Method for testing lignification degrees of plant cell walls
A measurement method and plant cell technology, which is applied in the field of confocal Raman microscopy to determine the degree of lignification of plant cell walls, can solve the problems of no research reports on the degree of lignification of plant cell walls under confocal microscopy, etc., to reduce the interference of fluorescence, reduce the Fluorescence interference, the effect of ensuring accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Study on the lignification process of different morphological regions of the fiber cell wall of Cornus alba
[0048] 1. Preparation of softening material
[0049] Cut Hongduanmu wood into cuboids with a size of 1 cm (along the grain direction) × 0.5 cm (chord direction) × 1 cm (radial direction, thickness direction) with a single-sided blade, and then soak them in boiling water (100°C) for 45 minutes to obtain softening material;
[0050] 2. Preparation of sample slices
[0051] Cut the softened material into a cross-section with a thickness of 20±2 μm along the radial direction of the softened material with a slide-away microtome to obtain a thin slice of the sample;
[0052] 3. Eliminate fluorescence interference
[0053] Soak the prepared sample sheet in sodium borohydride solution for 5 minutes, the mass percent concentration of sodium borohydride solution is 1%, sodium borohydride reacts with the carbonyl group in the sample sheet plant cells, the carbonyl group...
Embodiment 2
[0058] In addition to using Hongduanmu as raw material, to study the degree of lignification of the secondary wall of the vessel, the secondary wall of the ray parenchyma cell, and the secondary wall of the fiber cell, the soaking temperature of the preparation step of the softening material is 95, and the soaking time is 40 minutes; the thickness of the sample sheet It is 25±2 μm; without the step of eliminating fluorescence interference, that is, without soaking the sample sheet with sodium borohydride solution, the rest is the same as in Example 1.
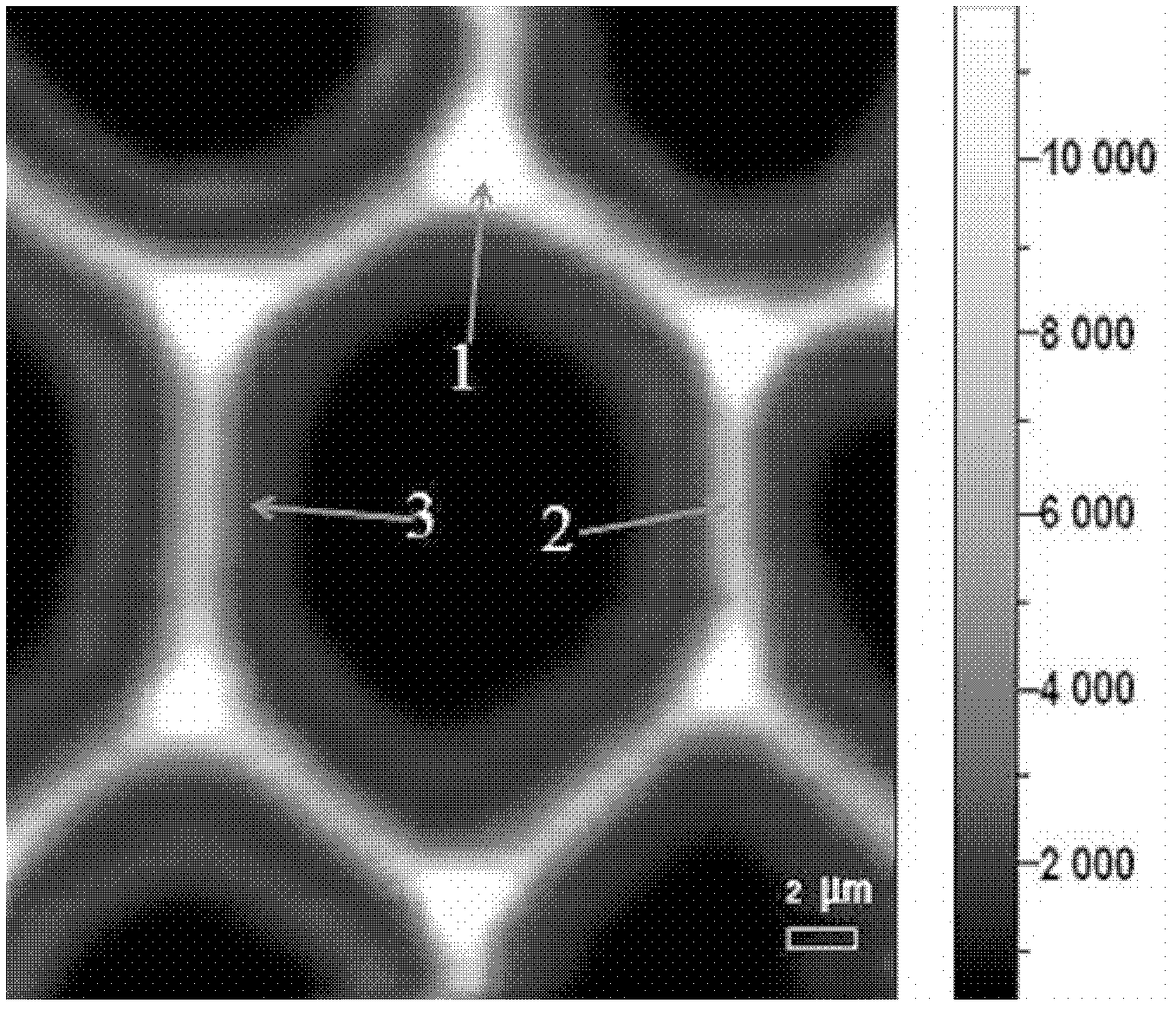
[0059] At 250~3250cm -1 Collect spectrum within the range, for 1580~1640cm -1 Ranges are integrated where 1606cm -1 The characteristic peak of the stretching vibration of lignin benzene ring C=C. 1655cm -1 The stretching vibration of coniferyl aldehyde C=O and the stretching vibration of coniferyl alcohol C=C are characteristic peaks.
[0060] The Raman images of the secondary wall of red endwood vessels, the secondary wall...
Embodiment 3
[0062] In addition to using Pinus yunnanensis as raw material to study the degree of lignification of different morphological regions of its fiber cells, the soaking time for the preparation of softened wood was 30 minutes, and the concentration of sodium borohydride solution in the step of eliminating fluorescence interference was 1.5%. Soaking time is except 7min, and all the other are identical with embodiment 1.
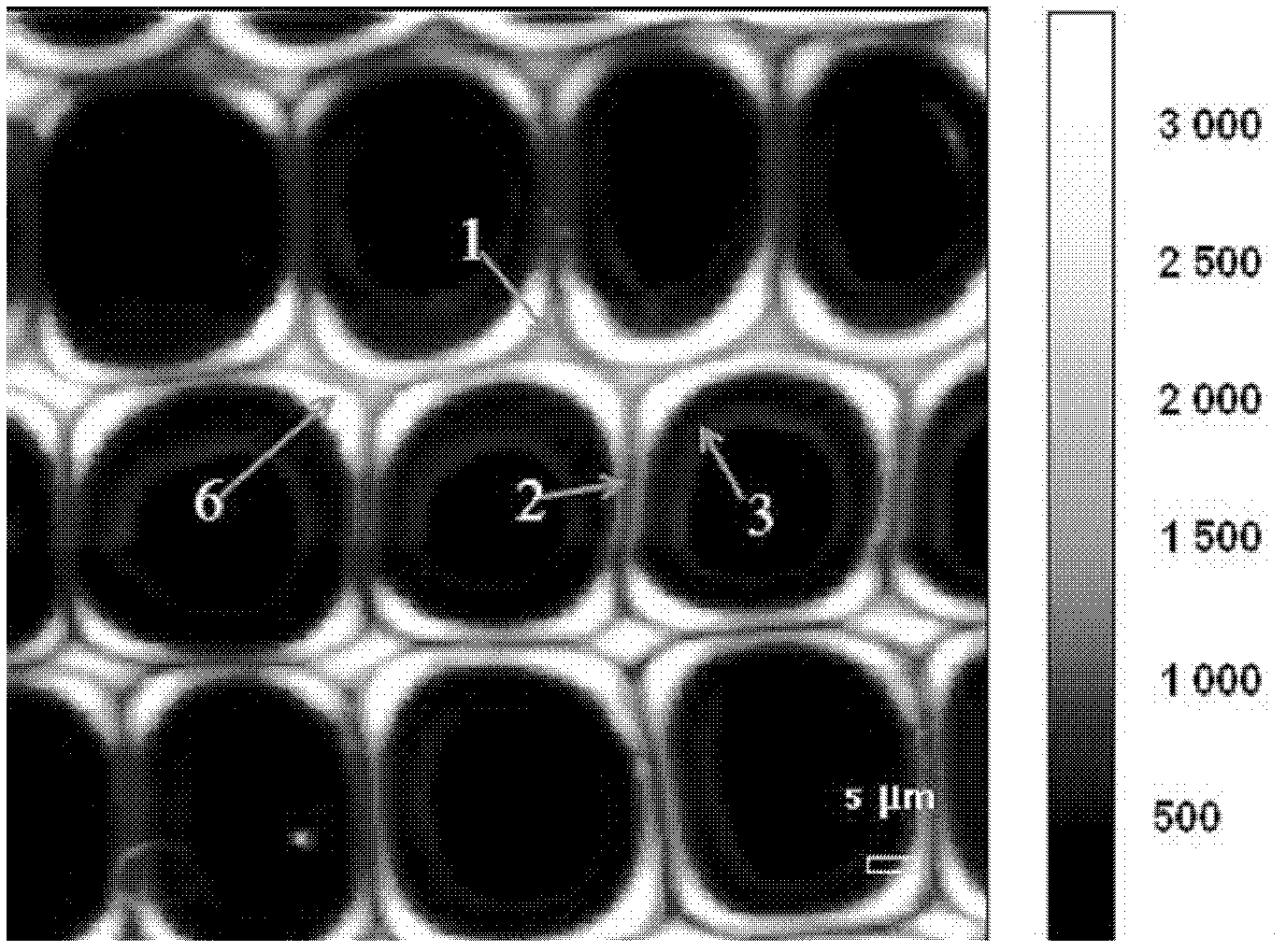
[0063] Raman microscope image of the stressed wood fiber cell wall of Pine yunnanensis image 3 Shown: from image 3 It can be seen that the lignification degree of the outer layer 6 of the secondary wall of the fibroblast near the cell corner is the highest, and the calculated value of the Gauss-Lorentz mixed function of the Raman signal intensity reaches 3000; the second is the cell corner 1, and its The Gauss-Lorentz mixed function calculated value of the Raman signal intensity is 2500; the calculated value of the Gauss-Lorentz mixed function of the Raman sig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com