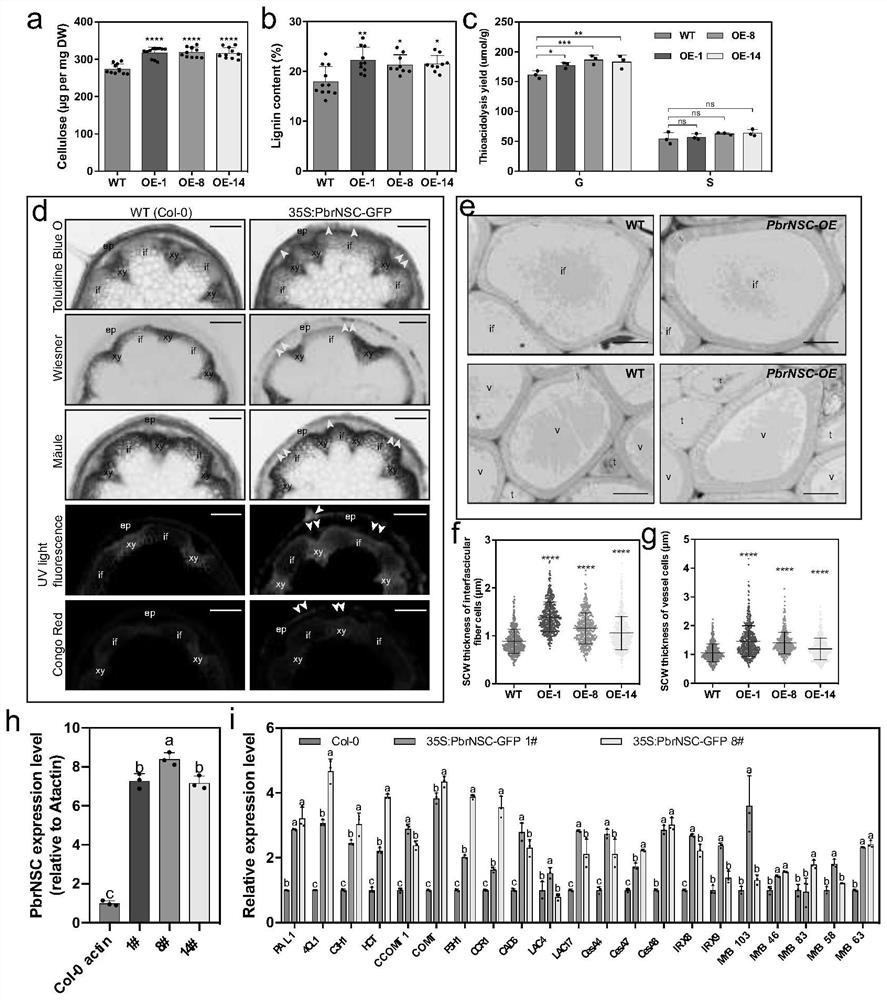
Pear PbrNSC gene and application thereof
ActiveCN114438093AAchieve friendlyReduce the cost of farmingPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a pear PbrNSC gene and application thereof. The invention discloses a PbrNSC gene which is separated from Dangshan pears and has the function of regulating and controlling the development of secondary cell walls of stone cells of pear fruits. The nucleotide sequence of the PbrNSC gene is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. Through instantaneous overexpression in pear fruits and a gene silencing technology, it is proved that PbrNSC can change the accumulation process of cellulose and lignin in secondary cell walls of fruit stone cells; in the PbrNSC-overexpressed transgenic arabidopsis thaliana inflorescence stem, the monomer contents of cellulose, lignin and G-type lignin are obviously increased, and the secondary cell walls of conduits and interbundle cells are obviously thickened. Therefore, the PbrNSC gene participates in regulating the formation of the secondary cell wall of the stone cell of the pear fruit.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cloning and application of a key gene peirx10 for xylan synthesis of moso bamboo
ActiveCN105925591BRepair Synthetic DefectsRepair secondary cell wall defectsEnzymesFermentationNucleotideMutant
The invention belongs to the fields of molecular biology and genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a Gts (glycosyltransferases) key gene PeIRX10 taking part in xylan synthesis. The gene has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No:1. The invention provides a powerful tool for knowing the formation of the secondary cell wall and illuminating the molecular basis of the fast growth of phyllostachys edulis tissues. The effects that the xylan synthesis defects in arabidopsis mutants can be overcome by using the PeIRX10, and the defects of the secondary cell wall in the arabidopsis mutants can be overcome in a complementary way are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Methods for manufacturing plant cell walls comprising chitin
InactiveUS20130091602A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesFiberChitin formation
Methods and means are provided for the modification of the reactivity of plant secondary cell walls, particularly in cotton cell walls found in cotton fibers. This can be conveniently achieved by expressing a chimeric gene encoding a Saprolegnia monoica chitin synthase in cotton plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com